SharePoint Automation: Best Practices, Use Cases and Recommended Tools
SharePoint automation can eliminate time-consuming tasks while reducing errors and freeing your team to focus on strategic work that actually drives business value.
SharePoint has come a long way from being just a document storage solution. Today, it’s a powerful platform that can handle complex business processes and eliminate much of the manual work that bogs down teams across organizations.
If you’ve ever found yourself manually routing documents for approval, sending the same notification emails over and over, or updating project statuses across multiple lists, you already know why automation matters. These repetitive tasks don’t just waste time—they’re prone to human error and can create bottlenecks that slow down entire workflows.
The good news is that SharePoint automation has become much more accessible, especially with Microsoft’s shift away from the old SharePoint Designer workflows. Microsoft 365 now uses Power Automate as the primary automation engine, giving you a more flexible and powerful way to connect SharePoint with other applications like Teams, Outlook, and Planner.
But automation isn’t limited to Microsoft’s built-in tools. Third-party solutions like Nintex and VirtoSoftware offer additional capabilities for organizations that need more advanced features or specific integrations. The key is understanding what’s available and choosing the right approach for your particular needs.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about SharePoint automation in 2025. We’ll cover the latest features, show you practical examples of what you can automate, and help you choose the right tools for your situation.
For those still working in SharePoint On-Premises environments, keep in mind that your automation options are different. While this article focuses primarily on SharePoint Online and Microsoft 365, we’ll point out where approaches diverge and recommend checking out our dedicated SharePoint workflows guide for on-premises solutions.
The goal isn’t to automate everything—it’s to identify the right processes that will give you the biggest impact with the least complexity. Let’s start by understanding exactly what SharePoint automation can do for your organization.
👉 New to SharePoint? No worries, check out this guide to learn more: SharePoint Overview: Your Ultimate Guide to Collaboration and Document Management
What Is SharePoint Automation, and How Does It Work
Before diving into specific tools and implementation strategies, it’s important to understand the fundamentals of SharePoint automation. This section will explain what SharePoint automation actually means, how it’s implemented in different environments, and what types of processes work best for automation. We’ll also look at the most common automation scenarios organizations implement and why automation has become essential for modern SharePoint deployments.
What is SharePoint automation?
At its core, a SharePoint workflow is an automated sequence of steps that handles repetitive tasks in your document management and business processes. Think of it as a digital assistant that watches for specific events and then takes action without requiring human intervention.
When we talk about SharePoint automation, we’re describing the replacement of manual tasks with smart, triggered processes. Instead of manually sending emails when someone uploads a document, updating statuses across multiple lists, or routing files to the right people, automation handles these actions automatically based on conditions you set up.
👉 Can SharePoint be used as a workflow tool? Absolutely. SharePoint works particularly well as a workflow platform when combined with Power Automate or third-party applications. Users can customize sequences of actions within lists, libraries, and other Microsoft 365 components to match their specific business needs.
SharePoint automation encompasses much more than just workflow scripts, though. It includes:
- Automatic list and library management—Creating and populating lists based on templates, organizing documents by metadata, or setting up folder structures when new projects start.
- Event-triggered scripts—Running automated processes when specific events occur, like when a document is uploaded, a list item is modified, or a deadline approaches.
- Cross-system integration—Connecting SharePoint with Teams for notifications, Outlook for email workflows, Dynamics for customer data, or Excel for reporting.
- Template-based automation—Using predefined templates to automatically create sites, documents, or tasks based on specific triggers or requests.
- Power Automate flows—Creating sophisticated automated processes that span multiple services and applications.
Here’s a practical example: When a new employee record is added to a SharePoint list, Power Automate can automatically create a task card in Microsoft Planner, send a welcome notification through Teams, update an Excel tracking sheet, and generate a checklist document in OneDrive. All of this happens without anyone having to manually coordinate these steps.
The flexibility to customize these action sequences makes SharePoint particularly valuable for organizations that need to adapt automation to their specific workflows rather than changing their processes to fit rigid software limitations.
How automation is implemented in SharePoint
SharePoint automation can be implemented through several different approaches, depending on your SharePoint version and organizational requirements:
- Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow) serves as the primary automation engine for SharePoint Online and Microsoft 365 environments. This cloud-based platform creates flows that connect SharePoint with other applications and services like Outlook, Teams, and Planner. Power Automate offers both simple templates for common scenarios and advanced logic for complex business processes.
- SharePoint Designer remains available for SharePoint On-Premises installations, though Microsoft has shifted focus to Power Automate for new development. Organizations with on-premises SharePoint still use Designer to create classic workflows, particularly for legacy systems that haven’t migrated to the cloud.
- Third-party automation tools like Virto Workflow Automation App or Nintex provide additional capabilities beyond what’s available in standard Microsoft tools. These solutions often offer more visual customization options, specialized actions for specific industries, and enhanced monitoring capabilities.
The implementation approach you choose depends on several factors: your SharePoint version (Online vs. On-Premises), the complexity of your processes, integration requirements with other systems, and your team’s technical expertise.
What can be automated in SharePoint?
SharePoint workflows help organizations reduce manual labor, increase process transparency, and ensure timely execution of routine tasks. Here are the most common automation scenarios:
- Document approval processes—Route files automatically to the appropriate approvers based on document type, author, or content. Set up multi-stage approval chains where different stakeholders review documents in sequence, with automatic escalation if approvals are delayed.
- HR process automation—Handle vacation requests from submission through approval, automatically notify HR departments about upcoming time off, and manage new employee onboarding workflows that create accounts, assign equipment, and schedule orientation sessions.
- Document routing and organization—Move files to appropriate folders or libraries based on metadata, content type, or business rules. Archive outdated documents automatically and ensure proper version control across your document repositories.
- Task creation and management—Generate tasks and subtasks automatically when new items are added to lists or when project statuses change. Assign work to team members based on workload, expertise, or availability.
- List and library operations—Update, delete, or modify fields in list items and documents automatically. Perform bulk operations on multiple items based on specific criteria or scheduled intervals.
- Notifications and reminders—Send messages through Teams, Outlook, or SharePoint when deadlines approach, task statuses change, or new files are added. Create escalation paths for overdue items.
- Financial process automation—Handle budget approvals, invoice processing, and purchase order workflows that include multiple approval stages and stakeholder notifications.
- Form processing and data handling—Process information collected through Power Apps forms, update databases automatically, and route responses to appropriate departments or individuals.
| Process type | Trigger event | Automated action | Business impact |
| Document management | File uploaded to library | Send approval request to manager | Faster review cycles |
| HR processes | Vacation request submitted | Route to manager → HR → Payroll | Streamlined time-off handling |
| Project management | Task status changed to “Complete” | Update project dashboard, notify team | Real-time progress visibility |
| Financial workflows | Invoice received | Route based on amount thresholds | Consistent approval hierarchy |
Typical processes that are most often automated
Based on common organizational needs, certain processes tend to be automated more frequently than others:
- HR processes dominate automation requests, including job application processing, new employee registration, birthday and anniversary notifications, and annual review scheduling. These processes involve predictable steps and clear approval hierarchies.
- Financial processes like expense report approval, budget request routing, invoice verification, and cost tracking benefit significantly from automation because they require consistent application of business rules and audit trails.
- IT processes including help desk ticket creation, system access requests, incident status tracking, and equipment provisioning work well with automation because they follow standardized procedures and require status updates across multiple systems.
- Project management tasks such as deadline reminders, automatic task distribution based on team member availability, progress reporting, and milestone notifications help keep projects on track without constant manual oversight.
- Document management processes including version control, change notifications, approval workflows, and archival procedures are natural candidates for automation because they involve repetitive actions with clear business rules.
Why SharePoint automation is important
SharePoint automation addresses several critical business challenges that affect organizations of all sizes:
- Speed improvements in routine operations free up employee time for higher-value activities. Tasks that previously took hours or days can be completed in minutes, allowing teams to focus on strategic work rather than administrative duties.
- Error reduction through automated processes eliminates the inconsistencies and mistakes that naturally occur with manual data entry and routing. Automated workflows follow the same steps every time, reducing the risk of missed approvals or incorrect information.
- Employee satisfaction increases when staff can focus on meaningful work instead of repetitive administrative tasks. Automation removes the frustration of manual processes and gives employees more time for creative and strategic activities.
- Process transparency improves when automation creates clear audit trails and status tracking. Managers can see exactly where items are in approval processes, and employees can track the progress of their requests without sending follow-up emails.
- Policy compliance becomes more reliable when automated processes consistently apply security rules, approval requirements, and document management policies. This is particularly important for regulated industries where compliance failures can result in significant penalties.
These benefits compound over time, creating organizational efficiencies that scale with your business growth rather than requiring proportional increases in administrative staff.
Using Power Automate with SharePoint
This section will explain what Power Automate is and why it’s become essential for SharePoint automation, walk you through the connection process, and show you how to get started with your first automated workflows. We’ll also explore the most common automation scenarios that organizations implement and discuss why Power Automate has become so popular among SharePoint users who want to streamline their processes without writing code.
What is Power Automate in SharePoint?
Power Automate in SharePoint is essentially your connection between SharePoint events and actions across the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. When something happens in SharePoint—like uploading a document, updating a list item, or changing metadata—Power Automate can trigger responses in other applications and services.
Power Automate is Microsoft’s cloud-based platform for creating automated workflows, called “flows,” between different applications and services. What makes it particularly valuable for SharePoint users is that it operates without requiring any coding knowledge, using a visual designer that lets you build logic through drag-and-drop actions.
The platform works by monitoring for specific triggers (events that start a workflow) and then executing a series of actions based on conditions you define. For SharePoint users, this means you can automate processes that previously required manual coordination across multiple systems.
Why is SharePoint Power Automate indispensable?
Here’s why Power Automate has become essential for SharePoint automation:
- Cross-application integration—SharePoint rarely operates in isolation. Most business processes involve multiple tools, and Power Automate bridges these gaps. You can connect SharePoint list updates to Teams notifications, Outlook emails, Planner tasks, and hundreds of other services.
- No-code accessibility—Unlike traditional SharePoint Designer workflows that required technical expertise, Power Automate uses a visual interface that business users can master. This democratizes automation, allowing the people who understand the processes to build the solutions.
- Cloud-native reliability—Power Automate runs in Microsoft’s cloud infrastructure, providing better uptime and scalability than on-premises solutions. Your workflows continue running even if your local systems experience issues.
- Advanced logic capabilities—While simple to use, Power Automate supports sophisticated scenarios including conditional logic, loops, variables, and error handling. This flexibility handles both basic notifications and complex approval processes.
How do I connect Power Automate to SharePoint?
The connection process is straightforward because Power Automate automatically integrates with SharePoint through the SharePoint connector. You don’t need to install additional software or configure complex settings—just specify which SharePoint site and list or library you want to work with.
Here’s the step-by-step process to connect Power Automate to SharePoint:
- Start by accessing Power Automate—Navigate to https://make.powerautomate.com and sign in with your Microsoft 365 credentials. The same account that gives you access to SharePoint will work for Power Automate.
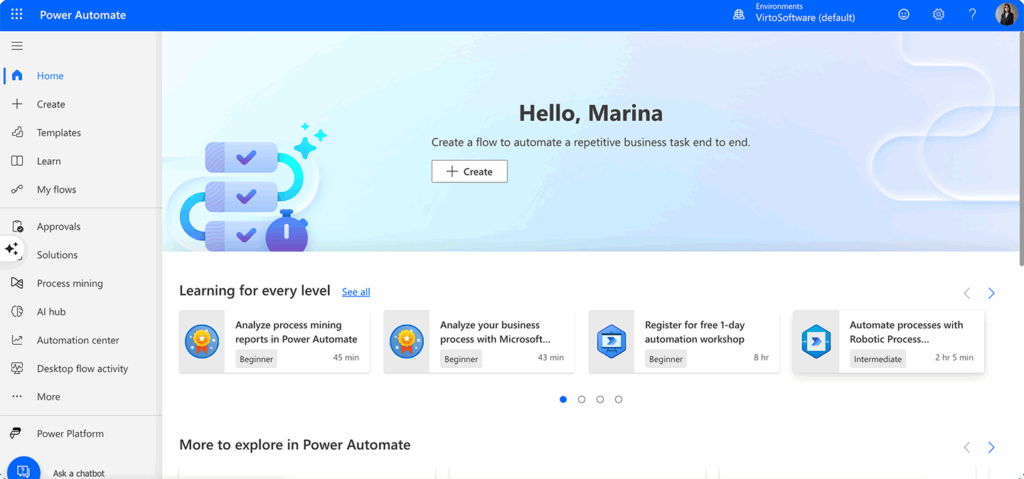
- Create a new flow—Click “Create” and choose the type of flow you want to build. For SharePoint automation, you’ll typically start with “Automated cloud flow” which responds to triggers, or “Scheduled cloud flow” for time-based processes.
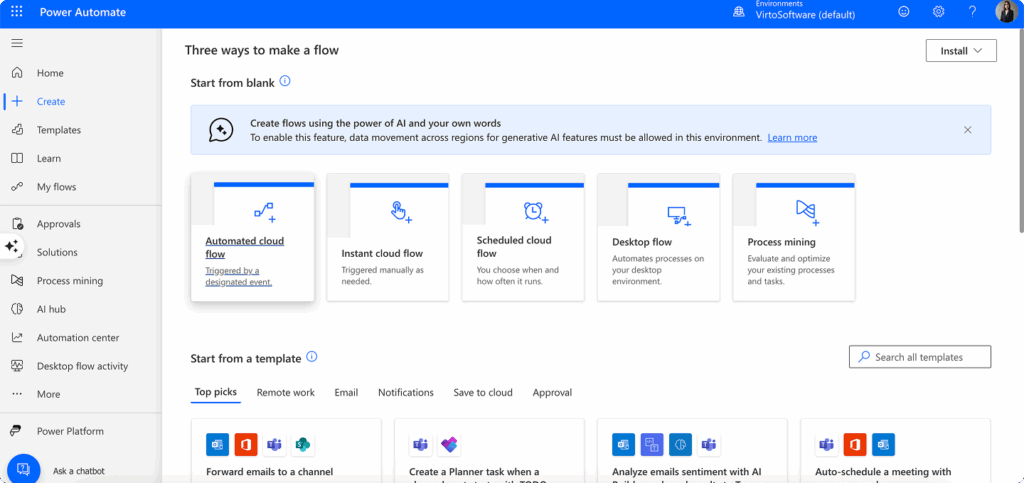
- Set up your trigger—Select a SharePoint trigger such as “When an item is created,” “When a file is created in a folder,” or “When an item is created or modified.” These triggers monitor your SharePoint environment for specific events.
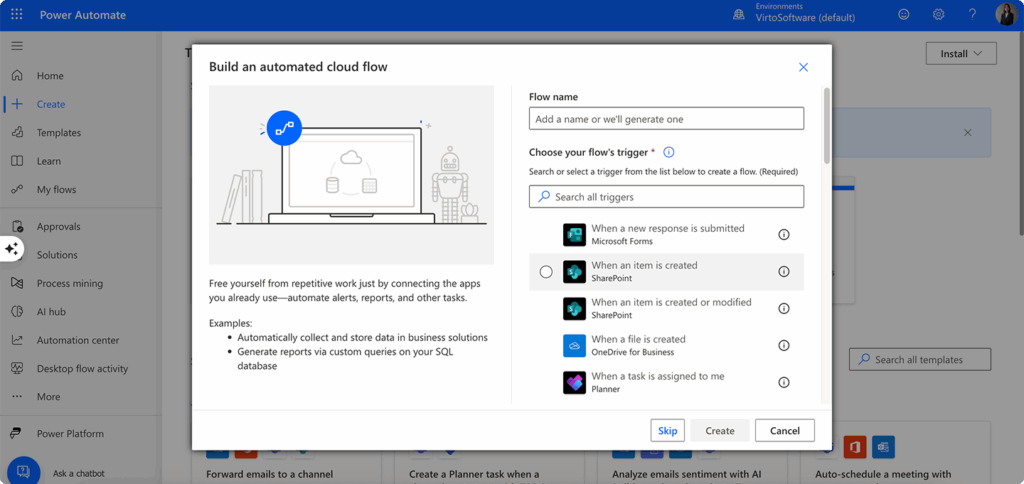
- Specify your SharePoint connection—Enter the URL of your SharePoint site and select the specific list or library you want to monitor. Power Automate will automatically establish the connection and verify your permissions.
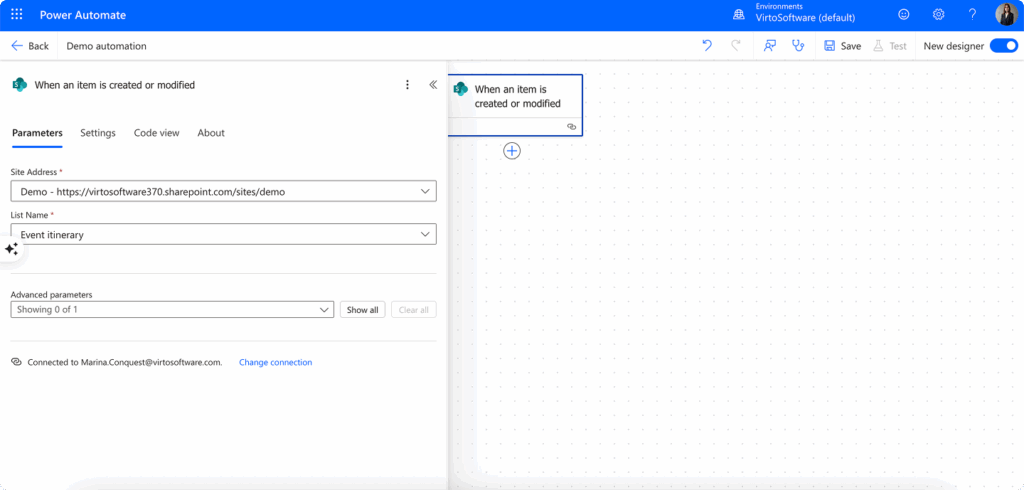
- Add your actions—Choose what should happen when the trigger fires. This might include sending emails, creating tasks in other applications, updating additional lists, or copying files to different locations.
The SharePoint connector provides access to dozens of triggers and actions, covering most common SharePoint operations like creating items, updating metadata, managing permissions, and working with files.

How do I enable Power Automate in SharePoint?
Power Automate is automatically enabled by default in most Microsoft 365 licenses, starting with Business Basic. If you have access to SharePoint Online and an appropriate license, you can create and run flows immediately—no additional setup required.
To start using Power Automate and SharePoint:
- Verify your licensing—Check that your Microsoft 365 subscription includes Power Automate. Most business plans include sufficient rights for standard SharePoint automation scenarios.
- Confirm SharePoint Online connectivity—Ensure your SharePoint site is connected to Microsoft 365. Power Automate works with SharePoint Online but has limited functionality with on-premises SharePoint installations.
- Access flows from SharePoint—In modern SharePoint lists and libraries, look for the “Automate” button in the toolbar. This provides direct access to Power Automate templates designed specifically for that list or library.
- Create flows from Power Automate portal—Alternatively, you can build flows directly in the Power Automate interface at make.powerautomate.com, which gives you access to more advanced features and templates.
The integration is designed to be immediate and accessible. Once you have the proper licensing, you can begin creating automated workflows within minutes.
👉 How to use Power Automate in SharePoint? Power Automate integrates directly with SharePoint through built-in connectors, allowing you to create automated workflows triggered by SharePoint events like file uploads or list item changes. Simply navigate to make.powerautomate.com, create a new automated flow, and select a SharePoint trigger such as “When an item is created” or “When a file is modified.” Choose your specific SharePoint site and list or library, then add actions like sending emails, creating tasks, or updating other systems. The visual drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to build logic with conditions, loops, and variables without any coding required. Once published, your workflow runs automatically in the background whenever the trigger conditions are met.
Common scenarios for using Power Automate in SharePoint
Understanding typical use cases for SharePoint Automate helps you identify automation opportunities in your own environment. Here are the most popular scenarios organizations implement:
- Notification workflows—Send email or Teams messages when documents are uploaded, list items are modified, or deadlines approach. These notifications can include relevant details from the SharePoint item and route to different people based on content or metadata.
- Approval processes—Route documents or requests through multi-stage approval workflows. Power Automate can send approval requests to managers, track responses, update SharePoint with approval status, and notify requestors of decisions.
- Task creation—Generate tasks in Microsoft Planner, To Do, or other task management systems when specific SharePoint events occur. For example, create a task when a project document is uploaded or when a support ticket is submitted.
- File management—Automatically move files between folders or libraries based on metadata, content type, or business rules. Archive completed projects, organize documents by department, or ensure files are stored in the correct locations.
- Data synchronization—Keep information consistent across multiple lists, libraries, or external systems. When a customer record is updated in SharePoint, automatically update related information in other locations.
- Reporting and analytics—Extract data from SharePoint lists and create reports in Excel, Power BI, or other analytics platforms. Schedule regular data exports or trigger reports when specific conditions are met.
- Integration with external systems—Connect SharePoint with CRM systems, databases, or third-party applications to ensure data flows smoothly between platforms.
Why Power Automate is popular among SharePoint users
Workflow automation with Microsoft Power Automate has gained widespread adoption for several compelling reasons:
- Visual simplicity—The drag-and-drop interface makes workflow creation accessible to business users without technical backgrounds. You can see the logic flow and understand how processes work at a glance.
- Extensive template library—Microsoft provides hundreds of pre-built templates for common SharePoint scenarios. These templates serve as starting points that you can customize for your specific needs, significantly reducing development time.
- Microsoft 365 ecosystem integration—Power Automate connects naturally with other Microsoft applications your organization already uses. This integration feels natural and doesn’t require learning new interfaces or authentication methods.
- Scalability for all organization sizes—Whether you’re a small team automating simple notifications or a large enterprise managing complex approval workflows, Power Automate scales to meet your needs without requiring different tools or approaches.
- Real-time processing—Workflows execute immediately when triggers fire, ensuring that automated processes keep pace with business operations rather than creating delays.
- Built-in error handling—Power Automate includes monitoring and error notification features that help you identify and resolve issues quickly when workflows encounter problems.
- Cost-effective automation—For organizations already using Microsoft 365, Power Automate provides significant automation capabilities without requiring additional licensing for most scenarios.
The combination of ease of use, powerful features, and tight integration with existing Microsoft tools makes Power Automate the natural choice for SharePoint automation in most organizations.
How to Get Started with Automation in SharePoint
Getting started with SharePoint automation can feel overwhelming, especially with so many tools and approaches available. This section provides a practical, step-by-step framework for implementing your first automated workflows successfully. We’ll walk you through identifying the right processes to automate, selecting appropriate tools for your environment, designing effective workflows, and ensuring smooth deployment. You’ll also learn best practices for testing, user adoption, and ongoing maintenance that will help your automation projects succeed from day one.
Can I automate SharePoint?
Yes, SharePoint can be automated using Power Automate, built-in solutions, or third-party tools. The approach you choose depends on your SharePoint version (Online vs. On-Premises) and the complexity of your specific tasks.
The key to successful SharePoint automation is starting with the right foundation. Rather than jumping straight into complex workflows, you need a systematic approach that ensures your automation efforts actually solve real problems and deliver measurable value.
Identify the business process that needs to be automated
Before touching any automation tools, spend time clearly defining which actions in your daily work are repetitive and consume significant manual effort. This discovery phase is crucial because automating the wrong process can create more problems than it solves.
Look for processes that have these characteristics:
- High frequency and repetition—Tasks that happen multiple times per day, week, or month are prime candidates. Examples include approving vacation requests, notifying teams about document uploads, or updating project status across multiple lists.
- Clear, predictable steps—Processes with well-defined sequences work best for automation. If the process requires significant human judgment or varies dramatically each time, it may not be ready for automation.
- Multiple system involvement—Tasks that require you to copy information between SharePoint, email, Teams, and other applications benefit greatly from automation.
- Time-sensitive requirements—Processes where delays cause problems, such as approval workflows or deadline notifications, are excellent automation candidates.
Common examples of processes worth automating include:
- Vacation or purchase request approvals
- New document notifications to specific teams
- Task assignment based on form submissions or list updates
- Project status updates that need to be reflected in multiple locations
- File archiving and organization based on age or metadata
At this stage, formulate a clear goal: what specific outcome do you want to achieve? Are you trying to reduce response time, eliminate manual errors, or free up staff for higher-value work? Having a concrete objective helps you measure success later.
Select the right automation tool
Once you’ve identified your target process, choose the appropriate tool based on your environment and requirements:
- Power Automate is the recommended choice for SharePoint Online and Microsoft 365 users. It provides the best integration with modern SharePoint features and connects easily with other Microsoft applications. Power Automate works well for most standard business processes and doesn’t require technical expertise to implement.
- SharePoint Designer remains relevant for organizations using SharePoint On-Premises. While Microsoft has shifted focus to Power Automate, SharePoint Designer still provides robust workflow capabilities for on-premises environments, particularly for legacy systems that haven’t migrated to the cloud.
- Third-party solutions like Nintex, Virto Workflow Automation App, or K2 make sense when you need advanced functionality that exceeds Power Automate’s capabilities. These tools often provide more sophisticated visual designers, specialized actions for specific industries, or enhanced monitoring and reporting features.
👉 Learn more about differences between Classic and Modern SharePoint experiences here: SharePoint Modern vs. Classic: Key Differences and Reasons to Migrate
Consider these factors when choosing your tool:
- Environment compatibility—Ensure the tool works with your SharePoint version
- Integration requirements—Consider what other systems need to be connected
- User expertise—Match the tool complexity to your team’s technical skills
- Budget constraints—Factor in licensing costs for third-party solutions
- Support and maintenance—Consider long-term maintenance requirements
Design and create a process template
Before building anything in your chosen tool, create a clear process map that documents how the automation should work. This planning step prevents confusion during implementation and helps you communicate the process to stakeholders.
- Document the current manual process—Write down every step someone currently performs manually. Include who does what, when they do it, and what information they need. This baseline helps you understand what the automation needs to replicate.
- Define your trigger clearly—Specify exactly what event should start the automated process. For example, “when an item is added to the ‘Vacation Requests’ list” or “when a file is uploaded to the ‘Contracts’ library.”
- Map out the decision points—Identify where the process needs to make choices based on data or conditions. For instance, “if the request amount is over $5,000, send to the department director; otherwise, send to the team manager.”
- Specify the actions—List each action the automation should perform, such as sending notifications, updating fields, creating tasks, or moving files. Be specific about what information should be included in each action.
- Identify the participants—Note who needs to be involved at each step and what permissions they need. This helps you configure security settings correctly.
Your process template might look like this:
- Trigger: New item created in “Purchase Requests” list
- Condition: If amount > $1,000, route to manager; if amount > $5,000, route to director
- Action: Send approval request email with item details
- Action: Update item status to “Pending Approval”
- Condition: If approved, update status and notify requestor; if rejected, update status and provide feedback
Once your process is mapped out, you can begin the technical implementation using your chosen tool’s visual designer or configuration interface.
Testing and launch
Testing is critical for automation success. A workflow that fails in production can disrupt business operations and reduce confidence in automation initiatives.
- Start with a test environment—If possible, create your automation in a separate SharePoint site or test environment. This allows you to verify functionality without affecting live business processes.
- Test all scenarios—Don’t just test the “happy path” where everything works perfectly. Test edge cases like missing data, unavailable users, permission issues, and system errors. What happens if someone deletes a required list item or if a user is out of office?
- Verify data accuracy—Ensure that information flows correctly between systems and that all required fields are populated properly. Check that dates, numbers, and text are formatted correctly in notifications and updates.
- Confirm permissions—Test that the automation has appropriate access to perform all required actions and that users receive proper notifications. Verify that the workflow respects existing SharePoint permissions and doesn’t inadvertently expose sensitive information.
- Performance testing—Run the automation with realistic data volumes to ensure it performs well under normal conditions. A workflow that works with 10 items might struggle with 1,000.
- Pilot with limited users—Before full deployment, run the automation with a small group of users who can provide feedback and help identify issues you might have missed.
Document any issues you discover and verify that your fixes don’t create new problems. Keep a record of test results to help with future troubleshooting.
End-user engagement and support
The best automation is worthless if users don’t understand how to work with it or don’t trust it to handle their processes correctly.
- Communicate the changes—Before launching automation, inform affected employees about what’s changing, why it’s changing, and how it will affect their daily work. Address concerns proactively and explain the benefits clearly.
- Provide training—Even simple automation can confuse users if they don’t understand the new process. Offer training sessions that show users how to interact with automated workflows and what to expect from the system.
- Create documentation—Write clear instructions for users who need to submit requests, respond to approval emails, or work with automated notifications. Include screenshots and step-by-step guidance.
- Establish feedback channels—Set up ways for users to report problems, suggest improvements, or ask questions. This might include a dedicated email address, Teams channel, or regular check-in meetings.
- Monitor adoption—Track how well users are adapting to the new automated processes. Low adoption rates often indicate training gaps or process design issues that need attention.
- Assign ongoing responsibility—Designate someone to maintain the automation, handle user questions, and make improvements based on feedback. Automation isn’t a “set it and forget it” solution—it requires ongoing attention.
Why start simple? Beginning with overly complex automation can lead to failures, user frustration, and resistance to future automation initiatives. A simple, successful automation builds confidence and demonstrates value, making it easier to tackle more complex processes later.
The most successful automation projects start with one narrow, well-defined process. Once that automation is running smoothly and users are comfortable with it, you can expand to more sophisticated workflows and broader process improvements. This incremental approach builds expertise within your team and creates a foundation for larger-scale automation initiatives.
SharePoint Automation Examples
Real-world examples help illustrate how SharePoint automation works in practice and can spark ideas for your own organization. These scenarios demonstrate common automation patterns that apply across different industries and business functions. Each example shows the manual process that gets automated, the automated workflow that replaces it, and the benefits organizations typically see.
Automatic approval of vacation requests
The manual process: Employees email their managers or fill out paper forms for time off requests. Managers respond via email, then manually notify HR and accounting departments. HR updates vacation tracking spreadsheets and manually blocks calendar dates.
The automated workflow:
- Employee fills out a vacation request form connected to a SharePoint list or uses a Power Apps form
- Power Automate automatically sends an approval request to the employee’s direct manager
- Manager receives an email with approve/reject buttons and can respond directly from their inbox
- Upon approval, the workflow automatically:
- Notifies HR and accounting departments with request details
- Updates the employee’s vacation balance in the tracking system
- Creates calendar entries to block the requested dates
- Sends confirmation to the employee with approved dates and updated balance
- If rejected, the employee receives an automatic notification with the manager’s reason
Business impact: Organizations typically see 75% reduction in processing time for vacation requests and eliminate the back-and-forth emails that often delay approvals. HR departments report significant time savings from not having to manually track balances and calendar updates.
Budget and purchase order approval
The manual process: Department heads submit budget requests or purchase orders via email with attachments. Finance teams manually route documents to appropriate approvers based on amount thresholds. Approvers respond via email, and finance manually tracks approval status and updates accounting systems.
The automated workflow:
- Requestor submits purchase request through a SharePoint form, including cost estimates and supporting documents
- Power Automate evaluates the request amount and automatically routes to appropriate approvers:
- Under $1,000: Team manager approval
- $1,000-$5,000: Department director approval
- Over $5,000: Finance director and executive approval
- Each approver receives detailed request information and can approve/reject with comments
- Upon final approval, the workflow:
- Generates a PDF approval document with all signatures and timestamps
- Creates a purchase order number and updates the financial tracking system
- Notifies the requestor and purchasing department
- Archives all documentation in the appropriate SharePoint library
Business impact: Companies report 60% faster approval cycles and improved spending visibility. Finance teams spend less time tracking approvals manually and have better audit trails for compliance purposes.
👉 Learn more about SharePoint document management in our dedicated articles:
How to Create and Manage a SharePoint Document Library
Optimize Your Business with SharePoint Document Management
SharePoint Form: Everything You Need to Know About Creating and Using Forms
Best Practices for SharePoint Document Management, Library, Folder Structure and Security
Overdue task notifications and escalation
The manual process: Project managers manually review task lists and deadline spreadsheets daily, then send individual reminder emails to team members with overdue items. When tasks remain overdue, managers manually escalate to supervisors via separate emails or meetings.
The automated workflow:
- SharePoint project lists track task deadlines and assignment information
- Power Automate runs daily checks for tasks approaching or past their due dates
- For tasks due within 3 days:
- Sends reminder notifications to assigned team members via email and Teams
- Includes task details, deadlines, and direct links to the SharePoint item
- For overdue tasks:
- Sends escalation notifications to the task owner and their manager
- Creates comments in the task item documenting the overdue status
- After 7 days overdue, escalates to department director level
- Weekly summary reports are automatically generated and sent to project stakeholders showing overall project health and overdue item trends
Business impact: Project completion rates improve by 40% due to proactive notifications. Managers report better visibility into project bottlenecks and can address issues before they impact deadlines.
New employee onboarding automation
The manual process: HR manually coordinates new hire processes across multiple departments, sending individual emails to IT for equipment setup, facilities for workspace preparation, and managers for orientation scheduling. Each department manually tracks their completion of onboarding tasks.
The automated workflow:
- Manager marks candidate status as “Hired” in the recruitment SharePoint list
- Power Automate triggers a comprehensive onboarding process:
- Creates tasks for IT department (setup accounts, order equipment, configure access)
- Notifies facilities team to prepare workspace and parking assignments
- Generates welcome email series to be sent to new employee before start date
- Creates calendar events for orientation sessions and first-week meetings
- Adds new employee to appropriate SharePoint sites, Teams channels, and distribution lists
- Updates organizational charts and directory information
- Each department receives task assignments with deadlines and can update completion status
- New employee receives automated welcome package with first-day information, building access details, and initial paperwork links
Business impact: Onboarding time reduces from 2-3 weeks to 3-5 days. New employees report better first-day experiences, and HR teams can focus on personal interaction rather than administrative coordination.
Project status updates and reporting
The manual process: Project managers manually collect status updates from team members via email or meetings, then update multiple tracking spreadsheets and presentation slides. Stakeholders receive inconsistent reports with varying levels of detail and formatting.
The automated workflow:
- Project tasks are managed in SharePoint lists or integrated with Microsoft Planner
- Team members update task progress directly in SharePoint or Planner
- Power Automate monitors for status changes and automatically:
- Updates project summary dashboards with current progress percentages
- Calculates project health metrics based on completed vs. overdue tasks
- Generates status reports in consistent formats for different stakeholder groups
- Sends weekly summary emails to project sponsors with key metrics and upcoming milestones
- Creates alerts when projects fall behind schedule or budget thresholds are exceeded
- Monthly executive reports are automatically compiled with data from all active projects and delivered to leadership teams
Business Impact: Project visibility improves dramatically, with stakeholders receiving timely, accurate information without requiring manual effort from project managers. Teams report 50% less time spent on status reporting activities.
Document review and version control
The manual process: Authors email draft documents to reviewers, who return comments via email or printed markups. Authors manually consolidate feedback, create new versions, and repeat the process. Final documents are manually uploaded to SharePoint with inconsistent naming and version tracking.
The automated workflow:
- Authors upload initial documents to a SharePoint “Review Required” library
- Power Automate automatically sends review requests to designated reviewers with document links and deadline information
- Reviewers use SharePoint’s built-in commenting and co-authoring features to provide feedback
- When all reviewers complete their input, the workflow:
- Notifies the author that review is complete
- Automatically moves the document to the “Review Complete” folder
- Creates a task for the author to address feedback and finalize the document
- Updates document metadata with review completion date and reviewer names
- Upon final approval, documents are automatically moved to the published library with proper version numbering and retention policies applied
Business impact: Document review cycles decrease by 45%, and version control errors are virtually eliminated. Teams report better collaboration and fewer instances of working with outdated document versions.
These examples demonstrate that successful SharePoint automation focuses on eliminating manual coordination tasks, improving communication consistency, and ensuring that routine processes happen reliably without human oversight. The key is identifying processes with clear steps and predictable decision points that can be translated into automated workflows.
When planning your own automation projects, look for similar patterns in your organization: approval workflows with defined hierarchies, notification processes that happen regularly, status updates that need to be synchronized across systems, and coordination tasks that involve multiple departments or systems.
Recommended SharePoint Automation Tools for Workflow Automation
Choosing the right tool depends on your SharePoint environment, complexity requirements, budget, and technical expertise. This section provides detailed insights into the most effective automation tools available today.
Tool overview
The following comprehensive analysis examines seven leading automation tools for SharePoint, each offering distinct advantages for different organizational needs and technical requirements. We’ll explore their latest 2025 features, pricing structures, and practical applications to help you make an informed decision. The tools range from Microsoft’s integrated solutions to specialized third-party platforms, covering everything from simple workflow automation to enterprise-grade process management.
1. Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow)
Power Automate remains the cornerstone of SharePoint automation for Microsoft 365 environments, with significant enhancements in 2025 that make it more powerful and accessible than ever.
Latest 2025 features:
- Copilot integration allows you to create workflows using natural language, making automation accessible to non-technical users
- Simplified OData editor (available June 2025) makes querying SharePoint lists and libraries much easier
- AI-powered automation with generative actions and intelligent document processing capabilities
- Enterprise-grade process maps for managing complex multi-flow automations with better visibility and control
- Enhanced observability tools provide detailed analytics and ROI tracking for your automation investments
Key capabilities: Power Automate offers deep integration with SharePoint through over 100 pre-built templates and more than 40 SharePoint-specific actions. You can automate everything from simple notifications to complex approval workflows that span multiple systems.
When to use: Power Automate is ideal when you’re working within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem and need cloud-based automation. It’s particularly effective for workflows that connect SharePoint with Teams, Outlook, Planner, and other Microsoft services.
Advantages:
- Included with most Microsoft 365 subscriptions, making it cost-effective
- Intuitive visual interface that business users can learn quickly
- Extensive template library reduces development time
- Strong integration with AI Builder for intelligent document processing
- Scalable from simple notifications to enterprise-wide process automation
Limitations:
- Premium connectors may require additional licensing costs
- Interface can become complex for very intricate workflows
- Customization options are more limited compared to specialized third-party tools
👉 Learn more about Copilot for SharePoint in our dedicated article: Copilot for SharePoint Explained: Features, Benefits, and Practical Usage
2. Power Apps
Power Apps complements Power Automate by providing the interface layer for SharePoint automation, particularly valuable for creating custom forms and applications that trigger automated workflows.
2025 enhancements:
- AI-assisted development helps build applications faster using natural language
- Shareable SharePoint connections (available April 2025) improve integration capabilities
- Enhanced offline capabilities for mobile scenarios
Best applications: Power Apps excels at creating custom interfaces for SharePoint data, building approval forms, and developing mobile applications that connect to SharePoint workflows. It’s particularly useful when you need to provide users with intuitive ways to interact with automated processes.
When to use: Choose Power Apps when you need custom forms, mobile applications, or specialized user interfaces that integrate with your SharePoint automation workflows.
3. Virto Workflow Automation App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365
Virto offers a compelling alternative for organizations needing more advanced workflow capabilities while maintaining a no-code approach.
Key features:
- Extensive action library with over 80 ready-to-use workflow actions
- Custom activity development with a remarkably fast 3-business-day turnaround
- SharePoint Designer integration for familiar workflow design experience
- Support for both Classic and Modern SharePoint experiences
- Enterprise-grade security with detailed documentation and support
Pricing structure:
- Business plan: $2.50 per user per month (billed annually)
- Enterprise plan: Custom pricing for large organizations
- Educational/Non-profit discount: 20% off available
- 14-day free trial with no credit card required
When to use: Virto is ideal for mid-size to large businesses that need more sophisticated workflow capabilities than Power Automate provides but don’t want to invest in expensive enterprise solutions. It’s particularly valuable if you have complex business processes that require custom actions.
Advantages:
- More workflow actions than standard Power Automate
- Quick customization turnaround for unique requirements
- Competitive pricing for the feature set
- Strong support and documentation
- Trusted by major organizations like Sony, FedEx, and Disney
[include banner of the app here: Try Virto Workflow Automation App for SharePoint Online]
4. Nintex Workflow
Nintex remains a powerful option for organizations needing advanced automation capabilities, though recent changes affect its long-term viability.
2025 updates:
- Table start events enable real-time workflow triggers from data changes
- Increased capacity supports up to 100 columns and 200,000 rows per table
- Enhanced user management with SCIM sync for identity provider integration
- Connection visibility improvements for better workflow management
Important consideration: Nintex Workflow for Office 365 reaches end-of-life in December 2025, making this a transitional option for organizations already using it.
Pricing:
- Standard Plan: $910 per month for unlimited users
- Advanced Plan: $1,400 per month (includes RPA capabilities)
- Enterprise Plan: Custom pricing
When to use: Nintex is suitable for organizations with complex automation requirements and existing Nintex investments, but new implementations should consider migration planning due to the Office 365 end-of-life timeline.
5. Nintex Automation Cloud (formerly K2)
Nintex Automation Cloud represents the company’s future-focused platform, designed for organizations needing comprehensive process automation.
2025 capabilities:
- Generative AI integration for rapid process creation and documentation
- Intelligent agents that enable real-time decision-making
- Solution Studio with reusable components for faster development
- Custom API support through Nintex Xtensions
Target organizations: This platform is designed for mid-market organizations with 100-300 SaaS tools that need to integrate cloud and on-premises systems.
Pricing:
- Starting at $15,000 per year with three service tiers
- High entry cost may limit adoption for smaller organizations
When to use: Consider Nintex Automation Cloud when you need enterprise-grade process automation across multiple systems and have the budget for a comprehensive solution.
6. Plumsail Actions
Plumsail Actions enhances existing Power Automate capabilities rather than replacing them, making it an excellent supplementary tool.
Specialized features:
- Advanced SharePoint operations beyond standard connector limitations
- Cross-site functionality for complex SharePoint scenarios
- Third-party integrations with services like Salesforce, Adobe Sign, and DocuSign
- Document processing capabilities for PDF and Office formats
When to use: Plumsail Actions is ideal when you’re already using Power Automate but need additional capabilities for document processing, cross-site operations, or specific third-party integrations.
Considerations:
- Pricing transparency is limited, requiring contact for detailed costs
- Dependency on Power Automate means it’s not a standalone solution
7. SkyBow Solution Studio
SkyBow focuses on rapid application development with automation capabilities, targeting organizations that need custom SharePoint solutions quickly.
Core features:
- Visual forms designer with drag-and-drop functionality
- Unlimited automation sequences with advanced logic support
- Data organization tools including master/detail views and calculations
- Advanced deployment features for safe publishing and version control
Trust indicators:
- 450+ organizations across 40+ countries use SkyBow
- Microsoft 365 integration provides seamless connectivity
- Proven track record in various industries and use cases
When to use: SkyBow is suitable for organizations needing custom SharePoint applications with embedded automation, particularly when rapid development is important.
Comparison and Selection Criteria
When choosing among these tools, consider these key factors:
Environment compatibility:
- SharePoint Online with Microsoft 365: Power Automate, Power Apps, Virto, Plumsail Actions
- SharePoint On-Premises: Nintex Workflow, SkyBow Solution Studio
- Hybrid environments: Nintex Automation Cloud, SkyBow Solution Studio
Complexity requirements:
- Simple to moderate workflows: Power Automate, Virto Workflow App
- Complex enterprise processes: Nintex Automation Cloud, SkyBow Solution Studio
- Custom integrations: Plumsail Actions, Nintex platforms
Budget considerations:
- Cost-effective: Power Automate (included with Microsoft 365), Virto ($2.50/user/month)
- Mid-range: Nintex Workflow ($910-$1,400/month)
- Enterprise: Nintex Automation Cloud ($15,000+/year)
Technical expertise:
- Business user friendly: Power Automate, Virto Workflow App
- IT department managed: Nintex platforms, SkyBow Solution Studio
- Developer augmented: Plumsail Actions, custom solutions
Integration needs:
- Microsoft-centric: Power Automate, Power Apps
- Multi-platform: Nintex Automation Cloud, Plumsail Actions
- SharePoint-focused: Virto Workflow App, SkyBow Solution Studio
| Tool | Best for | Starting price | Technical skill required | SharePoint integration |
| Power Automate | Microsoft 365 users | Included with M365 | Low | Excellent |
| Virto Workflow App | Mid-size businesses | $2.50/user/month | Low | Excellent |
| Nintex Workflow | Complex processes | $910/month | Medium | Good |
| Nintex Automation Cloud | Enterprise automation | $15,000/year | High | Good |
| Plumsail Actions | Power Automate enhancement | Contact for pricing | Low-Medium | Very Good |
| SkyBow Solution Studio | Custom applications | Contact for pricing | Medium | Very Good |
The right choice depends on balancing these factors against your specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and long-term automation strategy. Most organizations find success starting with Power Automate for basic needs and supplementing with specialized tools as requirements grow more complex.
Best Practices for Creating and Implementing Automation in SharePoint
Successful SharePoint workflow automation requires more than just technical implementation—it demands careful planning, user consideration, and ongoing maintenance. These best practices, drawn from real-world implementations across various organizations, will help you avoid common pitfalls and maximize the value of your automation investments.
Start with frequently repeated and simple processes
The temptation to automate everything at once is strong, but this approach often leads to project failure and user resistance. Instead, focus on processes that offer the best return on investment with the lowest implementation risk.
- Identify high-impact, low-complexity processes: Look for tasks that happen regularly—daily, weekly, or monthly—and require significant manual effort. These might include vacation request approvals, document routing notifications, or status updates across multiple lists. The key is finding processes where automation will save substantial time while being straightforward to implement.
- Establish clear success metrics: Before starting any automation project, define what success looks like. Are you trying to reduce processing time from hours to minutes? Eliminate approval bottlenecks? Reduce data entry errors? Having specific, measurable goals helps you choose the right processes to automate and demonstrates value to stakeholders.
- Build momentum with quick wins: Start with simple automations that deliver immediate, visible benefits. A notification workflow that saves employees from checking SharePoint lists manually might seem basic, but it builds confidence in automation and demonstrates practical value. These early successes make it easier to get support for more complex projects later.

Common first automation candidates:
- Email notifications when new documents are uploaded to specific libraries
- Automatic task assignments when project status changes
- Reminder emails for approaching deadlines
- Simple approval workflows with single approvers
- Document archiving based on age or status
Document all steps, conditions, and participant roles
Comprehensive documentation is critical for both successful implementation and long-term maintenance. Without clear documentation, automations become “black boxes” that no one understands when they need updates or troubleshooting.
- Create process flow diagrams: Visual representations of your automation help everyone understand how the process works. Include start and end points, decision points, and the sequence of actions. Use simple flowchart symbols that non-technical stakeholders can follow. Tools like Visio, Lucidchart, or even PowerPoint can create effective process diagrams.
- Define roles and responsibilities: Clearly specify who participates in each step of the automated process. Document not just who receives notifications or approvals, but also who has permissions to modify the automation, who should be contacted when issues arise, and who is responsible for maintaining the process over time.
- Document business rules and logic: Write down the conditions that trigger different actions in your automation. For example: “If the expense amount is over $500, route to department manager; if over $2,000, also include finance director.” These rules seem obvious during implementation but become unclear months later when someone needs to modify the workflow.
- Include error handling scenarios: Document what should happen when things go wrong. What occurs if an approver is unavailable? How does the system handle missing required information? What notifications are sent when a workflow fails? Planning for these scenarios prevents confusion and ensures business continuity.
Test automations thoroughly
Testing is where many automation projects fail, often because organizations rush to deploy without adequately validating their workflows. Comprehensive testing prevents embarrassing failures and ensures your automation works reliably in real-world conditions.
- Create a test environment: Whenever possible, build and test your automation in a separate SharePoint site or environment that mirrors your production setup. This allows you to experiment with different scenarios without affecting live business processes. Include test data that represents various real-world conditions.
- Test edge cases and exception scenarios: Don’t just test the “happy path” where everything works perfectly. What happens when required fields are empty? How does the automation handle special characters in names or extremely long text entries? What occurs when multiple people try to approve the same item simultaneously? These edge cases often reveal problems that cause automations to fail unexpectedly.
- Validate with real users: Include actual end users in your testing process. They often interact with systems in ways that developers don’t anticipate and can identify usability issues that technical testing misses. Have users perform typical tasks using realistic data and scenarios.
- Performance testing: Test your automation with realistic data volumes. A workflow that handles 10 items smoothly might struggle with 1,000 items. Consider how your automation will perform during peak usage periods and whether it might create bottlenecks in other systems.
- Create a testing checklist:
- All required fields are properly validated
- Notifications are sent to correct recipients with accurate information
- Approvals and rejections are processed correctly
- Error conditions are handled gracefully
- Performance is acceptable under realistic load
- Security permissions are properly enforced
- Integration with other systems works reliably
| Testing phase | Key validation points | Success criteria |
| Functional testing | Required fields validated, notifications accurate | All workflow paths execute correctly |
| User acceptance | Real users complete typical tasks | Users can complete processes without assistance |
| Performance testing | Realistic data volumes processed | Workflows complete within acceptable timeframes |
| Security testing | Permissions properly enforced | Only authorized users access sensitive information |
| Error handling | Edge cases and failures managed | Graceful failure with clear error messages |
👉 Learn more about SharePoint sites here:
- SharePoint Site Types Explained: Choosing the Right Site for Your Needs
- SharePoint Hub Sites: for Simplified Collaboration and Easy Navigation
- Understanding SharePoint Subsite: From Basics to Implementation
- SharePoint Communication Site: Improve Communication and Teamwork
Use variables, logical conditions, and branching
Well-designed automation adapts to different situations rather than following rigid, one-size-fits-all processes. Smart use of variables and conditional logic makes your workflows more flexible and valuable.
- Implement dynamic routing: Use conditions to route requests to different people based on criteria like department, amount, or request type. For example, HR requests might go to the HR manager, while IT requests go to the IT director. This eliminates the need for multiple similar workflows and makes maintenance easier.
- Store reusable information in variables: Variables allow you to store information once and reuse it throughout your workflow. Instead of looking up the same person’s email address multiple times, store it in a variable at the beginning of the process. This improves performance and makes workflows easier to understand and maintain.
- Create escalation paths: Build logic that handles situations where normal processes don’t work. If an approver doesn’t respond within a specified timeframe, automatically escalate to their manager. If a required system is unavailable, route the request through an alternative path or queue it for later processing.
- Use parallel processing when appropriate: Some workflow steps can happen simultaneously rather than sequentially. For example, when a purchase request is approved, you might simultaneously notify the requestor, create a purchase order, and update budget tracking. Parallel processing reduces overall completion time.
Example conditional logic:
If expense amount < $500
Route to direct manager
Else if expense amount < $2,000:
Route to direct manager, then department director
Else:
Route to direct manager, department director, then finance director
Involve end users early and often
Automation succeeds when users embrace it, not when they’re forced to use it. Early user involvement ensures your automation meets real needs and gains the support necessary for successful adoption.
- Conduct user interviews: Before designing your automation, talk to the people who currently perform the process manually. They understand the nuances, exceptions, and pain points that may not be obvious from documentation. These insights help you design automation that actually improves their work rather than creating new problems.
- Create user personas: Identify different types of users who will interact with your automation and understand their specific needs. A department manager approving requests has different requirements than an employee submitting them. Design your automation to serve each persona effectively.
- Prototype and get feedback: Show users mockups or early versions of your automation before full implementation. This allows them to identify issues when changes are still easy to make. Users often have suggestions that significantly improve the final solution.
- Provide comprehensive training: Don’t assume users will figure out your automation on their own. Provide training that covers not just how to use the new process, but why it’s changing and what benefits they’ll experience. Include both formal training sessions and reference materials users can consult later.
- Create super users: Identify enthusiastic users who can become automation champions within their departments. These super users can help train others, answer questions, and provide feedback for improvements. They often become your most valuable advocates for future automation projects.
Consider security, access rights, and compliance
Security and compliance considerations must be built into your automation from the beginning, not added as an afterthought. Poor security practices can expose sensitive information or create compliance violations.
- Apply principle of least privilege: Your automation should have only the permissions necessary to perform its functions. Don’t grant broad administrative rights when specific, limited permissions will suffice. This reduces security risk and ensures your automation doesn’t accidentally modify data it shouldn’t touch.
- Respect existing SharePoint permissions: Design your automation to work within SharePoint’s existing security model rather than bypassing it. If users don’t have permission to view certain documents manually, your automation shouldn’t expose that information through notifications or other means.
- Audit trail requirements: Many organizations have compliance requirements for tracking who did what and when. Ensure your automation creates appropriate audit trails and doesn’t obscure important information about user actions and system changes.
- Handle sensitive data appropriately: Be careful about what information your automation includes in emails, notifications, or logs. Sensitive data like employee salaries, personal information, or confidential business data should be handled with appropriate security measures.
- Test security scenarios: Verify that your automation behaves correctly when users have different permission levels. What happens when someone without appropriate permissions tries to interact with your workflow? Does it fail gracefully or create security vulnerabilities?
Plan for updates and maintenance
Automation isn’t a “set it and forget it” solution. Business requirements change, systems are updated, and organizations evolve. Planning for maintenance from the beginning ensures your automation remains valuable over time.
- Assign ownership: Designate someone as the owner of each automation, responsible for monitoring its performance, handling user questions, and making necessary updates. This person should understand both the technical implementation and the business process being automated.
- Schedule regular reviews: Set up periodic reviews of your automation to ensure it’s still meeting business needs. Are the original pain points still relevant? Have new requirements emerged? Has the business process changed in ways that affect the automation? Regular reviews help you identify needed updates before they become problems.
- Monitor performance and usage: Track how your automation is performing over time. Are workflows completing successfully? Are users actually using the automation as intended? Are there error patterns that suggest underlying issues? Most automation platforms provide analytics that help you understand usage patterns and identify problems.
- Version control and documentation: Maintain version control for your automation workflows and keep documentation current. When you make changes, document what was changed, why, and how it affects users. This information is invaluable for troubleshooting and future modifications.
- Plan for technology changes: Stay informed about updates to your automation platform and SharePoint. Microsoft regularly releases new features and occasionally deprecates old ones. Understanding these changes helps you plan updates and take advantage of new capabilities.
Use templates and standardize approaches
Standardization makes automation more efficient to develop, easier to maintain, and more consistent for users. Creating reusable templates and standard approaches accelerates future automation projects.
- Create workflow templates: Develop templates for common automation patterns like approval workflows, notification processes, and data synchronization. These templates provide starting points for new projects and ensure consistency across different automations.
- Standardize naming conventions: Use consistent naming conventions for workflows, variables, and components. This makes it easier for different team members to understand and maintain automations. Include naming standards for SharePoint lists, libraries, and metadata used by your automations.
- Develop reusable components: Create standard components that can be reused across multiple automations. This might include common approval logic, standard notification templates, or data validation routines. Reusable components reduce development time and ensure consistency.
- Document standard practices: Create documentation that describes your organization’s standard approaches to automation. This might include preferred tools for different scenarios, standard security practices, or guidelines for user interface design. Standard practices help new team members contribute more quickly and ensure consistency across projects.
Maintain transparency and establish monitoring
Users need to understand what’s happening with their requests and submissions. Transparency builds trust and reduces support requests, while monitoring helps you identify and resolve issues quickly.
- Provide status visibility: Give users ways to check the status of their requests without having to contact support. This might include automated status update emails, dashboard views, or integration with existing project management tools.
- Set up proactive monitoring: Configure monitoring that alerts you to problems before users report them. This might include notifications when workflows fail, when processing takes longer than expected, or when error rates increase. Proactive monitoring helps you maintain high reliability.
- Create clear error messages: When things go wrong, provide users with clear, actionable error messages rather than technical jargon. A message like “Your request couldn’t be processed because the Cost Center field is required” is much more helpful than “Error 404: Field validation failed.”
- Establish support procedures: Create clear procedures for users to get help when they encounter problems with automated processes. This might include help desk ticket categories, FAQ documents, or designated support contacts. Make sure support staff understand how your automations work so they can help users effectively.
- Regular communication: Keep users informed about automation updates, new features, and any changes that affect their work. Regular communication helps users feel informed and valued, which improves adoption and satisfaction.
| Metric category | Key indicators | Alert thresholds | Action required |
| Performance | Average completion time, queue length | >2x normal processing time | Investigate bottlenecks |
| Reliability | Success rate, error frequency | <95% success rate | Review error patterns |
| Usage | Daily/weekly volume, user adoption | 50% drop in usage | Check for process changes |
| User Satisfaction | Help desk tickets, user feedback | >5 tickets per week | Review user training needs |
Following these best practices significantly increases the likelihood that your SharePoint automation projects will succeed and continue providing value over time. Remember that automation is a journey, not a destination—start with solid foundations and continuously improve based on user feedback and changing business needs.
Conclusion on Power Automate SharePoint & SharePoint Automation
SharePoint has proven itself as a powerful platform for automating diverse business processes across organizations of all sizes. From simple document notifications to complex multi-stage approval workflows, SharePoint automation capabilities have matured significantly, offering practical solutions for the repetitive tasks that consume valuable time and resources in modern workplaces.
The combination of Power Automate and other no-code automation tools has democratized workflow creation, allowing business users to build sophisticated automations without extensive technical expertise. This shift means you can speed up routine operations, minimize human errors, and redirect your team’s focus toward strategic initiatives that drive real business value. The time savings alone—often measured in hours per week per employee—justify the investment in automation for most organizations.
The key to successful SharePoint automation lies in taking a measured, strategic approach. Start with simple scenarios that address clear pain points and deliver immediate value. A basic notification workflow or straightforward approval process can demonstrate the power of automation while building confidence and expertise within your team. As you gain experience and user acceptance, you can gradually scale to more complex automations that address sophisticated business requirements.
For organizations seeking a balance between Power Automate’s capabilities and more advanced workflow features, the Virto Workflow Automation App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365 offers a compelling solution. With over 80 ready-to-use actions, quick customization turnaround times, and competitive pricing at $2.50 per user per month, Virto provides the flexibility to create both simple and complex business processes without coding. The platform’s integration with SharePoint Designer and support for both Classic and Modern SharePoint experiences make it particularly valuable for organizations with diverse automation needs.
Consider scheduling a demo or learning more about the Virto Workflow Automation App at the site to see how it might fit your specific requirements.
To deepen your understanding of SharePoint automation and stay current with best practices, we recommend exploring these valuable resources:
Official Microsoft Resources:
- Power Automate SharePoint Overview
- Overview of Workflows in SharePoint
- Power Automate SharePoint Actions Reference
For more insights and practical guidance on SharePoint automation, workflows, and best practices, explore our dedicated SharePoint blog section, where you’ll find regular updates on new features, implementation strategies, and real-world use cases: