How to Manage Microsoft Teams Permissions Effectively
Dive into this practical guide on Microsoft Teams permissions and master the art (and science) of keeping your digital workspace secure, efficient, and ready for anything.
Microsoft Teams has become a workspace essential for organizations that rely on collaboration—especially those with hybrid or remote teams. With so many users, channels, and integrated apps, managing permissions isn’t simply a technical detail; it’s a foundation for security, compliance, and productivity. Teams permissions determine who can access sensitive conversations, share files, invite guests, or alter the configuration of a workspace. Overlooking these settings can lead to data leaks, accidental loss of information, or compliance headaches.
In this guide, you’ll find a practical breakdown of roles, permission levels, and policy controls in Teams. You’ll also see the latest updates, security enhancements, and proven strategies for configuring permissions in a way that keeps your environment safe and organized.
What Are Microsoft Teams Permissions?
Microsoft Teams permissions are not just a set of checkboxes buried in the settings menu—they are a carefully layered system of access rights that define what each person can see and do within teams, channels, and integrated apps. At a fundamental level, these permissions control actions such as creating channels, inviting new members, managing files, and connecting third-party tools.
There are several tiers to this structure:
- Team level: Controls who can manage the overall team, including adding or removing members, editing settings, and assigning roles.
- Channel level: Determines who can access and participate in specific channels, whether they are public, private, or shared.
- Applications: Governs which apps can be added, what data they access, and how deeply they integrate with your workspace.
- Administration: Reserved for those who manage global security and compliance policies through the Teams Admin Center.
Setting these permissions with care helps protect sensitive information, reduces the risk of accidental changes or deletions, and streamlines teamwork by clarifying responsibility. In larger organizations, tight permission management is even more critical; a single misconfiguration can expose confidential data or disrupt project workflows.
What are the roles and permissions in Microsoft Teams?
Microsoft Teams organizes access through clearly defined roles, each carrying a distinct set of capabilities. Understanding these is the first step to building a secure and well-ordered environment.
- Team owner: Owners have the highest authority within a team. They manage membership, assign other owners, set team policies, and control settings that affect how the team operates. Owners can also add or remove channels, configure tabs and apps, and oversee the team’s security posture. Best practice is to assign at least two owners to every team to prevent administrative lockout if one owner departs.
- Member: Members are internal users who participate in conversations, share files, and contribute to public channels. While they enjoy broad collaboration rights, their ability to alter team structure or settings is limited by what owners allow. Owners can fine-tune member permissions, restricting actions like creating channels or deleting messages if tighter control is needed.
- Guest: Guests are external users—partners, vendors, or clients—who join a team by invitation. Their access is intentionally limited: they can view and post messages, share files, and participate in discussions, but cannot create teams or channels. Owners can further restrict what guests can do, tightening controls to prevent data leaks or unauthorized sharing.
💡 Recent updates now allow guests and external collaborators to be reported for security issues, and provide admins with more control over their access and event participation.
It’s worth emphasizing that these roles are not static. Owners have the ability to promote members or demote owners as needed. The larger or more sensitive the team, the more deliberate these assignments should be. Limiting the number of owners and carefully reviewing guest access are simple steps that significantly reduce risk.
Getting permissions right in Teams is an ongoing process, not a one-time setup. The next sections will walk through how to fine-tune these settings for both everyday collaboration and the latest security requirements.
General Microsoft Teams Permissions Settings
Mastering permission settings is key to keeping your Microsoft Teams secure and under control. In this section, we’ll show you how to manage team-level permissions, assign roles smartly, and fine-tune access for members and guests. Every step is vital to shaping how your team collaborates and protects its data.
How do I manage and edit permissions in Teams?: Managing team-level permissions in Microsoft Teams
Team-level permissions act as the backbone for everything that happens within a Microsoft Teams workspace. These settings determine what members can do—ranging from creating new channels to editing messages, using mentions, and managing tabs. Managing these permissions isn’t a matter of ticking boxes and moving on; it requires thoughtful configuration to balance collaboration with control.
To review or change team-level permissions (if you’re a team owner), open Teams, select your team, and choose “Manage team.” Under the “Settings” tab, you’ll find options to:
- Allow or prevent members from creating and deleting channels.
- Enable or disable editing and deleting of messages.
- Control who can use @mentions for the team or individual members.
- Set restrictions on adding tabs, connectors, and apps.
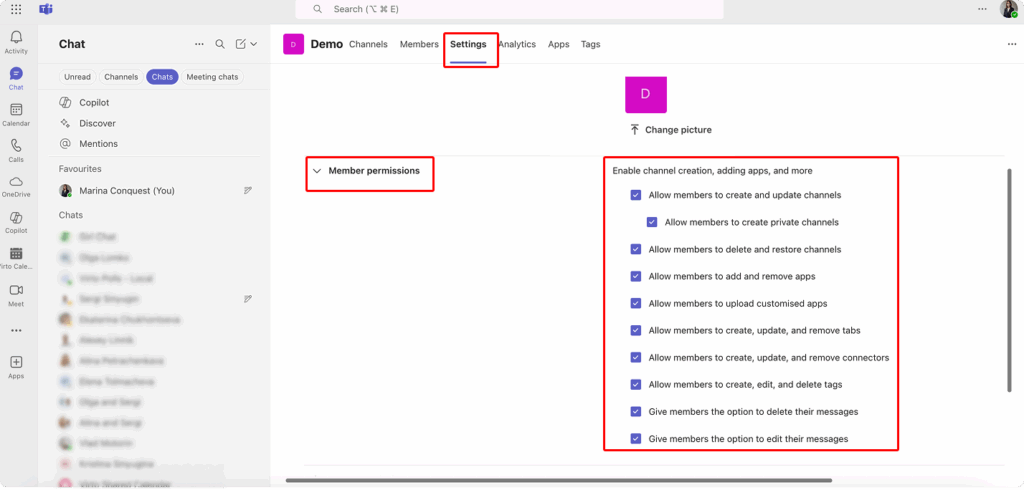
Carefully considering each of these options can help prevent unexpected changes, data loss, or disruptions to team workflows. For projects that involve sensitive information or require strict oversight, it’s wise to limit the ability to create channels or delete content to owners only.
How do I change permissions in Microsoft Teams?: Changing or assigning roles in Microsoft Teams
Role assignments in Teams are straightforward, but they have lasting impact. Only team owners have the authority to change roles—be it elevating a member to owner status or returning an owner to a standard member role. Assigning at least two owners per team is not just a best practice; it’s a safeguard against losing administrative control if someone leaves or changes roles.
To adjust roles:
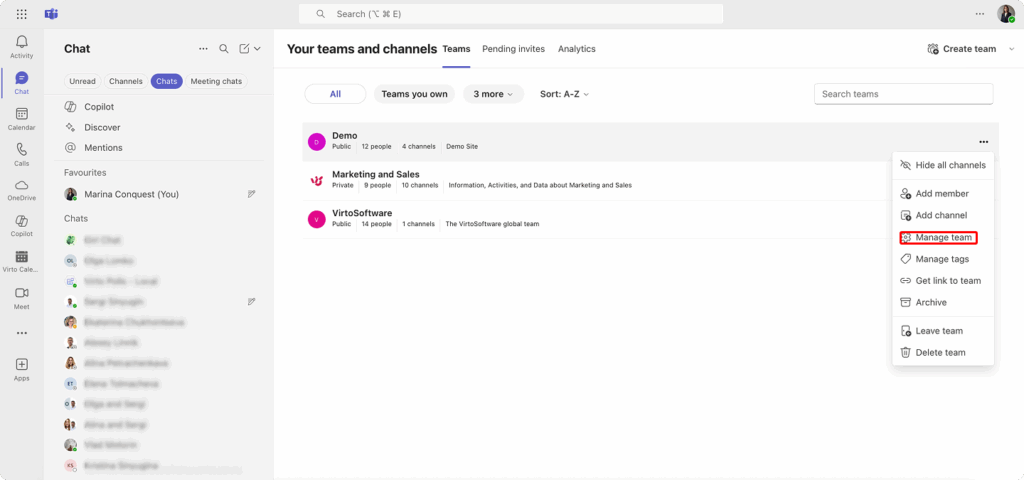
- Open the desired team in Teams.
- Click the three dots next to the team name and select “Manage team.”
- Under the “Members” tab, locate the person whose role you want to change.
- Use the dropdown menu next to their name to assign either “Owner” or “Member.”
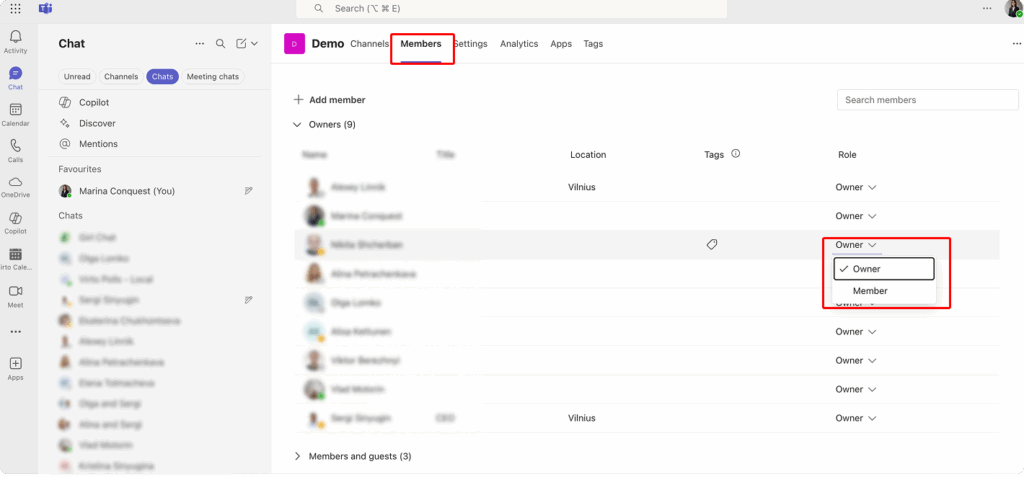
Owners should routinely review this list, ensuring each owner is genuinely responsible for team management. Avoid assigning owner status indiscriminately—it’s a common mistake that can lead to confusion and unintended changes.
Member and guest settings
Members and guests each bring different levels of access and responsibility. Members, as internal users, can typically participate in all public channels, contribute to discussions, and share files. However, owners can further restrict these actions if tighter control is needed.
Guests, on the other hand, are external collaborators with a limited set of permissions by default. Their access can be tailored further; for example, you might restrict guests from inviting others, deleting content, or using certain apps. To fine-tune these settings:
- Visit the Microsoft Teams Admin Center.
- Navigate to the “Org-wide settings” and select “Guest access.”
- Adjust the toggles to enable or disable features such as private calling, meeting scheduling, and file sharing for guests.
Reviewing both member and guest permissions on a regular basis is crucial. As projects evolve or personnel change, outdated access can introduce unnecessary risk. Owners and admins should treat this as a routine part of managing a secure and efficient Teams environment.
💡 Learn more about managing teams from the Microsoft Teams admin center: Manage teams in the Microsoft Teams admin center
Microsoft Teams Channel Permissions
Channel permissions are the backbone of controlling information flow and access within each team in Microsoft Teams. Channels aren’t one-size-fits-all—they can be standard, private, or shared, each with unique controls and best practices to match your team’s needs.
What are MS Teams channel permissions?
Channels serve as focused spaces for conversations, file sharing, and collaboration within a team. Permissions at the channel level decide who can participate, post, edit, or manage content. This means you can create open spaces for general discussion or more restricted areas for confidential projects.
Standard channels are accessible to all team members, while private and shared channels offer more selective participation. Setting channel permissions thoughtfully helps protect sensitive data, limits distractions, and ensures the right people have access to the right conversations.
👉 How do I give permission to Microsoft Teams? To give permission in Microsoft Teams, you assign users to roles such as owner, member, or guest within a team or channel, and adjust their access using the Teams Admin Center or team settings.
How to set permissions for standard channels
In standard channels, team owners are responsible for defining what members can do. Owners can allow or restrict actions such as creating new tabs, adding apps or connectors, and deleting messages. These options are managed centrally through the team’s settings:
- Open the team, select “Manage team,” and go to the “Settings” tab.
- Under “Member permissions,” adjust capabilities like adding or deleting tabs, connecting apps, or removing messages.
Restricting certain actions in high-traffic or sensitive channels helps maintain order and prevents accidental loss of important information. Regularly reviewing these settings ensures they stay aligned with the team’s current needs.
Private and shared channels
Not every conversation belongs in the open. Private channels are available only to a select group of team members invited to participate. This is ideal for discussions involving budgets, personnel, or confidential projects. Importantly, team owners cannot access the contents of a private channel unless they are explicitly added as members.
Shared channels, on the other hand, are designed for cross-team or even cross-organization collaboration. They allow you to bring in people from outside your team—or even outside your company—without granting them access to the entire team’s content. Access to shared channels is managed separately and offers a flexible way to work with external partners or other departments.
Both private and shared channels require careful management. Owners should review membership lists regularly and ensure permissions match the sensitivity of the information being discussed.
Tips for setting up permissions securely
Effective channel management is equal parts diligence and strategy. Consider these recommendations:
- Clearly label channels based on the type of information they contain—general, restricted, or confidential.
- Assign a responsible owner for each channel, even within a larger team, to keep membership and access up to date.
- Schedule regular audits of channel permissions and activity, especially for private or shared spaces.
- Take advantage of Microsoft Purview and other compliance tools to monitor sensitive data and enforce security policies.
A disciplined approach to channel permissions keeps your collaboration focused, your data protected, and your teams working smoothly—even as projects and participants change.
App Permission Settings
Applications are at the heart of Microsoft Teams, enhancing its functionality well beyond chat and meetings. But every app introduces potential risks. Managing app permissions isn’t just about boosting productivity—it’s your front line against data leaks, privacy breaches, and unauthorized integrations.
Managing app permissions
Teams admins are responsible for overseeing which apps are available, what data they can access, and how deeply they integrate with your organization’s environment. The Teams Admin Center is the central hub for these controls. Here, administrators can:
- Allow or block specific apps from Microsoft, third parties, or internally developed solutions.
- Control what permissions each app can request from users, such as access to messages, files, calendars, or user profiles.
- Set policies that determine which apps appear in the Teams app store for your users.
Recent updates now require administrators to review and approve apps—especially those from third-party developers—before deployment. Detailed security and certification information is provided for each app, supporting informed decisions and compliance with internal policies.
How to change app permissions
Changing or revoking app permissions is a straightforward process in the Teams Admin Center. To review the current list of installed apps and their permissions:
- Go to the Teams Admin Center.
- Navigate to “Teams apps” and select “Manage apps.”
- Click on any app to view its permissions and security details.
- From here, you can approve, block, or configure access as needed.
For bulk changes, the latest enhancements now allow admins to manage Microsoft 365-certified apps using rule-based controls, making large-scale governance more efficient.
👉How do I add permissions to Microsoft Teams app? To add permissions for a Teams app, use the Teams Admin Center to create or edit app permission policies, allowing or blocking specific apps for users or groups, and reviewing app permissions before deployment.
Security policies
App permission policies are your primary tool for ensuring only approved and secure apps are available to users. With these policies, you can:
- Allow only apps that meet your organization’s security standards.
- Restrict installation of third-party or non-certified apps.
- Block specific categories of apps, such as those integrating with social media or external chat services.
- Apply different policies to various groups—such as stricter controls for guests or sensitive departments.
Some app permissions require extra scrutiny. Pay particular attention to apps that request access to private chats, calendars, or the ability to send messages on users’ behalf. The principle of least privilege should guide every decision: grant only the permissions an app truly needs.
💡 With new DLP and sensitivity label options available through Microsoft Purview, administrators can now enforce more granular controls to prevent accidental sharing of sensitive data. Read more: Security and compliance overview.
Regularly review both installed apps and their granted permissions. Removing outdated or unused integrations reduces your attack surface and helps maintain compliance with industry standards. A disciplined, proactive approach to app permissions is essential for a secure Teams environment.
How Do I Change Microsoft Teams Settings?: Configuring General Teams Settings
Configuring organization-wide Teams settings sets the foundation for security, collaboration, and compliance across your company. The right setup prevents mistakes, streamlines administration, and ensures every user works within clear, consistent boundaries.
Where to find the main settings
Most global Microsoft Teams settings reside in the Microsoft Teams Admin Center, accessible at admin.teams.microsoft.com. This web-based control panel brings together all the critical categories you’ll need:
- Org-wide settings: Manage domains, external access, and guest collaboration.
- Teams settings: Adjust notifications, message policies, and member or guest permissions.
- Teams apps: Oversee app installation, access, and security policies.
- Meetings & calls: Define video and audio settings, enable or restrict recording, and control device permissions.
- Files: Configure SharePoint and OneDrive integration for secure file storage and sharing.
- Messaging: Set rules for editing or deleting messages, using GIFs, stickers, or memes.
- Templates & policies: Establish standardized team templates with preset channels, permissions, and apps.
How to change team and channel settings
To fine-tune settings for a specific team or channel:
- Open Microsoft Teams and select the appropriate team.
- Click the three dots next to the team name and choose “Manage team.”
- Under the “Settings” tab, you’ll see options for Microsoft Teams member permissions, guest permissions, and channel management.
- Adjust features such as channel creation, message editing, and the use of connectors or tabs according to your team’s needs.
For broader changes—like organization-wide policies or app restrictions—return to the Admin Center. Here, you can assign policies globally or tailor them for specific users, departments, or groups.
Tips for organizing a secure environment
A secure, well-organized Teams environment results from more than just initial setup. Consider these recommendations as part of your ongoing management routine:
- Regularly review access levels for both members and guests, especially when roles change or staff leave.
- Use team templates to standardize structure, permissions, and apps for different departments or project types.
- Limit access to sensitive data through private channels and robust security policies.
- Set message and file retention policies that match both internal and regulatory requirements.
- Apply separate, stricter policies for guests—minimizing their access to chats, files, and applications where possible.
- Enable notifications and reminders to help users stay on top of important updates, meetings, or policy changes.
Taking a proactive approach with these settings reduces risk, builds consistency, and frees up time for more strategic work. Regular audits and timely adjustments keep your Teams deployment running smoothly as your organization evolves.
Recent Updates to Microsoft Teams Permissions (2024–2025)
Microsoft Teams is evolving rapidly, with significant security and administrative updates rolling out in late 2024 and 2025. Staying up to date with these changes is essential for every admin and security-conscious team.
Mandatory security updates for Teams clients:
- Microsoft now requires Teams desktop clients to update to the latest version within 90 days of release.
- Users on outdated versions will be blocked until they update, with enforcement ramping up through April and May 2025 across platforms.
- Action: Ensure your organization’s update policies are in place so users are not locked out of Teams.
External collaboration enhancements:
- Starting April–May 2025, users can report security concerns about external collaborators directly from chats and meetings.
- New policies for town hall event access give admins stricter control over who can attend.
Advanced app management and bulk controls:
- Since October 2024, admins must review security and certification details before deploying apps and extensions.
- From August 2025, you can bulk-manage Microsoft 365-certified apps using rule-based controls in the Teams Admin Center, making large-scale governance more efficient.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and sensitivity labels:
- Microsoft recommends leveraging Microsoft Purview to set up DLP policies, preventing accidental sharing of sensitive data.
- Sensitivity labels can now be applied to teams and meetings, further regulating access to confidential information.
Administrative UX and policy improvements:
- As of December 2024, you can configure external access policies directly in the Teams Admin Center (previously only via PowerShell).
- New policies allow organizers/presenters to control content visibility and meeting features more granularly, including new controls for transcription, recording, and display names (rolling out through early 2025).
- External meeting participants can now join via one-time passcode (OTP), enhancing security for guests without managed accounts.
Staying informed about these updates is critical for compliance and operational continuity. Make it a habit to review Microsoft’s release notes and update your internal documentation and training accordingly.
💡 Review these and other updates here: Release notes for Microsoft Teams admin features
Common Mistakes When Working with MS Teams Permissions
Even the best administrators can make mistakes when configuring permissions in Microsoft Teams. These missteps can silently create security gaps, cause confusion, and expose sensitive data. Identifying and avoiding these common pitfalls is critical for managing Teams effectively at scale.
Assigning all participants as owners
It might seem convenient to grant everyone owner status, especially in smaller teams. However, this approach quickly becomes a liability. Owners have sweeping powers: they can remove members, change roles, delete channels, and alter critical security settings. When too many users hold these privileges, tracking changes becomes difficult, and the likelihood of accidental or unauthorized modifications rises sharply.
Recommendation: Assign owner status only to those who genuinely need it—typically team leads or project managers who understand both the goals and the governance of the team. Everyone else should remain a member.
No control over guests
Guests bring valuable perspectives but, without careful oversight, can access more than intended. Unrestricted guest access means external users might see historical messages, files, and even sensitive discussions. There’s also the risk that guests can invite others or use applications unsuited for external collaboration.
Recommendation: Review guest access settings in the Teams Admin Center. Limit guest permissions to the bare minimum needed for collaboration, and disable their ability to invite others or remove content unless absolutely necessary. Regularly audit the guest list and remove anyone who no longer needs access.
Ignoring application privacy settings
Third-party apps often request broad permissions—sometimes more than they truly require. Without paying attention, administrators may inadvertently grant access to messages, calendars, or files to apps that store data externally or lack proper encryption.
Example: An employee installs a project management bot that requests access to messages and calendars. If not checked, the bot could copy sensitive information to an external server, bypassing company policies.
Recommendation: Approve apps centrally and review their permissions carefully. Maintain a whitelist of trusted applications and block anything that doesn’t meet your organization’s standards.
Not using the Teams Admin Center
Relying solely on manual settings in the Teams interface is limiting. Important controls—such as group-wide policies, bulk permission management, and robust auditing—are only available in the Admin Center. Without this tool, it’s easy to miss inconsistencies or overlook gaps in security.
Recommendation: Always use the Teams Admin Center for comprehensive management. This approach ensures that policies are enforced consistently and changes can be tracked or rolled back if needed.
Neglecting security policies and templates
Letting teams develop without standardized policies or templates often leads to inconsistent structures, unauthorized applications, and unpredictable access rights. This lack of uniformity makes oversight difficult and can slow down collaboration.
Recommendation: Establish templates and default security policies for different types of teams or departments. This ensures every new workspace starts with the right structure and controls from day one.
Avoiding these pitfalls isn’t just about following rules—it’s about building an environment where people can work confidently, knowing their data and conversations are protected. Regular reviews, clear role assignments, and disciplined use of administrative tools are the hallmarks of effective Teams management.
Recommendations for Admins and Teams
Nailing permissions in Microsoft Teams isn’t a one-and-done task—it’s an ongoing effort blending technical controls with smart habits. These recommendations will help admins and team leads create a secure, efficient workspace while empowering users to collaborate with confidence.
Practical tips
The following practical tips serve as a reliable checklist for maintaining strong, well-managed permissions in Microsoft Teams.
- Assign owners responsibly: Limit owner roles to those who are truly accountable for team settings, membership, and security. Avoid the temptation to give everyone administrative rights—this step alone reduces risk and confusion.
- Regularly review the guest list: External users can easily slip through the cracks. Make it a habit to audit the guest list in the Teams Admin Center. Remove anyone whose access is no longer necessary, especially after projects wrap up or partnerships change.
- Manage apps centrally: Use the Teams Admin Center to control which apps can be installed and what level of access they require. Block apps that don’t meet your organization’s privacy and security standards, with particular scrutiny for those requesting message or file access.
- Use team templates with pre-configured permissions: Templates streamline the creation of new teams, ensuring consistent structure, channels, and permission settings. This not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of inconsistent or insecure configurations across departments.
- Implement a periodic audit policy: Establish a regular schedule for reviewing all permissions, including roles, apps, and guest access. These audits help catch outdated privileges and surface potential security gaps before they become problems.
- Assign a point person for access management: Even in smaller teams, designating someone to oversee access rights keeps permissions up to date and reduces the risk of oversights.
Documentation and support
Reliable documentation is the backbone of any successful Teams deployment. Whenever possible, consult official Microsoft resources for the most accurate and up-to-date guidance:
- Official Microsoft documentation: The Microsoft Teams documentation covers every aspect of permissions, policies, and app administration.
- Microsoft Learn: Microsoft Learn offers free courses and hands-on labs to deepen your understanding of Teams and Microsoft 365 administration.
- Microsoft Admin Center: Access the Microsoft Admin Center to manage users, apply policies, and review security recommendations.
Encourage your team to refer to these resources when questions or unusual scenarios arise. Staying current with Microsoft’s updates ensures that your permissions strategy keeps pace with new features and security enhancements.
Team training recommendations
Technical controls are only half the picture; well-informed users make the biggest difference in maintaining a secure Teams environment. Make training a regular part of your organization’s routine:
- Run short, focused sessions on permissions, data protection, and safe collaboration in Teams.
- Create and share an internal guide outlining how to handle access—covering topics like inviting guests, managing roles, and responding to security incidents.
- Clarify the differences between owners, members, and guests, so everyone understands their responsibilities and boundaries.
Confident, well-trained users are your best defense against misconfigurations and accidental exposure of sensitive information. Equip your teams with the knowledge they need to make smart, secure decisions every day.
Additional Tools for Teams—VirtoSoftware Apps
While Microsoft Teams offers robust built-in controls for managing permissions, third-party apps can further simplify, automate, or enhance your governance and collaboration. These tools are especially valuable for large organizations, project-heavy teams, or those seeking better oversight and coordination. Below are several recommended apps and how they contribute to secure, efficient Teams management.
Virto Notifications & Reminders App
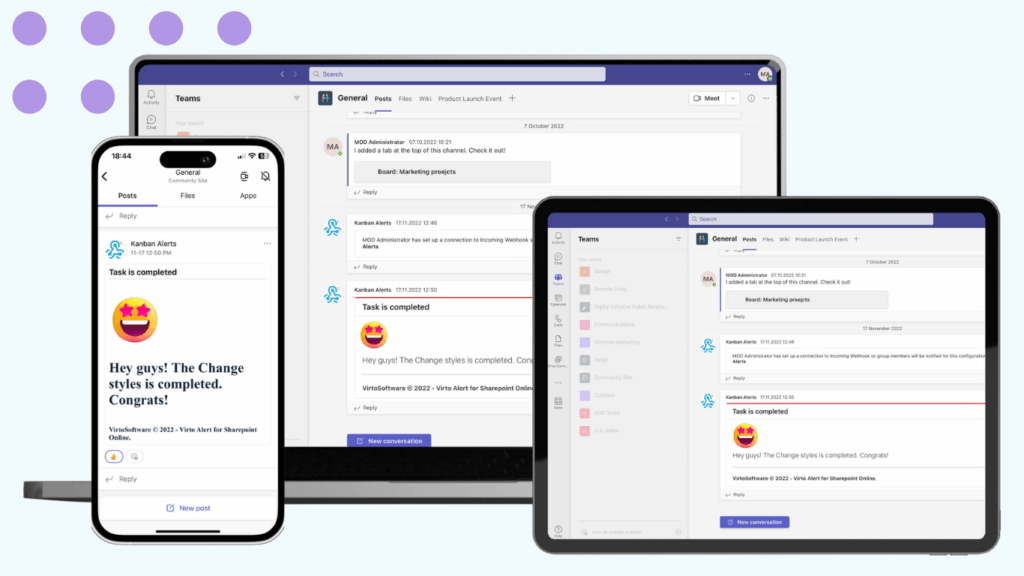
The Virto Notifications & Reminders App is a powerful solution for automating alerts, reminders, and notifications in Microsoft Teams. Seamlessly integrated with Microsoft 365 and SharePoint, it ensures team members are promptly informed about critical updates, deadlines, or compliance events—all directly within Teams channels.
Purpose: Automates notifications and reminders in Teams channels based on key triggers across Microsoft 365 and SharePoint.
How it helps with permissions:
- Ensures critical permission changes (e.g., a sensitive file shared with a guest) trigger immediate alerts to admins or compliance officers.
- Delivers escalation notifications if unacknowledged changes linger, reducing the risk of overlooked security gaps.
- Automates compliance alerts (e.g., when restricted file types are uploaded), reinforcing your organization’s security policies.
Key features:
- Real-time and scheduled alerts in Teams.
- Integration with SharePoint, Outlook, iCalendar.
- Condition-based custom alerts for granular control.
Best for: Admins and compliance teams who need timely awareness of changes that could impact access, privacy, or compliance.
Virto Kanban Board App
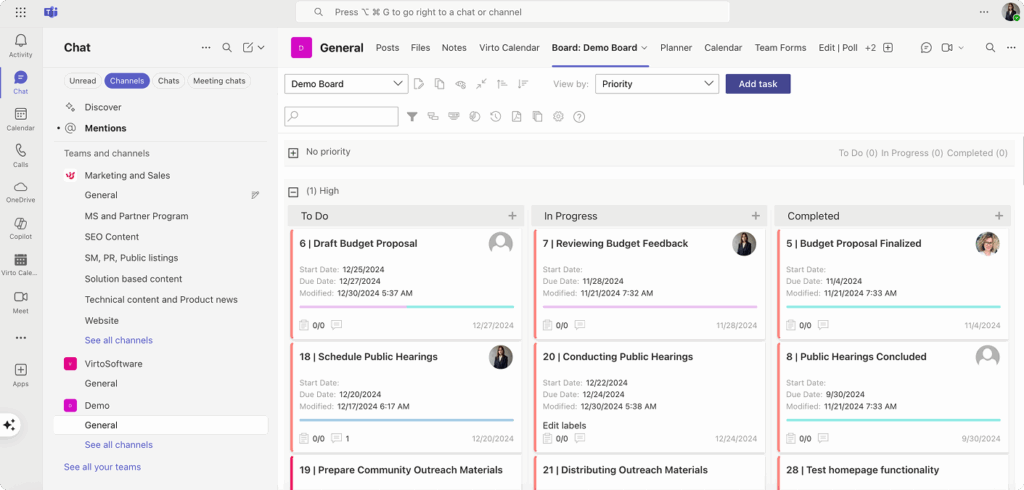
The Virto Kanban Board App delivers visual project and task management right inside Microsoft Teams. Featuring drag-and-drop boards, detailed task cards, and real-time progress tracking, this app empowers teams to streamline workflows, assign tasks, and track milestones—all without ever leaving Teams.
Purpose: Brings visual project and task management into Microsoft Teams without switching between apps.
How it helps with permissions:
- Assigns task ownership and visibility to specific users or groups, ensuring only authorized personnel can update or view sensitive project data.
- Facilitates transparent backlog management, so task visibility aligns with defined team roles.
- Enables reporting and auditing of who changed what, supporting accountability.
Key features:
- Informative task cards with role-based assignment.
- Cross-platform accessibility (Teams, SharePoint, Azure).
- Built-in reporting and capacity management.
Best for: Project leads and managers who want to align task access with user roles, avoiding accidental information leaks or unauthorized edits.
Virto Calendar App
The Virto Calendar App is a robust scheduling tool for Microsoft Teams. It enables users to overlay multiple calendars (Outlook, Google, iCal), categorize events, and manage meetings and resources—all within a visually rich, unified interface directly embedded in Teams.
Purpose: Centralizes scheduling, overlaying unlimited calendars (Microsoft 365, Google, iOS, more) into Teams.
How it helps with permissions:
- Lets you manage who can view, create, or edit events—useful for confidential meetings or resource bookings.
- Granular calendar sharing: assign view-only or edit rights per user or group.
- Supports color-coding and event categorization for quick visibility into who has access to what.
Key features:
- Unlimited calendar overlays.
- Enterprise-level security and mobile support.
- Detailed access and event controls.
Best for: Organizations managing sensitive events, shared resources, or requiring strict control over who sees or edits calendar items.
Virto Shared Calendar App

The Virto Shared Calendar App provides an easy and intuitive solution for managing shared calendars in Microsoft Teams. With features like color-coding, anonymous sharing links, and seamless access for internal and external users, it’s perfect for collaborative scheduling without the hassle of complex setups.
Purpose: Enables quick creation and management of simple shared calendars within Teams, with anonymous or permission-based access.
How it helps with permissions:
- Facilitates calendar sharing with internal or external stakeholders, without requiring Microsoft accounts.
- Lets you generate secure links with either view-only or edit access, ideal for client or vendor coordination.
- Provides instant tagging and color-coding for easy event organization and permission tracking.
Key features:
- Anonymous calendar sharing and granular permissions.
- Cross-platform (Teams or standalone web app).
- No complex training or setup required.
Best for: Teams needing lightweight, flexible calendar sharing—especially when external or cross-tenant collaboration is required.
💡 Tip: When adopting third-party apps, always review their own permission models and integration points. Make sure app access aligns with your company’s broader security policies. Regularly audit which apps are installed, what permissions they require, and who can manage them—using both the Teams Admin Center and any app-specific controls.
Summary: Integrating specialized apps like VirtoSoftware’s suite can significantly strengthen your control, visibility, and responsiveness around permissions in Microsoft Teams. Combined with Microsoft’s native features, these tools help ensure your collaboration stays both productive and secure.
Conclusion on Microsoft Teams Roles and Permissions
Effective permission management in Microsoft Teams is not just a technical detail—it’s the bedrock of secure, efficient, and transparent teamwork. By establishing clear access controls, you protect sensitive data, streamline collaboration, and ensure everyone understands their role and responsibilities.
Regular audits of team roles and permissions are essential. They help you quickly spot and correct over-permissioning, detect guests who no longer need access, and adapt to organizational changes. Centralized administration—using the Teams Admin Center and standardized templates—ensures consistency, reduces manual errors, and saves valuable time, especially as your Teams environment grows.
Don’t overlook the added value that Microsoft 365 integrations and professional solutions like VirtoSoftware Apps for Teams bring to your organization. Tools such as Virto Calendar, Kanban Board, and Notifications & Reminders transform Teams into a true productivity powerhouse, unlocking advanced scheduling, project management, and alerting features that go far beyond the basics.
Take the next step:
- Schedule a demo or download free trial versions of the discussed apps directly from VirtoSoftware’s website to see firsthand how these solutions can elevate your Teams experience.
- Explore additional best practices, troubleshooting guides, and real-world use cases on our blog.
For deeper learning and ongoing support, consult these official Microsoft resources:
- Manage team settings and permissions in Microsoft Teams
- Team owner, member, and guest capabilities in Microsoft Teams
- Assign team owners and members in Microsoft Teams admin center
- Microsoft Teams apps permissions and consent
- Set guest permissions for channels in Microsoft Teams
- Manage app permission policies in Microsoft Teams
And from the VirtoSoftware blog and knowledge base: