Microsoft Teams Governance for Enhanced Collaboration and Security
Discover how proper governance frameworks not only enhance security but dramatically boost productivity by creating clarity, consistency, and confidence across your entire Teams environment.
As organizations increasingly rely on Teams for daily operations, establishing proper governance becomes essential. Microsoft Teams governance refers to the framework of policies, procedures, and controls that guide how Teams is used within an organization.
Effective Teams governance isn’t merely about imposing restrictions—it’s about creating a structured environment where collaboration can thrive while maintaining security and compliance. Without proper governance, organizations risk facing challenges such as information sprawl, security vulnerabilities, and inconsistent user experiences that can undermine the platform’s benefits.
Good governance practices help ensure that sensitive data remains protected, access permissions are appropriately configured, and workflows stay streamlined and efficient. This balanced approach enables organizations to harness the full potential of Teams while mitigating risks associated with unmanaged collaboration tools.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive understanding of Microsoft Teams governance, highlighting its importance in the modern workplace. We’ll explore best practices, common challenges, and practical strategies for implementing effective governance frameworks. Additionally, we’ll examine available tools and techniques that can help organizations enhance their Teams environment, ultimately leading to improved collaboration, security, and organizational efficiency.
What Is Microsoft Teams Governance?
In this section, we’ll explore the fundamental concept of Microsoft Teams governance, its core principles, implementation strategies, and why it’s crucial for organizations of all sizes. We’ll examine how proper governance structures support security, access management, and workflow optimization across the Teams platform.
Defining Microsoft Teams governance
Microsoft Teams governance refers to the comprehensive framework of policies, procedures, controls, and best practices that guide how Teams is deployed, configured, used, and managed within an organization. This framework encompasses everything from user permissions and team creation to content lifecycle management and compliance requirements.
Governance isn’t about restricting collaboration but rather providing guardrails that ensure Teams is used effectively, securely, and in alignment with organizational objectives. It establishes clear boundaries and expectations while enabling users to maximize the platform’s collaborative potential.
👉What is Microsoft Teams information governance? Microsoft Teams information governance is a comprehensive framework for managing content lifecycle, security, and compliance across your Teams environment. It encompasses retention policies that automatically preserve or delete content based on regulatory requirements, sensitivity labels that protect confidential information, and data loss prevention controls that prevent unauthorized sharing. Information governance also includes eDiscovery capabilities for legal and compliance investigations, along with information barriers that prevent communication between specific groups when necessary.
Core principles of Teams governance
Effective Teams governance is built on several foundational principles:
- Team creation and management: Establishing clear guidelines for when and how teams should be created, including naming conventions, approval processes, and ownership responsibilities. This helps prevent team sprawl and duplication while ensuring appropriate oversight.
- Access control: Defining who can access what within Teams through carefully managed permissions, guest access policies, and sensitivity labels. Proper access management ensures information remains available to those who need it while being protected from those who don’t.
- Security policies and settings: Implementing appropriate security measures such as multi-factor authentication, conditional access policies, and data loss prevention rules to safeguard sensitive information and maintain compliance.
- Compliance management: Ensuring Teams usage adheres to regulatory requirements through retention policies, eDiscovery capabilities, and communication compliance features that monitor and protect organizational communications.

Standardized usage through clear communication
A critical aspect of successful Teams governance is clear communication of standards and expectations to all users. When employees understand the established governance framework—including team creation criteria, channel organization principles, and file management practices—they’re less likely to create redundant structures or deviate from best practices.
For example, if users know that teams should be created based on specific projects or functional departments rather than ad-hoc topics, and that this process requires managerial approval, they’ll be more inclined to search for existing teams before requesting new ones. This standardized approach reduces confusion, improves navigation, and enhances the overall Teams experience.
Importance across organizations of all sizes
While larger enterprises with complex organizational structures may have more intricate governance needs, Microsoft Teams governance is equally important for small and medium-sized businesses. Organizations of all sizes benefit from clear guidelines that promote consistent usage patterns and prevent common pitfalls such as information silos, excessive team proliferation, and inconsistent security practices.
Whether managing ten users or ten thousand, establishing governance practices that scale with your organization ensures Teams remains a valuable collaboration tool rather than a source of digital chaos.
What do governance Teams do?: Security, access, and workflow optimization
The ultimate goal of Microsoft Teams governance is threefold:
- Ensuring security: Protecting sensitive organizational data from unauthorized access, leakage, or misuse through appropriate controls and policies.
- Managing access: Providing the right people with the right level of access to teams, channels, and content while maintaining appropriate boundaries between departments, projects, and external collaborators.
- Optimizing workflow: Creating a structured, intuitive environment where collaboration flows naturally, information is easily discoverable, and processes are standardized.
When these elements work in harmony, Teams becomes more than just a communication platform—it transforms into a secure, efficient workspace that enhances productivity and supports organizational objectives while minimizing risk.
Teams Governance Updates 2025
While there haven’t been major overhauls specifically labeled as “governance” updates, several security and compliance enhancements have been introduced that significantly impact how organizations can govern their Teams environments. Here’s a comprehensive look at these updates through March 2025.
Security enhancements with governance implications
Microsoft has introduced several security features in early 2025 that provide administrators with enhanced control over their Teams environment. These features help organizations mitigate risks associated with external communications and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or social engineering attempts.
Brand impersonation protection for Teams messaging
Introduced in January 2025, this feature helps IT administrators identify if external users are impersonating commonly targeted brands during their initial contact with enterprise users via Teams messages. This governance enhancement helps prevent social engineering attacks and protects organizational data by flagging potential phishing attempts early.
Block malicious users feature
A critical governance addition from January’s updates allows admins to prevent users in their organization from collaborating with specific external people. Administrators can now set up block lists, and when someone is added to this list, internal users cannot engage in 1:1 or group chats with these blocked individuals. Any existing chats will have the blocked user automatically removed, providing admins with finer control over external communications.
Copilot access controls for multi-tenant organizations
Released in February 2025, this admin policy enables or disables Copilot access in meetings between Business-to-Business members in Multi-Tenant Organization setups. Teams admins can now toggle the ‘Allow Copilot for B2B members’ setting, giving organizations more granular control over AI capabilities in cross-organizational contexts.
Compliance features that support governance strategies
Effective governance requires robust compliance capabilities to meet regulatory requirements and internal policies. The early 2025 updates include several enhancements to Microsoft Teams’ compliance toolkit that enable organizations to better manage, retain, and protect their communications data.
Microsoft Purview support for town halls
A February 2025 addition extends eDiscovery capabilities to Town Hall events in Teams, ensuring compliance by preserving and managing event data effectively. This enhancement supports organizations in meeting regulatory requirements by making it easier to search and retrieve specific information from large-scale team events.
Default transcription policy update
Microsoft changed the default transcription policy from ‘off’ to ‘on’ for new tenants, aligning with the recording policy. While not removing any existing admin controls, this change encourages broader transparency and record-keeping by making transcription more readily available, supporting governance through better documentation of meetings.
Customer key support expansion
While not a 2025 release (it’s been in public preview since late 2020), Customer Key support for Teams has continued to mature and is worth noting in any governance discussion. This encryption capability lets organizations control the encryption keys Microsoft uses to encrypt Teams data, enhancing compliance capabilities for organizations with specific regulatory requirements.
Governance of external collaboration
As organizations increasingly collaborate across organizational boundaries, Microsoft has strengthened Teams’ capabilities for managing these external interactions. The early 2025 updates provide more granular controls over how users can engage with external parties, helping maintain security and compliance without hindering legitimate collaboration.
Meeting controls for external participation
A new admin policy introduced in the first quarter of 2025 allows organizations to control which meetings their users can attend—whether internally hosted or externally hosted meetings. This helps organizations meet compliance requirements and strengthen controls around Teams meetings by preventing employees from joining potentially unauthorized external sessions.
UX improvements for multi-tenant organization users
This February update improved the experience when Microsoft Teams users interact with users in another tenant that belongs to their organization (common in conglomerates or after mergers and acquisitions). Key changes include removing the possibility of split 1:1 chat threads, providing richer profile information, removing the “External” label, and introducing support for an optional admin-configurable label—all helping to maintain governance while improving the user experience.
Workplace monitoring tools
Effective governance requires good visibility into how Teams is configured and used across the organization. Microsoft has enhanced its administration capabilities in early 2025 with tools that help IT professionals identify misconfigurations, monitor adherence to best practices, and ensure that Teams deployments align with organizational policies.
Best practice configuration monitoring dashboard
A significant addition to the Teams Admin Center in February 2025 helps administrators recognize the importance of Microsoft-recommended best practices and understand their impact on users when not followed. This dashboard provides administrators with valuable insights into their Teams configuration, making it easier to identify areas where governance policies might need adjustment.
Looking forward
While early 2025 hasn’t seen a dramatic overhaul of Teams governance features, Microsoft continues to iteratively enhance security, compliance, and administrative control capabilities that support effective governance strategies. Organizations should continue monitoring the Microsoft 365 Roadmap for upcoming features and regularly review their Teams governance policies to incorporate these incremental improvements.
👉 For more information on these and other updates, browse through the following resources:
- Release notes for Microsoft Teams, last updated March 12, 2025
- What’s new in Microsoft Teams, last updated May 7, 2023
- Microsoft 365 Roadmap, last updated December 18, 2024
- Microsoft Teams Governance: Best Practices, Plans & Templates, published February 12, 2024
- Plan for governance in Teams, last updated October 25, 2023
- Version update history for Teams app deployments, last updated February 12, 2025
- Overview of security and compliance, last updated February 10, 2025
- What’s New in Microsoft Teams | January 2025, published January 31, 2025
- What’s New in Microsoft Teams | February 2025, published February 28, 2025
- Microsoft Teams Update 2025: Your Complete Guide, published January 14, 2025
- Teams Release notes for Government Cloud feature releases, last updated March 12, 2025
Why Is Microsoft Teams Governance Important?
In this section, we’ll examine the critical reasons why implementing robust governance for Microsoft Teams is essential for organizations. We’ll explore how proper governance frameworks protect your data, enhance teamwork, ensure compliance, and mitigate various organizational risks. We’ll also look at the potential consequences of inadequate governance and how these issues can impact your business operations.
The multiple benefits of strong Teams governance
| Benefits | Challenges |
| Enhanced security and compliance | Balancing control with user flexibility |
| Reduced digital clutter and improved findability | Securing buy-in from business units |
| Clear ownership and accountability | Maintaining governance as Teams evolves |
| Consistent user experience across teams | Resource requirements for implementation |
| Lower support costs and IT overhead | Enforcing policies without restricting innovation |
| Simplified onboarding for new users | Adapting governance to different departments |
| Better alignment with organizational structure | Managing governance across complex organizations |
| Improved data protection and privacy | Training users on governance processes |
Let’s explore the benefits of Teams governance first:
Data security
Effective Teams governance establishes crucial safeguards for your organization’s sensitive information. By implementing proper access controls, permission settings, and data classification measures, you can ensure that confidential data remains protected. Governance policies determine which users can access specific teams and channels, what content they can view or edit, and how information can be shared internally and externally.
These controls prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and enable organizations to implement data loss prevention (DLP) policies that identify, monitor, and protect sensitive information across the platform. With proper governance, you can also enforce encryption standards and implement conditional access policies that restrict Teams access based on user identity, device compliance, and network location.
Efficient teamwork
Well-designed governance structures create an environment where collaboration flourishes. By establishing clear guidelines for team creation, channel organization, and content management, governance helps eliminate confusion and streamlines workflows. Users can more easily locate relevant information, connect with appropriate team members, and focus on productive work rather than navigating a chaotic digital environment.
Standardized naming conventions, consistent team structures, and properly maintained channels all contribute to a more intuitive user experience. Additionally, governance policies can help manage the lifecycle of teams, ensuring that outdated or unused teams are archived or deleted, which keeps the environment clean and relevant.
Regulatory compliance
For many organizations, regulatory compliance isn’t optional—it’s mandatory. Microsoft Teams governance plays a vital role in meeting compliance requirements across various regulatory frameworks, including:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): Governance helps organizations manage personal data properly within Teams, ensuring appropriate data handling, retention, and deletion processes.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): For healthcare organizations, governance ensures patient information shared via Teams remains protected and compliant.
- FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority): Financial institutions must maintain specific records of communications, which Teams governance helps manage.
- Industry-specific regulations: Various sectors have their own compliance requirements that can be addressed through proper governance Teams.
By implementing appropriate retention policies, communication compliance tools, and audit capabilities, organizations can demonstrate compliance with these regulatory standards and prepare for potential audits.
Risk reduction
Strong governance significantly reduces various organizational risks:
- Non-compliance risks: Without proper governance, organizations may inadvertently violate regulatory requirements, leading to potential legal consequences and financial penalties. Governance frameworks help establish the necessary controls and documentation to demonstrate compliance.
- Unauthorized access risks: Inadequate governance can leave sensitive information vulnerable to unauthorized access, both internally and externally. By implementing proper permission structures and access controls, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of sensitive information being accessed by unauthorized users.
- Information leakage risks: Governance policies help prevent accidental or intentional sharing of confidential information through features like sensitivity labels, DLP policies, and external sharing restrictions.
The consequences of inadequate governance
Organizations that neglect governance Microsoft Teams often face numerous challenges:
- Redundant channels and teams: Without clear guidelines for team creation, users typically create duplicate teams and channels, leading to fragmented conversations and scattered content. This proliferation makes information discovery difficult and creates confusion about which spaces are authoritative.
- Unoptimized workflows: Poor governance results in inconsistent processes across teams, creating inefficiencies and frustration. Users waste time searching for information across multiple redundant teams or attempting to determine the correct channels for specific discussions.
- Collaboration and coordination issues: When teams are created haphazardly without proper structure, cross-departmental collaboration becomes challenging. Important stakeholders may be excluded from relevant conversations, and critical information might not reach the right people.
- Monitoring and control difficulties: Without governance, IT administrators and security teams struggle to maintain oversight of Teams usage. This makes it difficult to audit activities, ensure compliance, and identify potential security risks.
- Data sprawl and retention problems: Ungoverned Teams environments often suffer from uncontrolled data growth, with files saved inconsistently across numerous locations. This complicates data retention management and increases storage costs.
- Security vulnerabilities and data breaches: Perhaps most critically, inadequate governance increases the risk of security incidents. Without proper controls, sensitive information may be inadvertently exposed to unauthorized users, potentially leading to data breaches with serious reputational and financial consequences.
Organizing Microsoft Teams Governance Planning
Effective governance of Microsoft Teams requires a methodical approach that aligns with your organization’s specific needs, industry requirements, and overall IT strategy. This section explores how to create a structured governance plan that balances security and compliance requirements with user productivity. We’ll cover how to assess your business requirements, create practical templates, develop sustainable procedures, and implement solutions that simplify ongoing governance management.
Assessing your business needs: What policies and tools do you need?
Before implementing any governance strategy for Teams, it’s crucial to understand what your organization truly needs. This assessment phase helps prevent both over-governance (which can stifle productivity) and under-governance (which can create compliance risks).
Begin by answering these key questions:
- What regulatory requirements must you meet? Different industries face different compliance mandates (HIPAA, GDPR, FINRA, etc.) that influence what policies you need.
- How is Teams currently being used in your organization? Conduct an audit of existing Teams usage patterns to identify governance gaps and user needs.
- What are your current pain points? Whether it’s unmanaged external access, data leakage concerns, or sprawling unused teams, identifying specific problems helps focus your governance efforts.
- What is your organizational risk tolerance? Organizations with higher security needs may require stricter controls than those with more flexible working environments.
Based on this assessment, prioritize governance areas that present the highest risk or greatest need for your organization. Common focus areas include:
- Team creation and lifecycle management
- Guest access and external sharing controls
- Information protection and data loss prevention
- Compliance and records management
- App governance and third-party integration management
Remember that your governance needs will likely evolve over time, so build flexibility into your planning process from the start.
Creating governance MS Teams templates: Standardizing your approach
Templates streamline governance implementation and ensure consistency across your Teams environment. Developing standardized documentation and configurations helps both administrators and end users understand expectations and requirements.
Key templates to consider developing include:
- Teams governance policy document: Create a comprehensive reference document that outlines your organization’s Teams governance framework, including:
- Roles and responsibilities for governance stakeholders
- Security and compliance requirements
- Approved usage scenarios and prohibited activities
- Escalation procedures for policy violations
- Team creation request template: Standardize how teams are requested and approved to prevent sprawl:
- Purpose and business justification for the team
- Required team owners and members
- Expected lifecycle (temporary vs. permanent)
- Data sensitivity classification
- Integration requirements
- Team configuration templates: Leverage Microsoft’s team templates feature to create pre-configured templates for common scenarios in your organization (departments, projects, events, etc.) with:
- Predefined channels structure
- Required apps and integrations
- Default security settings aligned with your governance policies
- Appropriate sensitivity labels
- Access review checklists: Develop standardized processes for periodic access reviews:
- Schedule and frequency for reviews
- Owner responsibilities during reviews
- Documentation requirements
- Remediation procedures for identified issues
- External collaboration request form: Create a standardized process for requesting and approving external access:
- Business justification for external collaboration
- Duration of required access
- Data sensitivity assessment
- Required security controls
These templates should be living documents that evolve as your Teams environment and business needs change. Store them in a central location (ideally within Teams itself) where stakeholders can easily access and reference them.
👉Where can I find Microsoft Teams governance templates? You can find Microsoft Teams governance templates in several locations, including the Microsoft Adoption Hub, the Microsoft Teams admin documentation center, and the Microsoft 365 community resources. Microsoft provides governance quick start guides and planning templates that cover essential governance elements like access controls, lifecycle management, and security policies.
Developing and implementing governance procedures
Having well-defined policies and templates is only effective if they’re integrated into your day-to-day business processes. This integration requires clear procedures and stakeholder buy-in.
- Define and assign clear roles and responsibilities: Governance is a shared responsibility that involves multiple stakeholders:
- IT administrators: Responsible for technical implementation and monitoring
- Information security: Oversees security configurations and risk assessments
- Compliance officers: Ensures regulatory requirements are met
- Team owners: Manage membership and content within their teams
- End users: Adhere to usage policies and report issues
Document these roles clearly, including escalation paths and decision-making authority.
- Establish regular governance review cycles: Governance is not a “set and forget” activity. Implement regular review cycles:
- Weekly monitoring of key metrics and alerts
- Monthly reviews of team creation and usage patterns
- Quarterly assessment of policies and procedures
- Annual comprehensive governance strategy review
- Create automated workflows where possible: Reduce manual effort by automating governance processes:
- Team provisioning based on approved requests
- Periodic access reviews with automatic notifications
- Lifecycle management with automated archival of inactive teams
- Compliance scanning with alerts for potential violations
- Develop training and communication plans: Governance success depends on user understanding and adoption:
- Create role-specific training for administrators, team owners, and end users
- Develop clear documentation for governance procedures
- Establish regular communication channels for updates and reminders
- Celebrate compliance successes to reinforce positive behaviors
- Implement feedback mechanisms: Governance should adapt to changing business needs:
- Create channels for users to provide feedback on governance processes
- Monitor help desk tickets related to Teams governance
- Conduct periodic surveys to assess governance effectiveness
- Establish a governance committee to evaluate and implement improvements
By integrating these procedures into your operational rhythm, governance becomes a natural part of how Teams is managed rather than an afterthought or burden.
Implementing teams governance solutions
While Microsoft provides native governance capabilities within Teams and the broader Microsoft 365 ecosystem, many organizations benefit from additional tools to simplify governance management, especially in complex environments.
- Leverage native Microsoft tools: Start with the built-in capabilities:
- Microsoft Purview: For compliance management, data classification, and retention
- Microsoft Entra ID: For identity governance, access reviews, and entitlement management
- Teams Admin Center: For policy management and configuration monitoring
- PowerShell: For automation and bulk administration tasks
- Microsoft Graph API: For custom governance solutions and reporting
- Consider third-party governance solutions: Evaluate specialized tools that extend Microsoft’s native capabilities:
- Advanced analytics platforms: For deeper insights into Teams usage patterns and compliance
- Governance automation tools: To streamline provisioning, lifecycle management, and reporting
- Enhanced security solutions: For additional data protection and threat detection
- Cross-platform governance tools: For unified governance across multiple collaboration platforms
- Custom dashboards: For executive visibility into governance metrics and compliance status
- Build integrated governance workflows: Create end-to-end governance processes that span multiple tools and systems:
- Connect team provisioning to your service desk or HR systems
- Integrate compliance monitoring with your security operations center
- Link governance metrics to executive dashboards
- Automate documentation of governance activities for audit purposes
- Monitor and measure governance effectiveness: Implement metrics to track governance program success:
- Reduction in unauthorized access incidents
- Improved compliance audit results
- Decrease in support tickets related to Teams management
- User satisfaction with governance processes
- Executive confidence in Teams security and compliance
Remember that successful Teams governance isn’t about implementing the most restrictive policies possible—it’s about finding the right balance that protects your organization while enabling productive collaboration. Regular assessment and refinement of your governance approach ensures it remains aligned with both your security requirements and business objectives as your Teams environment evolves.
How to Use Microsoft Teams Most Effectively?: Microsoft Teams Governance Best Practices
Implementing Microsoft Teams without proper governance often leads to chaos—scattered information, security vulnerabilities, and frustrated users. This section outlines practical best practices that balance administrative control with user productivity, ensuring your Teams environment remains secure, compliant, and efficient. Rather than focusing on theoretical governance frameworks, we’ll explore actionable strategies that IT professionals can implement immediately to improve their MS Teams governance posture.

Establishing clear access and governance policies
Effective Teams governance begins with clearly defined access controls that match your organizational structure and security requirements.
Who can create Teams and manage resources
Implementing proper creation controls prevents team sprawl while ensuring legitimate collaboration needs can be met:
- Selective team creation rights: Consider restricting team creation to specific departments, roles, or individuals rather than allowing everyone to create teams by default. This balanced approach prevents duplicative teams while maintaining flexibility.
- Creation justification process: Implement a lightweight approval workflow where users provide a business justification, expected lifespan, and data sensitivity classification when requesting a new team.
- Naming conventions and prefixes: Enforce team naming standards (e.g., “DEPT-PROJECT-PURPOSE”) through naming policies to improve discoverability and organization. Use prefix or suffix requirements to identify team types or sensitivity levels.
Rights and responsibilities assignment
Clear role definition prevents confusion and ensures appropriate administration:
- Multiple team owners requirement: Configure policies requiring at least two owners per team to prevent “orphaned” teams when a single owner leaves the organization.
- Owner responsibilities documentation: Create clear guidelines outlining what team owners are responsible for—membership management, content moderation, app approvals, and compliance enforcement.
- Delegated administration model: For larger organizations, implement a hub-and-spoke governance model where departmental “Teams champions” receive specialized training and delegated administration rights for their business units.
Templating for standardization
Templates dramatically improve governance adherence while simplifying the user experience:
- Custom templates library: Develop organization-specific templates for common scenarios (departments, projects, events) with pre-configured channels, tabs, and settings aligned with governance requirements.
- Sensitivity-based templates: Create templates with different security configurations based on data sensitivity levels—applying appropriate retention policies, DLP rules, and access restrictions automatically.
- Template reviews and updates: Establish a quarterly review process for templates to ensure they remain aligned with changing business needs and incorporate feedback from users.
Organizing teams and channels effectively
Thoughtful organizational structure improves findability, encourages appropriate information sharing, and promotes consistent governance.
Logical structure alignment
The Teams architecture should mirror your organization’s work patterns:
- Information architecture planning: Before widespread Teams deployment, develop an information architecture that maps how different departments, projects, and cross-functional teams will collaborate.
- Channel purpose statements: Require descriptive purpose statements for each channel to clarify what content belongs there, preventing channel proliferation and improving navigation.
- Hub sites for cross-team discovery: For organizations with numerous teams, implement SharePoint hub sites connected to related teams to improve cross-team navigation and content discovery.
Public vs. private team guidelines
Clear guidance on visibility settings prevents both unnecessary information restriction and inappropriate sharing:
- Default visibility recommendations: Provide clear guidelines on when to create public versus private teams, with public teams preferred for departmental collaboration and private teams for sensitive projects.
- Visibility decision tree: Develop a simple decision tree tool that helps team creators determine the appropriate visibility setting based on content sensitivity, participant scope, and compliance requirements.
- Periodic access reviews: Implement quarterly reviews of private team membership to ensure access remains appropriate as organizational roles change.
Security and compliance configuration
Teams governance must address both security threats and compliance requirements through appropriate technical controls.
Data protection configuration
Protect sensitive information through appropriate preventive controls:
- Sensitivity labels integration: Apply sensitivity labels to teams that automatically configure appropriate sharing restrictions, encryption, and access controls based on data classification.
- Conditional access policies: Implement conditional access to restrict Teams access based on user location, device compliance, risk level, and authentication methods.
- Data loss prevention rules: Configure DLP policies to detect, warn, and prevent sharing of sensitive information patterns (credit card numbers, social security numbers, health information) within Teams conversations and files.
Meeting corporate standards
Ensure Teams configurations align with broader organizational security requirements:
- Security baseline application: Apply your organization’s security baseline configurations to Teams, including authentication requirements, encryption standards, and device management policies.
- Regulatory mapping documentation: Create clear documentation showing how Teams settings map to specific regulatory requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA, etc.) to simplify compliance validation.
- Compliance attestation process: Develop a process for regularly validating and documenting Teams compliance status for audit purposes.
Team lifecycle management
Proactive lifecycle management keeps your Teams environment organized while reducing security and compliance risks associated with abandoned workspaces.
Creation and end-of-life processes
Implement processes that address the entire team lifecycle:
- Purpose-driven creation: Require team creators to specify project timelines, business purpose, and expected archival dates during the provisioning process.
- Automated expiration policies: Configure Microsoft 365 Group expiration policies to automatically prompt team owners to renew or archive teams based on activity and age.
- Graduated archival process: Implement a multi-stage archival process that transitions teams from active to read-only before final deletion, with appropriate notifications and data export options.
Managing inactive teams
Prevent Teams sprawl through proactive management of unused workspaces:
- Activity monitoring automation: Create automated reports identifying teams with low activity levels for review by IT and team owners.
- Recertification requirements: Require team owners to periodically confirm the continued need for inactive teams through automated workflows.
- Content preservation planning: Develop clear guidelines for preserving important content from decommissioned teams through SharePoint records management or export processes.
Third-party app governance
Proper app governance balances security requirements with user productivity by enabling approved integrations while preventing risks.
App approval process
Establish a structured approach to app evaluation and approval:
- App risk assessment framework: Develop criteria for evaluating third-party apps based on data access requirements, vendor security practices, and compliance implications.
- Tiered approval model: Implement different approval requirements based on app risk levels—low-risk apps available to all, medium-risk requiring department approval, and high-risk requiring security team review.
- App usage justification: Require business justification documentation for app approval requests, including intended use cases and expected business benefits.
Installation and default configuration
Control which apps are available and how they’re deployed:
- Curated app catalog: Create a pre-approved app catalog organized by department and function to help users find appropriate tools without requiring individual approvals.
- Default permission boundaries: Configure default permission boundaries for third-party apps, limiting unnecessary data access while enabling core functionality.
- App installation monitoring: Implement monitoring of app installation patterns to identify unauthorized installations or unusual usage that might indicate security concerns.
Auditing and monitoring practices
Regular monitoring ensures governance policies are working effectively and identifies potential issues before they become serious problems.
Activity monitoring implementation
Establish comprehensive monitoring across your Teams environment:
- Security monitoring integration: Connect Teams activity logs to your security information and event management (SIEM) system for centralized monitoring of potential security issues.
- Usage pattern analytics: Implement analytics that track collaboration patterns to identify both governance successes and potential areas for improvement.
- Automated anomaly detection: Configure alerts for unusual activity patterns that might indicate security breaches, such as excessive file downloads or unusual access times.
Compliance verification
Regularly validate governance effectiveness through targeted checks:
- Randomized compliance sampling: Conduct periodic reviews of randomly selected teams to verify compliance with naming conventions, appropriate membership, and proper configuration.
- Guest access audits: Regularly review external access permissions to ensure guests only have access to appropriate teams and that access is revoked when no longer needed.
- Configuration drift monitoring: Implement monitoring to detect changes to governance-related configurations that may have been modified outside of approved processes.
Employee training and policy management
Effective governance requires both technical controls and user understanding of proper collaboration practices.
Targeted training programs
Develop role-specific training that addresses governance requirements:
- Role-based training paths: Create different training modules for end users, team owners, and administrators that focus on their specific governance responsibilities.
- Scenario-based learning: Develop practical training scenarios that show users how to accomplish common tasks while adhering to governance policies.
- Microlearning updates: Provide short, focused training updates when policies change or new governance features are introduced.
Evolving policy management
Ensure governance policies remain relevant and effective over time:
- Feedback collection mechanisms: Establish channels for users to provide feedback on governance policies and suggest improvements.
- Regular policy review cycle: Schedule quarterly reviews of governance policies to address emerging threats, incorporate new capabilities, and remove unnecessary restrictions.
- Governance effectiveness metrics: Define and track metrics that measure governance success, such as policy compliance rates, security incident reductions, and user satisfaction with governance processes.
The most successful governance approaches evolve continuously, adapting to changing business requirements while maintaining appropriate controls over an increasingly complex digital workplace.
Using Tools for Microsoft Teams Governance
Effective MS Teams governance requires more than just policies and procedures—it requires practical tools that simplify implementation, monitoring, and enforcement. This section explores the technical arsenal available to IT administrators for governing Teams environments, highlighting both native Microsoft solutions and how they can be extended for more comprehensive governance. We’ll examine specific use cases for each tool, provide configuration guidance, and explain how these tools work together to create a cohesive governance ecosystem.

Microsoft Teams governance tools for security and access management
Microsoft provides several powerful platforms specifically designed to help organizations implement consistent security policies and manage access rights across their Teams deployments.
Microsoft 365 Compliance Center
The Compliance Center offers a unified hub for implementing governance controls that extend beyond basic admin settings:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) for Teams
- Configure advanced DLP policies that prevent sharing of sensitive information patterns like credit card numbers, health information, or custom data types specific to your organization
- Set up real-time policy tips that educate users when they attempt to share regulated content in Teams chats or channels
- Create incident reports that alert security teams when policy violations occur, with detailed forensic information
- Communication compliance
- Monitor Teams messages for inappropriate content, harassment, or sensitive information using machine learning-based detection
- Implement custom lexicons to detect industry-specific terminology that might indicate compliance risks
- Configure risk-based workflows that escalate potential violations to appropriate reviewers
- Advanced eDiscovery integration
- Create eDiscovery cases that preserve Teams conversations, files, and meeting content for investigation or litigation
- Apply legal holds specifically to Teams content while maintaining end-user productivity
- Use advanced search and analytics to identify relevant content across Teams conversations and files
- Insider risk management
- Configure risk indicators that identify suspicious Teams usage patterns that might indicate data theft or leakage
- Create risk management workflows that correlate Teams activities with other Microsoft 365 behaviors for comprehensive risk assessment
- Implement automated incident responses when high-risk behaviors are detected
💡 Configuration tip: Create compliance policies that target specific departments or teams rather than applying blanket policies organization-wide. This allows for differentiated governance based on sensitivity and risk profiles.
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD)
Azure AD provides the identity foundation for MS Teams governance, offering sophisticated controls that go beyond basic user management:
- Conditional access for Teams
- Implement location-based access policies that restrict Teams access from high-risk countries or unsecured networks
- Configure device compliance requirements that ensure Teams can only be accessed from managed devices
- Implement risk-based authentication that triggers MFA when suspicious sign-in behaviors are detected
- Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
- Implement just-in-time privileged access for Teams administrators to reduce standing permission risks
- Configure approval workflows for elevation to Teams admin roles
- Implement time-bound administrative access that automatically expires after a specified duration
- Access reviews
- Schedule automated reviews of guest access across Teams
- Create attestation workflows where team owners periodically recertify external user access
- Implement automated removal of access when reviews aren’t completed
- Entitlement management
- Create access packages that bundle Teams memberships with other resources for consistent lifecycle management
- Implement approval workflows for access requests based on business justification
- Configure automatic expiration of access based on time or inactivity
- Dynamic group membership
- Configure rules-based team membership that automatically updates as employee attributes change
- Ensure consistent access governance as employees move between departments or projects
- Reduce manual membership management burden on team owners
💡 Implementation strategy: Consider creating a dedicated Microsoft Entra ID security group of “Teams Power Users” who receive additional governance privileges and responsibilities, creating a middle tier between regular users and full administrators.
Microsoft Information Protection
Information protection capabilities provide granular content-level governance controls that follow data throughout its lifecycle:
- Sensitivity labels for Teams
- Create and apply sensitivity labels that automatically configure privacy settings, guest access permissions, and external sharing controls
- Implement visual markings on sensitive content shared in Teams to maintain awareness of information sensitivity
- Enforce encryption on highly sensitive content that persists even when downloaded from Teams
- Retention policies
- Configure differentiated retention schedules for various teams based on content type and regulatory requirements
- Implement preservation of critical business records within Teams conversations and files
- Automate deletion of transient content to reduce compliance risks
💡 Advanced deployment tip: Create sensitivity label policies that automatically apply appropriate labels to teams based on naming patterns or department ownership, reducing the manual classification burden on users.
Microsoft Teams Governance Solution Platforms for Monitoring and Auditing
Effective governance requires visibility into how Teams is being used, enabling administrators to identify risks, ensure compliance, and optimize configurations.
Below we’ll take a look at some of the Microsoft Teams governance platforms that can help you implement consistent policies, automate lifecycle management, enhance security controls, and provide comprehensive reporting—all while maintaining the intuitive user experience that makes Teams such a powerful collaboration hub.
Microsoft Teams Admin Center
The Teams Admin Center offers powerful governance capabilities that many organizations underutilize:
- Policy analytics
- Review policy assignment reports to identify inconsistencies or gaps in governance coverage
- Track policy changes over time to detect unauthorized modifications
- Compare policy configurations across your environment to identify standardization opportunities
- Teams usage reports
- Monitor team creation patterns to identify potential governance bypass or teams sprawl
- Track channel usage to identify inactive or redundant teams that may require cleanup
- Analyze app usage data to ensure compliance with approved app policies
- Messaging policies
- Implement differentiated chat and channel policies for different user groups based on compliance requirements
- Configure URL scanning and filtering to prevent sharing of malicious content
- Control which message types can be edited or deleted to support compliance requirements
- Meeting policies
- Enforce recording and transcription requirements for regulated communications
- Control which meeting features are available based on sensitivity and compliance needs
- Implement lobby configurations that prevent unauthorized access to sensitive meetings
💡 Advanced usage: Create custom admin roles in the Teams Admin Center that delegate specific governance responsibilities to departmental IT contacts, distributing the governance workload while maintaining central oversight.
Microsoft 365 Audit Logs
Audit logs provide detailed forensic information essential for governance verification and incident response:
- User activity monitoring
- Track file access and sharing activities across Teams to detect potential data leakage
- Monitor administrative changes to Teams settings to ensure configuration integrity
- Track external user activities to identify potential security risks
- Compliance investigation
- Search detailed activity logs to investigate potential policy violations
- Export activity data for integration with security information and event management (SIEM) platforms
- Create custom alerts for high-risk activities that require immediate response
- Custom alert policies
- Configure automated alerts for suspicious activities like mass downloads or unusual access patterns
- Create notification workflows that alert security teams when governance-related settings are modified
- Implement volume-based alerts that detect unusual spikes in sharing or communication activities
💡 Integration capability: Connect Microsoft 365 audit logs to Power Automate workflows to create custom governance processes like automatically notifying team owners when sensitive actions occur within their teams.
Microsoft Purview Portal
The Purview portal provides unified data governance capabilities that complement Teams-specific tools:
- Data catalog integration
- Create a searchable catalog of sensitive data sources accessible through Teams
- Implement automated data classification for content stored in Teams-connected SharePoint sites
- Provide governance context to users about data they access through Teams
- Data map visualization
- Visualize how data flows through Teams to identify potential governance gaps
- Track cross-team information sharing to ensure appropriate boundaries
- Monitor external collaboration patterns to identify potential compliance risks
- Automated data discovery
- Identify where sensitive information is stored across Teams-connected repositories
- Discover unmanaged teams containing regulated information that requires additional controls
- Identify redundant, obsolete, or trivial (ROT) content that can be safely removed
💡 Advanced implementation: Create integrated workflows between Purview data discovery and Teams governance processes to automatically apply appropriate controls when sensitive data is detected in Teams environments.
Extending Native Tools with APIs and Custom Solutions
For organizations with advanced governance requirements, Microsoft’s native tools can be extended through APIs and custom development:
- Microsoft Graph API for Teams
- Develop custom governance dashboards that provide organization-specific metrics and insights
- Create automated provisioning workflows that enforce governance requirements during team creation
- Implement custom lifecycle management solutions tailored to specific business processes
- Power Platform integration
- Create Power Apps interfaces for governance processes like team requests and access reviews
- Implement Power Automate workflows for governance tasks like periodic team owner notifications
- Develop Power BI dashboards for governance metrics and compliance reporting
- Microsoft Teams governance PowerShell scripts
- Automate routine governance tasks like identifying orphaned teams or excessive permissions
- Create scheduled jobs that verify governance compliance and remediate common issues
- Implement batch operations for governance updates across multiple teams simultaneously
💡 Custom development tip: Start with Microsoft’s sample governance scripts available on GitHub and customize them to your specific requirements before investing in completely custom solutions.
Integrated Governance Toolchain
The most effective governance implementations integrate multiple tools into a coherent ecosystem:
- Unified monitoring and alerting
- Centralize governance alerts from multiple systems into a single dashboard for comprehensive visibility
- Implement correlation rules that identify governance risks spanning multiple activities or services
- Create severity-based escalation paths for different types of governance violations
- Automated compliance workflows
- Implement end-to-end workflows that connect detection of governance issues with remediation actions
- Create approval processes that balance governance requirements with business flexibility
- Automate documentation of governance activities for audit and compliance reporting
- Governance metrics and reporting
- Develop comprehensive governance scorecards that track compliance across multiple dimensions
- Implement trend analysis to identify emerging governance challenges before they become critical
- Create executive-friendly visualizations that communicate governance status to leadership
Remember that governance tools are most effective when they’re part of a broader governance strategy that includes clear policies, defined roles and responsibilities, and regular review processes. The tools enable and enforce your governance approach, but they don’t replace the need for thoughtful governance planning.
Recommendations for Improving Microsoft Teams Governance
While establishing a solid governance foundation is essential, truly effective Teams governance must continually evolve to address emerging threats, adapt to organizational changes, and leverage new capabilities. This section provides strategic recommendations for organizations looking to elevate their MS Teams governance beyond basic compliance to achieve operational excellence. We’ll explore practical enhancements that balance security with usability, focusing on proactive approaches rather than reactive measures.
Periodic security audits: Moving beyond basic compliance
Traditional security audits often focus narrowly on policy compliance, missing the broader security landscape. A more effective approach implements continuous security validation that anticipates threats rather than simply documenting configurations.
Advanced configuration reviews
Transform standard configuration checks into strategic security assessments:
- Security posture comparison: Benchmark your Teams security configurations against industry peers and Microsoft’s recommended security baselines, identifying where your organization may be under-protected or over-restricted.
- Risk-based configuration assessment: Prioritize audit focus based on the potential impact of configuration weaknesses—for example, paying special attention to settings affecting regulated data or executive communications.
- Configuration drift analysis: Implement automated tools that detect gradual changes in security configurations over time, identifying settings that have been incrementally weakened through multiple small changes.
Leveraging advanced security analytics
Modern audit approaches incorporate behavioral analytics and threat intelligence:
- Unified security signal analysis: Combine Microsoft 365 Audit Logs with signals from Microsoft Defender for Office 365, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, and Microsoft Sentinel to create a comprehensive security picture spanning Teams and related services.
- Behavioral baseline monitoring: Establish normal usage patterns for Teams to identify anomalies—such as unusual after-hours access, atypical file download volumes, or unexpected external sharing patterns.
- Attack path analysis: Conduct regular simulations to identify potential attack paths involving Teams (such as phishing via Teams messages leading to lateral movement through connected resources), then implement targeted controls to disrupt these paths.
Proactive security notification systems
Move beyond basic alerts to implement intelligent notification systems:
- Contextual security alerting: Configure graduated alerting based on event context—for example, treating sensitive data access differently based on user location, device security posture, and previous behavioral patterns.
- Alert intelligence enrichment: Automatically supplement security alerts with contextual information like user risk scores, data sensitivity classifications, and relationship to other recent alerts.
- Sequential pattern detection: Implement alert correlation that identifies suspicious sequences of actions across Teams and connected services, such as unusual account activity followed by configuration changes and large data transfers.
💡 Implementation tip: Create a dedicated Teams security working group that meets monthly to review audit findings, emerging threats, and enhancement opportunities, including representatives from security, compliance, and business units.
Compliance management: strategic approaches
Effective compliance management goes beyond merely implementing technical controls to creating an integrated compliance ecosystem that adapts to changing requirements.
Advanced data governance implementation
Transform compliance from a checkbox exercise to a strategic advantage:
- Regulatory mapping framework: Create a comprehensive mapping between specific regulatory requirements (GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001) and your Teams configurations, ensuring clear traceability for auditors and identifying potential compliance gaps.
- Data jurisdiction controls: For multinational organizations, implement data boundary controls that ensure Teams data remains within appropriate geographic regions to meet local data sovereignty requirements.
- Compliance risk modeling: Develop a risk-based compliance model that quantifies potential compliance exposures in Teams, allowing prioritization of mitigation efforts based on risk severity and likelihood.
Enhanced Data Loss Prevention strategies
Implement next-generation DLP approaches that balance security with productivity:
- Contextual DLP policies: Create context-aware DLP rules that adjust sensitivity based on user behavior, message recipients, and business purpose—for example, allowing greater flexibility for verified business partners while maintaining strict controls for unknown external domains.
- Machine learning classification: Leverage trainable classifiers to identify sensitive content patterns specific to your organization that standard DLP rules might miss, such as proprietary business terminology or industry-specific references.
- Endpoint DLP integration: Extend Teams DLP protection to endpoint devices, ensuring consistent protection even when data moves from Teams to local applications.
Strategic retention implementation
Transform retention from a storage management tool to a strategic compliance asset:
- Event-based retention triggers: Implement retention policies triggered by business events rather than fixed timeframes—for example, retaining project team content until project completion plus a defined period.
- Adaptive retention framework: Create a multi-tier retention framework that automatically adjusts retention periods based on detected content sensitivity, rather than applying blanket policies to all teams.
- Preservation indexing: Implement enhanced content indexing for retained Teams content to ensure it remains searchable and useful for knowledge management even after the original team is archived.
💡 Advanced strategy: Consider implementing litigation hold templates for different types of legal matters, allowing rapid deployment of appropriate preservation controls when litigation becomes likely.
Governance automation: Beyond basic workflows
True governance automation moves beyond simple task automation to creating intelligent governance systems that adapt to organizational needs.
Intelligent team lifecycle automation
Create self-adapting lifecycle management systems:
- Activity-based archival intelligence: Develop nuanced archival algorithms that consider not just message activity but also file access patterns, meeting frequency, and business context before flagging teams for archival.
- Predictive lifecycle management: Implement machine learning models that predict when teams are likely to become inactive based on usage patterns, allowing proactive engagement with owners before automatic archival.
- Graduated archival process: Create a multi-stage archival process that transitions teams from active to read-only to archived to deleted, with appropriate notifications and export options at each stage.
Conditional access enhancements
Implement sophisticated access controls that balance security and usability:
- Risk-adaptive authentication: Configure authentication policies that dynamically adjust requirements based on real-time risk assessment—increasing security requirements when suspicious patterns are detected while streamlining access for typical usage.
- Session management controls: Implement granular session controls that limit what users can do in Teams based on their access context—for example, preventing file downloads from unmanaged devices while still allowing meeting participation.
- Continuous access evaluation: Enable real-time policy enforcement that can revoke Teams access mid-session if risk conditions change, rather than only evaluating risk at login time.
Integration-driven automation
Leverage cross-platform integrations to create comprehensive governance workflows:
- HR-driven access management: Integrate with HR systems to automatically adjust Teams access based on employment status changes, department transfers, and role changes.
- Project management integration: Connect project management systems to Teams lifecycle management, automatically creating teams at project initiation and archiving them at project completion.
- Service desk integration: Link governance processes to your service management platform, creating auditable request workflows for governance exceptions while maintaining centralized documentation.
💡 Implementation strategy: Create a governance automation roadmap that starts with high-volume, low-risk processes before progressing to more complex scenarios, building organizational confidence in automation while developing internal expertise.
Advanced monitoring and analytics
Transform monitoring from passive observation to strategic insights that drive governance improvements.
Predictive governance analytics
Move beyond descriptive analytics to anticipate governance needs:
- Governance health scoring: Develop a composite governance health score that combines multiple metrics (policy compliance, security posture, user behavior, etc.) to provide an at-a-glance view of your Teams governance effectiveness.
- Trend analysis and forecasting: Implement predictive analytics that identify emerging governance challenges before they become critical—such as predicting potential data spillage risks based on changing collaboration patterns.
- Comparative benchmarking: Analyze your MS Teams governance metrics against industry benchmarks to identify areas where your organization may be under- or over-governed relative to peers.
Enhanced visualization and reporting
Create actionable insights through sophisticated data presentation:
- Role-based dashboards: Develop customized governance dashboards tailored to different stakeholders—executive summaries for leadership, detailed compliance metrics for risk managers, and operational indicators for IT administrators.
- Governance journey mapping: Create visual representations of governance maturity progress over time, highlighting improvements and identifying areas for continued development.
- Impact analysis visualization: Develop visualizations that demonstrate the business impact of governance controls—showing both governance benefits (reduced risk, improved compliance) and costs (administrative overhead, user friction).
Operational intelligence integration
Connect governance monitoring with broader operational systems:
- Security operations integration: Link governance Teams monitoring with your security operations center to provide context for security incidents and enable rapid response to governance violations.
- Business intelligence correlation: Connect Teams usage patterns with business outcomes to identify how governance controls affect productivity and collaboration effectiveness.
- Executive reporting automation: Create automated executive briefings that translate technical governance metrics into business-relevant insights for leadership review.
💡 Advanced implementation: Consider developing a “Governance Digital Twin” that models your Teams environment and simulates the impact of potential governance changes before implementation, allowing you to optimize controls for both security and usability.
Strategic team and channel management
Effective governance requires strategic approaches to organizational structure that balance control with collaboration needs.
Architectural governance approaches
Move beyond tactical naming conventions to strategic information architecture:
- Collaboration architecture council: Establish a cross-functional governance body that oversees Teams structures from both technical and business perspectives, ensuring alignment with organizational needs.
- Functional decomposition mapping: Create a systematic approach to determining team structures based on business function mapping rather than organizational charts, focusing on work patterns rather than reporting lines.
- Information flow optimization: Analyze how information needs to flow across your organization and design team structures that facilitate appropriate sharing while maintaining necessary boundaries.
Enhanced template strategies
Transform templates from static patterns to dynamic collaboration facilitators:
- Business process-aligned templates: Create templates specifically designed around key business processes (customer onboarding, product development, regulatory filing) with appropriate apps, connectors, and governance controls.
- Outcome-based templates: Design templates focused on business outcomes rather than team types, incorporating best practices, required resources, and governance controls specific to the desired result.
- Intelligent template recommendations: Implement a recommendation system that suggests appropriate templates based on the team purpose, participants, and organizational context.
Knowledge management integration
Connect team structures with broader knowledge management strategies:
- Cross-team knowledge indexing: Implement solutions that index content across teams while respecting access boundaries, improving discoverability without compromising security.
- Expertise location integration: Connect Teams with expertise location systems to help users find subject matter experts across organizational boundaries.
- Lifecycle-aware knowledge preservation: Create automated processes that identify and preserve valuable knowledge assets when teams are archived, ensuring critical information remains accessible.
💡 Strategic approach: Consider implementing a “Teams Center of Excellence” that combines governance responsibility with user experience design, ensuring that governance controls enhance rather than hinder the collaboration experience.
Remember that governance improvement is a journey rather than a destination—regular assessment, stakeholder feedback, and incremental enhancement should be built into your governance operating model to ensure sustained effectiveness in an ever-changing technological and regulatory landscape.
Microsoft Teams Governance Checklist
To summarize the governance strategies we’ve discussed throughout this article, here’s your essential Microsoft Teams governance checklist to help transform your digital workplace:

How Virto Software Improves Microsoft Teams Governance
While Microsoft provides native governance capabilities within Teams, third-party solutions can significantly enhance these foundations by addressing specific governance challenges. VirtoSoftware has developed a suite of specialized apps that extend Teams’ native capabilities, providing targeted governance improvements without overwhelming complexity. This section explores how VirtoSoftware’s apps can strengthen your Teams governance strategy, focusing on practical governance enhancements rather than merely adding features.
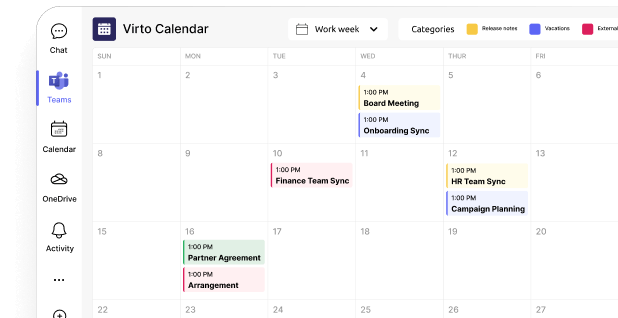
Virto Calendar for Microsoft Teams: Enhancing scheduling governance
Calendar management might not immediately come to mind when thinking about Teams governance, but controlling how scheduling information is created, shared, and accessed is a critical governance component for many organizations. Virto Calendar addresses several key governance challenges related to scheduling and time management.
Access control and information protection
Virto Calendar enhances information protection through granular access controls:
- Graduated permission model: Implement differentiated calendar access rights—from view-only to full editing privileges—ensuring users only have the access level appropriate to their role and reducing the risk of unauthorized schedule modifications.
- Source-specific access controls: Configure different permission levels for different calendar sources, allowing sensitive calendars (executive schedules, confidential projects) to have stricter access controls than general team calendars.
- Audit-ready permission management: Maintain clear documentation of who has what level of access to calendar information, supporting compliance requirements for information access governance.
Lifecycle management support
Calendar systems often become cluttered with outdated information, creating governance risks. Virto Calendar helps implement lifecycle management for time-based information:
- Project lifecycle visualization: Create calendar views that track project timelines from inception to completion, facilitating proper governance of project-related information throughout its lifecycle.
- Category-based retention: Apply different color codes and categories to different types of calendar entries based on their purpose, aligning with broader information governance policies.
Cross-platform governance enhancement
One of the most challenging aspects of calendar governance is maintaining consistent controls across diverse calendar platforms. Virto Calendar specifically addresses this challenge:
- Unified governance layer: Apply consistent governance policies across multiple calendar sources (Outlook, SharePoint, Google, iCalendar) through a single management interface.
- Centralized policy application: Implement organization-wide calendar governance standards that persist regardless of which calendar platform users access.
- Cross-platform audit capability: Maintain visibility into calendar activities across platforms, closing potential governance gaps between systems.
Virto Kanban Board App: Governance through structured workflows

Task management is a core component of information governance—ensuring work is properly assigned, tracked, and documented. Virto Kanban Board enhances Teams’ governance capabilities by providing structured workflows with appropriate controls.
Granular access management
The Kanban Board app provides sophisticated permission controls that support governance requirements:
- Role-based board access: Implement different permission levels for different stakeholders—owners with full control, contributors who can modify specific cards, and viewers with read-only access—ensuring appropriate governance of task information.
- Column-level permissions: Configure permissions for specific workflow stages, allowing for governance controls that vary based on the status of work items (e.g., requiring additional approvals for tasks moving to “Complete” status).
Governance-enhancing information structure
Effective governance requires clear organization and categorization of information, which the Kanban Board app facilitates:
- Standardized task templates: Create governance-compliant templates for common task types, ensuring consistent documentation and appropriate metadata collection.
- Required field enforcement: Configure mandatory information fields for different card types, ensuring that governance-required information is always captured.
- Customizable workflow states: Design workflow stages that align with governance requirements, ensuring appropriate reviews and approvals before tasks advance to completion.
Automated compliance documentation
The Kanban Board supports governance through automated tracking and documentation:
- Activity logging: Maintain detailed records of all board activities, providing an audit trail of who changed what and when.
- Status change tracking: Document the progression of tasks through workflow stages, creating evidence of proper governance processes.
- Automated reporting: Generate compliance reports showing task completion, approval status, and governance metrics without manual data collection.
Virto Notifications & Reminders: Governance through awareness
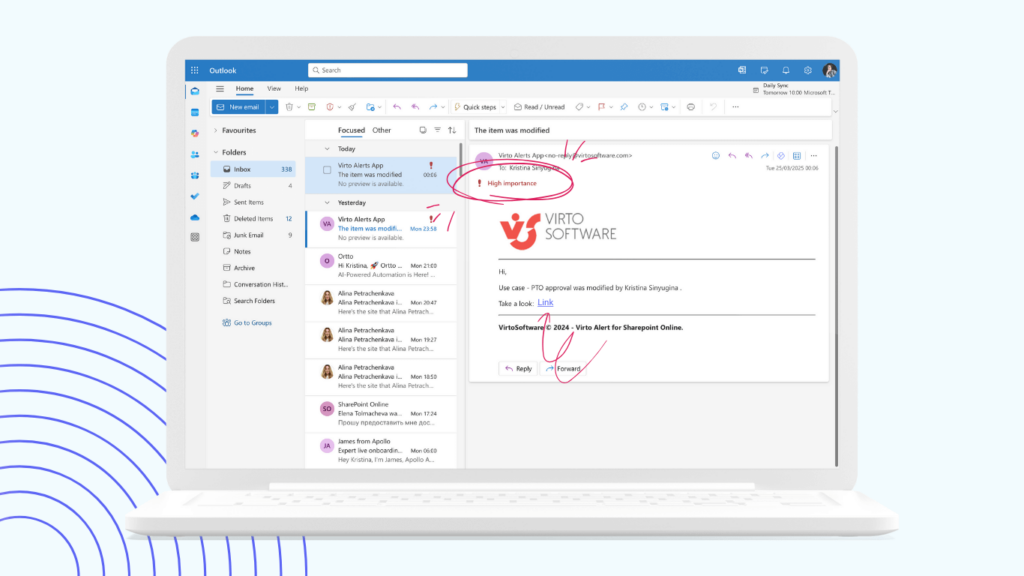
Effective governance requires timely awareness of obligations, deadlines, and changes. Virto’s Notifications & Reminders app strengthens governance by ensuring appropriate stakeholders receive relevant information at the right time through a sophisticated alerting system that works seamlessly within the Teams environment.
Targeted compliance notifications
The app enhances governance through precise, condition-based communications:
- Intelligent alert routing: Configure notifications to target only relevant stakeholders based on specific conditions, eliminating the governance risks associated with over-notification (alert fatigue) or under-notification (missed compliance issues).
- Scheduled governance alerts: Program recurring compliance reminders for cyclical governance requirements like access reviews, policy acknowledgments, and periodic security checks, ensuring consistent governance awareness.
- Webhook integration for security events: Connect Teams channels with security monitoring systems through the webhook connector, automatically routing security alerts to appropriate governance stakeholders without manual intervention.
Governance process automation
The Notifications app enables sophisticated governance workflows that reduce manual oversight:
- SharePoint integration for document compliance: Automatically alert governance stakeholders when compliance-critical documents in SharePoint are modified, ensuring timely review of potential policy violations.
- Multi-platform alert consolidation: Centralize governance notifications from various Microsoft 365 services into Teams channels, creating a unified governance communication hub that prevents alerts from being overlooked.
- Custom alert templates: Create standardized notification formats for different types of governance events, ensuring consistent communication of critical information like severity levels, response requirements, and escalation paths.
Preventing governance violations
The Notifications app includes preventive capabilities that help organizations avoid governance issues before they occur:
- Early warning system: Configure alerts to trigger when predefined conditions indicate potential governance risks, allowing intervention before violations occur.
- User-friendly setup interface: Implement sophisticated governance alerts without requiring deep technical skills, enabling governance teams to directly manage their notification needs without IT dependence.
- Cross-channel consistency: Maintain uniform governance messaging across multiple teams and channels, ensuring consistent understanding of governance requirements throughout the organization.
Unlike generic third-party apps that may create governance complications through inconsistent security models or incompatible data handling, VirtoSoftware deep integration with Microsoft 365 ensures that governance enhancements build upon rather than conflict with Microsoft’s native capabilities, creating a coherent governance experience across your digital workplace.]
Conclusion: Transforming Microsoft Teams Through Strategic Governance
As organizations increasingly depend on Microsoft Teams as their digital workplace hub, the importance of thoughtful governance cannot be overstated. Throughout this article, we’ve explored how proper governance creates the foundation for secure, compliant, and productive collaboration—striking the delicate balance between organizational control and user empowerment.
While governance is often viewed primarily through a security and compliance lens, its impact extends far beyond risk mitigation. Well-designed governance delivers significant productivity benefits through streamlined navigation, reduced duplication, clearer boundaries, and appropriate automation.
Implementing effective Teams governance requires both strategic vision and tactical execution. We recommend a phased approach that balances immediate security needs with long-term governance maturity. Start with critical policies around team creation, guest access, and retention. Establish clear ownership for Teams administration. Design governance processes that can scale with your organization, focusing on automation rather than manual enforcement. Regularly review effectiveness through usage metrics and user feedback, making adjustments as your organization evolves.
While Microsoft provides robust native governance capabilities, many organizations benefit from extending these foundations with specialized solutions. VirtoSoftware’s suite of Teams applications complements Microsoft’s governance framework by providing enhanced visibility, control, and user experience in several key areas. Virto Calendar enhances scheduling governance through granular permission controls. Virto Kanban Board supports governance through structured workflows, ensuring proper documentation and approvals. Virto Notifications & Reminders strengthens governance through precision alerting that ensures time-sensitive communications reach appropriate stakeholders.
These tools don’t replace Microsoft’s native governance capabilities—they extend them, providing the additional granularity and functionality that many organizations require to implement comprehensive governance without sacrificing user experience.
We encourage you to browse through VirtoSoftware website for more information, install free version of the discussed apps, and schedule a free demonstration to ask any questions before committing to a subscription.
For further insights and guidance on Microsoft Teams governance, explore the following resources:
📌 Official Microsoft resources:
- Plan for governance in Teams
- Governance quick start for Microsoft Teams
- Teamwork Governance – Microsoft Adoption
📌 VirtoSoftware blog articles: