SharePoint Secure File Sharing: Methods, Best Practices, and Advanced Tips
Discover how to harness SharePoint's file sharing, navigate complex permission structures, and implement bulletproof security practices that keep your sensitive data protected while enabling seamless collaboration with both internal teams and external partners.
File sharing sits at the heart of what makes SharePoint valuable for organizations of all sizes. Companies consistently choose this platform when they need more than just storage—they need a system that can centrally house documents while providing precise control over access, collaboration, and security.
SharePoint excels at balancing accessibility with protection. You can store everything in one centralized location, create detailed permission structures, enable real-time collaboration, and still satisfy the compliance requirements that regulated industries face. This comprehensive approach explains why so many organizations rely on SharePoint as their primary document management solution.
This article covers every aspect of SharePoint file sharing, from the basic operations you’ll perform regularly to advanced configurations that can reshape how your team handles documents. We’ll examine the security features that protect sensitive information, explore access management strategies that grow with your organization, and demonstrate how VirtoSoftware solutions can expand SharePoint’s functionality beyond its standard offerings.
How File Sharing Works in SharePoint
This section breaks down SharePoint’s file sharing fundamentals, covering its core architecture, permission systems, and the various methods available for sharing documents. We’ll explore how document libraries function as the foundation for file organization, examine the flexible permission structures that control access, and walk through the different sharing options that make collaboration possible both within your organization and with external partners.
SharePoint as a collaborative platform
SharePoint is Microsoft’s cloud-based platform designed to store, organize, and facilitate collaboration on files within teams and organizations. Built as part of the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, it serves as a centralized hub where teams can manage their documents, coordinate projects, and maintain version control across their collaborative work.
One of SharePoint’s primary use cases is enabling secure file sharing with colleagues, departments, and external partners. This capability transforms how organizations handle document collaboration, moving away from email attachments and scattered file storage toward a unified system that maintains security while promoting accessibility.
Document libraries: The foundation of SharePoint organization
All documents and files in SharePoint live within document libraries, which function as structured containers organized by sites, departments, or projects. Think of each library as an intelligent “folder” that can be flexibly configured to match your organization’s access requirements and workflow patterns.
These libraries accommodate any file type your organization works with—text documents, spreadsheets, presentations, media files, PDFs, and specialized formats. The system doesn’t impose restrictions on file types, making it versatile enough to handle diverse content needs across different departments and projects.
Granular permission management in SharepPoint secure file sharing
SharePoint’s strength lies in its sophisticated permission system, which allows individual access rights to be configured for each library with remarkable precision:
User and group assignment: Access can be assigned to specific users or entire groups, such as the marketing team, project stakeholders, or external consultants. This group-based approach simplifies management when team compositions change.
Permission levels: SharePoint offers multiple permission tiers to match different collaboration needs:
- View only: Users can read and download files but cannot make changes
- Edit: Users can modify existing files and create new ones within the library
- Full control: Complete administrative access, including permission management and library configuration
Flexible scope: Permissions operate at multiple levels, giving administrators control over access both at the library level as a whole and for individual files or folders within that library. This granularity ensures that sensitive documents can be protected while maintaining open collaboration on general project files.
How to use SharePoint to share files: Methods
SharePoint provides several distinct approaches to file sharing, each suited to different collaboration scenarios:
Share via link
Link sharing offers the most flexible approach to file access. You can generate links with specific access parameters tailored to your security requirements:
- View-only links: Recipients can read and download files without editing capabilities
- Editable links: Allow recipients to modify documents and contribute to collaborative work
- Restricted access: Links can be limited to specific users or configured with expiration dates for temporary access
These links prove particularly valuable for short-term access needs or when collaborating with external participants who need quick, straightforward access to specific documents.
Email invitation
SharePoint’s email invitation system sends direct access invitations to specific users’ email addresses. This method provides greater control over recipient identification and creates an audit trail of who received access permissions. Email invitations work particularly well when you need to be precise about access distribution and prefer not to share links that could potentially be forwarded.
Integration with Microsoft Teams and Outlook
SharePoint’s deep integration with other Microsoft 365 applications streamlines file sharing within existing workflows. You can share files directly within Teams conversations, channel discussions, or attach them to Outlook emails without creating duplicate copies. This integration eliminates the friction of switching between applications and ensures that all collaborators work with the same version of each document.
The seamless connection between these platforms means that SharePoint becomes an invisible but powerful foundation for teamwork, supporting collaboration without requiring users to master a separate file management system.
How Do I Share Files with SharePoint?
The process of sharing files in SharePoint adapts to your specific needs and security requirements. Most sharing begins by navigating to the relevant document library, selecting the file or folder you want to share, and choosing the appropriate sharing method from SharePoint’s interface. The system then guides you through setting permission levels, specifying recipients, and configuring any time-based restrictions or access limitations that align with your organization’s policies.
Are There Any Significant Updates to SharePoint Secure File Sharing?
SharePoint’s file sharing capabilities have undergone substantial enhancements in recent years, with Microsoft focusing on strengthening security, improving external collaboration, and streamlining administrative control. These updates reflect the evolving needs of hybrid work environments and increasing regulatory compliance requirements.
Microsoft Entra B2B integration: A security revolution
The most transformative update is SharePoint’s enhanced integration with Microsoft Entra B2B (formerly Azure AD B2B), which has replaced the older one-time passcode system for external sharing. This change fundamentally improves how organizations manage guest access and external collaboration.
Under the new system, when you share files with external users not in your directory, SharePoint creates guest accounts that are managed through Microsoft Entra settings. External collaborators can now authenticate using their existing work or school accounts, and IT administrators gain the ability to manage these guest relationships through the same directory controls used for internal users.
This integration proves particularly valuable for organizations that regularly collaborate with the same external partners, as it eliminates the friction of repeated authentication while maintaining enterprise-level security controls. Guest accounts are now treated as managed entities within your security framework rather than temporary access points.
Advanced link expiration controls
SharePoint now offers comprehensive link expiration settings that provide granular control over temporary access. Organizations can configure expiration periods ranging from 1 to 730 days for anonymous links, and 30 to 730 days for guest access links.
The system allows administrators to set different default expiration periods based on data sensitivity levels. For instance, you might configure 60-day expiration for general collaborative documents while setting 30-day limits for sensitive financial reports. This flexibility helps organizations align their SharePoint policies with broader data governance requirements and regulatory compliance needs.
Microsoft recommends a 60-day default expiration period, which aligns with GDPR compliance requirements while providing sufficient time for meaningful collaboration. These settings can be implemented through PowerShell commands, enabling automated policy enforcement across large organizations.
Enhanced download restrictions
A significant security enhancement allows administrators to block file downloads for shared links while maintaining view access. This feature addresses the common concern of preventing unauthorized copying of sensitive documents shared with external parties.
The download restriction capability operates at the site level and requires SharePoint advanced management licenses (P1/P2). Administrators can implement these restrictions using PowerShell commands, with options to exclude specific groups or site owners from the download blocks when business requirements demand it.
This feature proves particularly valuable when sharing confidential documents with external reviewers, legal counsel, or regulatory bodies where document access is necessary but local copying must be prevented.
Refined tenant and site-level control
SharePoint’s 2025 updates have improved the hierarchical control system between tenant-wide and site-specific sharing settings. The platform now applies the most restrictive setting between the two levels, giving organizations better control over security policies.
This enhancement allows for more nuanced security approaches. For example, HR departments can have external sharing completely disabled while project sites working with external contractors maintain sharing capabilities. The system ensures that security policies cascade appropriately without requiring complex workarounds or exceptions.
Streamlined permission management
The platform has enhanced its group-based permission system, making it easier to manage access for Microsoft 365 group-connected team sites. Rather than managing individual file or folder permissions, administrators can add external users directly to groups, ensuring consistent access across all group resources.
This approach simplifies permission management significantly, particularly for organizations with complex project structures involving both internal teams and external partners. Group membership changes automatically propagate across all associated SharePoint resources, reducing administrative overhead and minimizing permission errors.
PowerShell automation capabilities
SharePoint’s 2025 updates have expanded PowerShell automation capabilities, allowing administrators to implement sophisticated sharing policies through scripted commands. Organizations can now automate repetitive tasks like setting sharing capabilities, configuring expiration dates, and managing external user access.
These automation capabilities prove essential for large organizations that need to maintain consistent policies across hundreds or thousands of SharePoint sites. Automated scripts ensure policy compliance while reducing the time IT teams spend on routine permission management tasks.
Zero-trust security integration
Reflecting broader security trends, SharePoint has strengthened its zero-trust security capabilities. The platform now supports continuous verification processes, micro-segmentation strategies, and least-privilege access principles as standard features rather than add-on configurations.
These enhancements mean that SharePoint automatically adjusts access privileges based on user behavior, location, device compliance, and other contextual factors. The system no longer assumes trust based on initial authentication but continuously validates access rights throughout each session.
Impact on daily operations
The enhanced security features provide greater confidence when sharing sensitive documents, while the improved automation capabilities reduce administrative burden. External collaboration becomes more seamless through better integration with Microsoft Entra, and the granular control options ensure that security policies can be tailored to specific business requirements rather than forcing organizations to accept one-size-fits-all approaches.
For organizations already using SharePoint, these updates represent evolutionary improvements that enhance existing workflows rather than requiring fundamental changes to established processes. The enhancements build upon familiar SharePoint concepts while adding the security and control features that modern business environments demand.
Step-by-step Instructions: How to Share a File or Folder in SharePoint
This section provides a comprehensive walkthrough of SharePoint’s file sharing process, from locating your documents to configuring advanced security settings. We’ll cover each step of the sharing workflow, explore the various access control options available, and examine the additional security features that help protect your shared content. By the end of this section, you’ll understand how to share files effectively while maintaining appropriate security controls for different collaboration scenarios.
Sharing a file or folder: complete step-by-step process of how to share files in SharePoint
The following walkthrough takes you through SharePoint’s standard file sharing process, which remains consistent whether you’re sharing a single document or an entire folder. These steps apply to most SharePoint environments, though some options may vary depending on your organization’s security policies and administrator settings.
Step 1: Navigate to your content
Begin by opening the SharePoint site where your target file or folder is located. You can access this through your Microsoft 365 portal, direct site URL, or through Teams if the site is connected to a specific team workspace.
Step 2: Access the document library
Once on your SharePoint site, navigate to the document library containing the file or folder you want to share. Document libraries are typically listed in the site’s navigation menu or displayed prominently on the site’s homepage.
Step 3: Locate and select your file
Find the specific file or folder you want to share within the document library. You have two options for accessing the sharing menu:
- Hover method: Position your cursor over the file or folder name until you see the three-dot menu button appear, then click it
- Right-click method: Right-click directly on the file or folder name
Both approaches will display a context menu with various file management options.
Step 4: Initiate sharing
From the context menu that appears, locate and click the “Share” option. This action opens SharePoint’s sharing configuration window, where you’ll define all access parameters for your shared content.
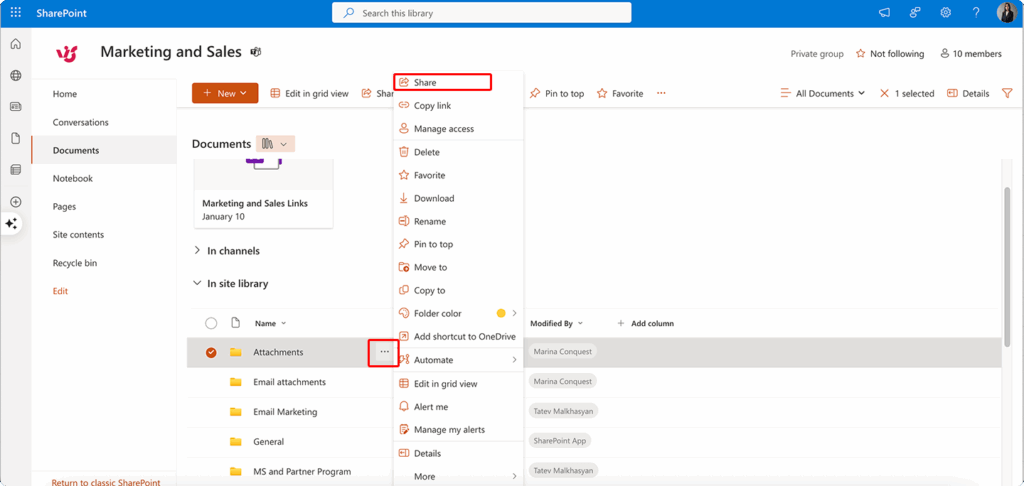
👉 So, how to share a file in SharePoint? Here’s how to share a file on SharePoint: Navigate to your SharePoint document library and locate the file you want to share. Hover over the file name and click the three-dot menu, then select “Share” from the options. In the sharing dialog, specify recipients by entering email addresses or selecting users from your organization’s directory. Configure the appropriate permission level (view-only or edit access) and set any necessary expiration dates or restrictions. Click “Send” to deliver email invitations to recipients or copy the generated link for manual distribution.
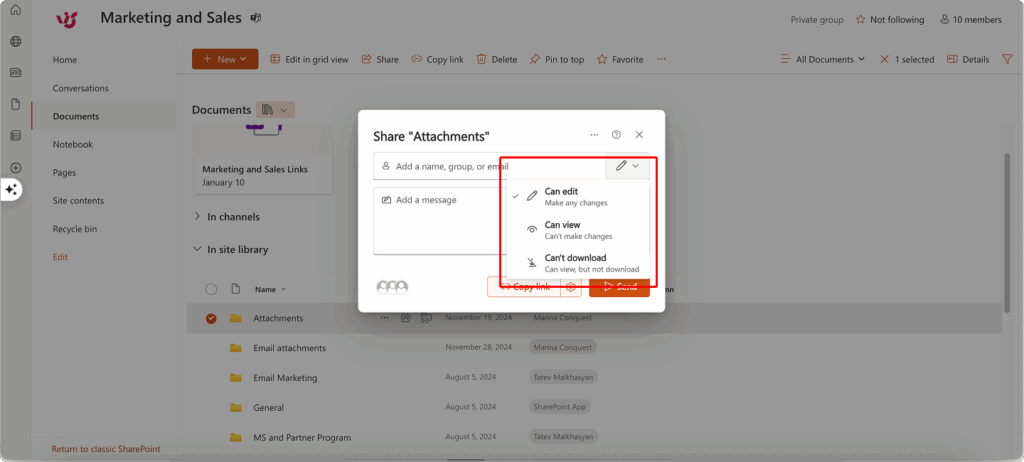
Configuring access settings for SharePoint secure file sharing
Once the sharing window opens, you’ll see several configuration options that control how recipients can access and interact with your shared content. The interface is organized into logical sections that guide you through setting permissions, defining access levels, and establishing security parameters. Take time to review each option carefully, as these settings determine both the functionality available to recipients and the security posture of your shared files.
Recipient selection
The sharing window presents several options for defining who can access your shared content:
Specific internal users: Add colleagues from your organization by typing their names or email addresses. SharePoint’s search function will suggest matches from your organizational directory as you type.
External users by email: If your administrator has enabled external sharing, you can invite people outside your organization by entering their email addresses. These recipients will receive access invitations and may need to create guest accounts depending on your organization’s settings.
User groups: Instead of adding individuals, you can share with entire groups such as “Marketing Team” or “Project Alpha Members.” This approach simplifies permission management and automatically includes new group members in shared access.
Anyone with link: This option creates a link that provides access without requiring login credentials. Use this setting cautiously, as it creates the broadest possible access to your content.
👉 How to share a document on SharePoint? Here’s how to share documents on SharePoint: Open the SharePoint site containing your document and browse to the relevant document library. Right-click on the document or use the three-dot menu next to its name, then choose “Share.” Add recipients by typing their email addresses or selecting from your organization’s user list, then choose whether they can view or edit the document. You can also add a personal message explaining the purpose of sharing and set link expiration dates if needed. Complete the process by clicking “Send” to notify recipients via email.
Access level configuration for SharePoint file share
SharePoint offers multiple permission levels to match your collaboration requirements:
View only: Recipients can read, download, and print files but cannot make modifications. This setting works well for sharing final reports, reference materials, or documents requiring approval before changes.
Edit access: Allows recipients to modify existing files, create new documents within shared folders, and participate in collaborative editing. This level suits active project work where multiple contributors need modification rights.
Download restrictions: When using “view only” settings, you can additionally prohibit downloading to prevent recipients from saving local copies. This feature helps maintain control over sensitive documents while still allowing review access.
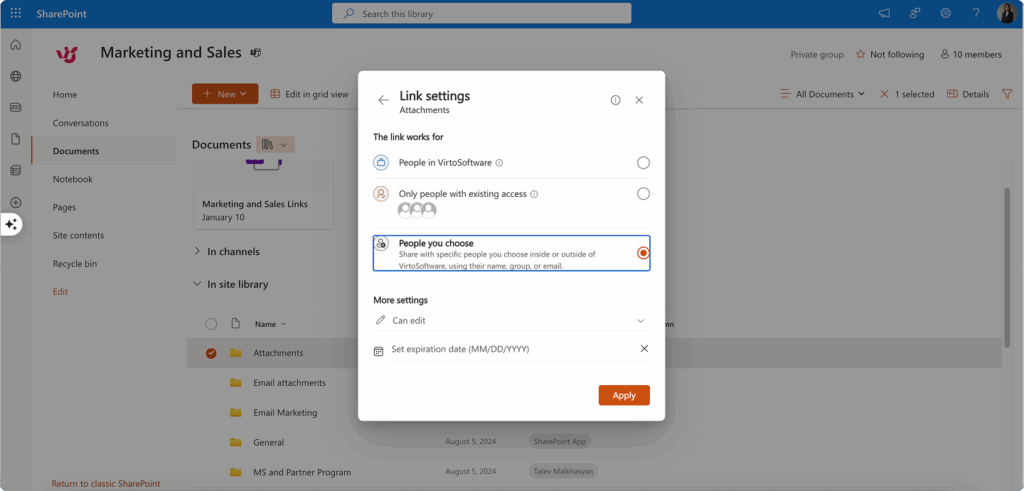
Time-based access controls
SharePoint’s link expiration feature helps maintain security by automatically revoking access after specified periods:
Expiration date setting: Configure links to expire after predetermined timeframes, such as 7 days for temporary project reviews or 30 days for extended collaboration periods. The system supports expiration periods from 1 to 730 days depending on your administrator’s policies.
Automatic revocation: Once the expiration date passes, SharePoint automatically disables the shared links, ensuring that temporary access doesn’t become permanent inadvertently.
Personal messages and context
The sharing interface includes an optional message field where you can provide context for recipients:
Invitation explanations: Add brief descriptions of why you’re sharing the content, what actions you expect from recipients, or any relevant deadlines.
Usage instructions: Include specific guidance about how recipients should interact with the shared content, especially useful for external collaborators unfamiliar with your organization’s processes.
Advanced link settings when using SharePoint to share files
Beyond the basic sharing options, SharePoint provides several advanced security features that give you granular control over how shared links function. These settings are particularly valuable when sharing sensitive documents or when you need to maintain strict access controls. The availability of these features depends on your organization’s SharePoint configuration and licensing level.
Restricted user access
For enhanced security, you can limit link access to specific individuals rather than allowing broad sharing:
Email-specific links: Generate links that only work for designated email addresses, preventing unauthorized forwarding or sharing.
Verification requirements: Recipients using restricted links may need to verify their identity through email confirmation before accessing shared content.
Password protection
When enabled by your administrator, SharePoint allows password protection for shared links:
Password configuration: Set custom passwords that recipients must enter before accessing shared files. This adds an additional security layer beyond email verification.
Password distribution: Remember that passwords must be communicated separately from share links to maintain security effectiveness.
Link forwarding controls
SharePoint provides options to prevent recipients from sharing access with others:
Disable forwarding: When available, this setting prevents recipients from sharing your links with additional users, maintaining tighter control over access distribution.
Audit trail maintenance: Restricting forwarding helps ensure that access logs accurately reflect who has viewed or modified your shared content.
👉 NB: The feature availability depends on your organization’s SharePoint admin settings, your SharePoint plan (some advanced features require premium licenses), and tenant-level policies set by IT administrators.
Finalizing and sending
After configuring all your sharing preferences, you’re ready to activate the sharing and deliver access to your recipients. This final stage confirms your settings and initiates the delivery process, whether through automated email invitations or by generating links for manual distribution.
Completing the share process
After configuring all your desired settings, click the “Send” button to activate your sharing configuration. SharePoint will then process your settings and deliver access according to your chosen method:
Email invitations: Recipients receive email notifications containing access links and any personal messages you included. These emails typically arrive within minutes of sharing.
Manual link distribution: If you prefer to control how links are distributed, you can copy the generated share link and send it through your preferred communication channels.
Verification and follow-up
SharePoint provides confirmation when sharing is successful, and you can monitor access through the platform’s sharing management tools. Recipients can typically access shared content immediately after receiving their invitations, though external users may need to complete guest account setup processes depending on your organization’s security requirements.
This step-by-step process ensures that you can share files securely while maintaining appropriate control over access levels, timeframes, and recipient permissions. The flexibility of SharePoint’s sharing system accommodates everything from quick document reviews to complex, long-term collaborative projects.
How to Share SharePoint Files with External Users
External file sharing transforms SharePoint from an internal collaboration tool into a powerful platform for engaging with partners, contractors, and clients. This section explores how to safely extend your SharePoint environment beyond organizational boundaries while maintaining security and control. We’ll examine the different types of external access available, walk through the configuration process, and highlight the security considerations that ensure your data remains protected throughout external collaborations.
External sharing capabilities in SharePoint
SharePoint allows you to securely share files and folders not only within your organization, but also with external users including partners, contractors, and clients. This capability enables seamless collaboration across organizational boundaries without requiring external parties to have access to your internal systems or forcing you to rely on less secure alternatives like email attachments.
However, external sharing requires properly configuring access settings and coordinating actions with your IT department to avoid data leaks. The flexibility that makes external sharing powerful also introduces security considerations that demand careful attention to permission levels, access duration, and recipient verification.
Understanding external access types
SharePoint provides two distinct approaches to external access, each offering different levels of control and security:
Specific users (Microsoft Account/Guest Account)
This method provides the highest level of control over external access. External users must sign in using either an existing Microsoft account or by creating a guest account specifically for accessing your organization’s content. This approach enables you to track user activity, maintain audit trails, and ensure that access remains tied to verified identities.
When you share content with specific external users, SharePoint typically creates guest accounts in your organization’s Azure Active Directory (now Microsoft Entra), allowing IT administrators to manage external users alongside internal accounts. This integration provides comprehensive oversight and enables consistent application of security policies.
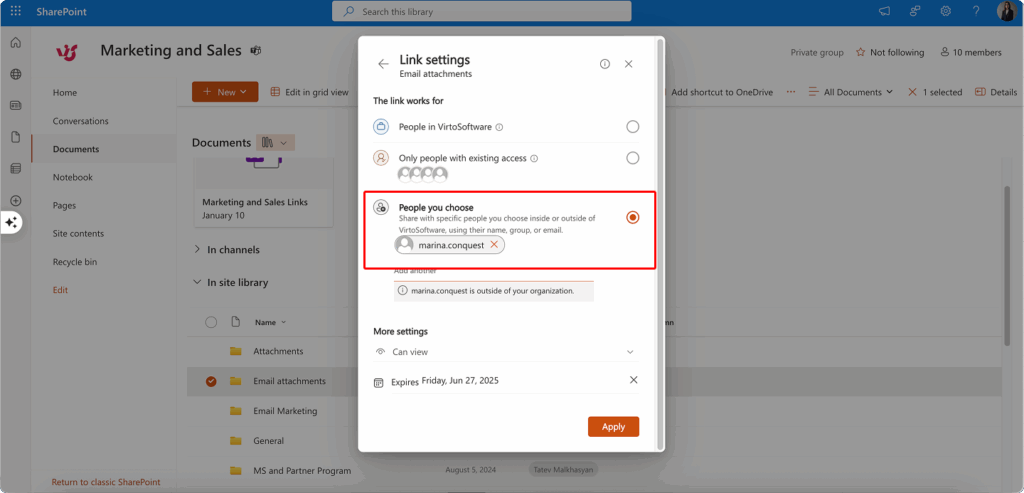
Anonymous access (Anyone with the link)
Anonymous links offer convenience at the cost of control. Anyone who obtains the link can access shared content without signing in or providing identification. While this approach eliminates friction for recipients, it also removes your ability to track who accesses the content or revoke access for specific individuals.
Use anonymous links only for non-sensitive data that you’re comfortable sharing broadly. Consider scenarios like public announcements, marketing materials, or general reference documents that don’t contain confidential information.
Setting up external access in SharePoint
Configuring external access involves several sequential steps that ensure both functionality and security. The process requires verifying permissions at multiple levels, selecting appropriate access types, and implementing the specific sharing configurations that match your security requirements. Each step builds upon the previous one, so it’s important to complete them in order.
Verify site-level permissions
Before sharing content externally, ensure that external access is enabled at the site level. This configuration requires administrative rights and involves several steps:
Navigate to your site settings, then locate the “Access and permissions” section. Within this area, find “Access for external users” or similar terminology depending on your SharePoint version. Verify that the “Allow sharing with external users” option is active.
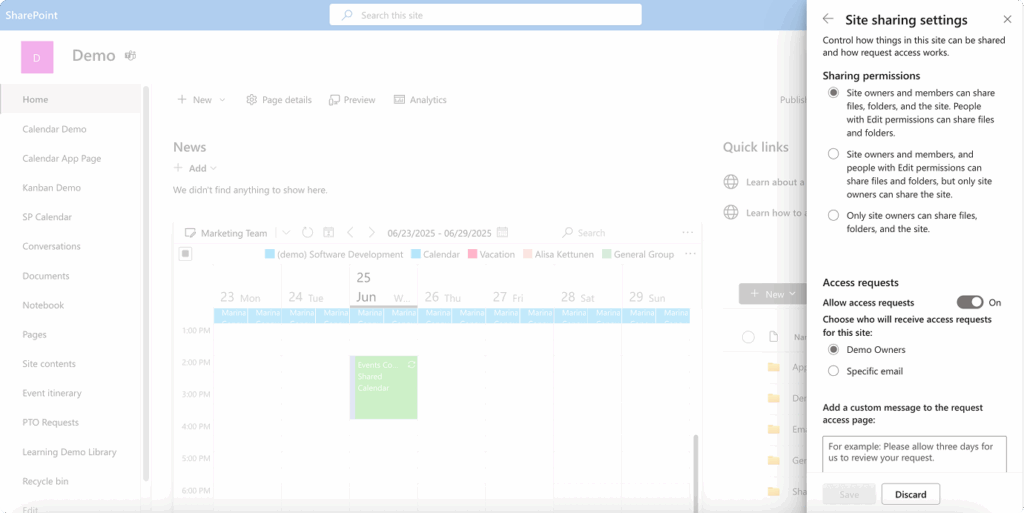
If this option is disabled, contact your IT administrator, as site-level sharing restrictions may be in place for security or compliance reasons.
Determine appropriate access type
Based on your content sensitivity and collaboration requirements, choose between the two main external access options:
Authenticated access: Requires external users to sign in with Microsoft accounts, providing maximum control and audit capabilities. Choose this option for sensitive documents, ongoing collaborations, or when you need to track access patterns.
Anonymous access: Allows link-based access without sign-in requirements. Reserve this option for non-sensitive content where convenience outweighs security concerns and where broad, untracked access is acceptable.
Configure external sharing
Once you’ve determined the appropriate access type, proceed with the sharing configuration:
Navigate to the document library containing the files you want to share externally. Select your target file or folder and click “Share” to open the sharing configuration window.
In the access settings interface, specify the email address of the external user you want to grant access to. Set the desired permissions level—either view-only for review purposes or edit access for collaborative work.
Configure time-based restrictions if necessary, setting expiration dates that align with your project timelines or security policies. Consider whether to require sign-in with an account or allow access without authentication, keeping in mind your organization’s external sharing policies.
Advanced security options for external links
When using link-based sharing, SharePoint offers several additional security features:
Password protection: Set passwords that external users must enter before accessing shared content. Remember to communicate passwords through separate channels from the sharing links to maintain security effectiveness.
Download prevention: If your SharePoint environment includes advanced security settings, you can prevent external users from downloading files while still allowing them to view content online.
Link sharing restrictions: Configure settings to prevent recipients from sharing your links with additional users, maintaining control over access distribution.
Distribution and user management
After configuring your sharing settings, you can distribute access through two primary methods:
Email invitations: SharePoint sends automated email notifications to specified recipients, including access links and any personal messages you’ve included. This method creates the clearest audit trail and ensures recipients receive proper context for the shared content.
Manual link distribution: Copy generated share links and distribute them through your preferred communication channels. This approach gives you more control over how and when recipients receive access information.
When sharing with external users via email, SharePoint often creates guest accounts for recipients in Azure Active Directory, enabling your IT team to manage external users through the same systems used for internal account management.
Can I use SharePoint to share files with external users?
Yes, SharePoint’s external sharing capabilities are specifically designed to facilitate secure collaboration with users outside your organization. The platform provides robust tools for controlling access levels, monitoring usage, and maintaining security while enabling the external partnerships that modern business demands.
The key to successful external sharing lies in understanding your organization’s security requirements, choosing appropriate access methods for different types of content, and maintaining ongoing oversight of external access patterns. When configured properly, SharePoint’s external sharing features provide a secure, auditable alternative to less controlled sharing methods while supporting the collaborative relationships that drive business success.
Security When Sharing Files in SharePoint
File sharing security in SharePoint extends far beyond simple access control—it encompasses comprehensive risk management, regulatory compliance, and organizational reputation protection. This section examines why security considerations are paramount when sharing documents, identifies the key risks that organizations face, and provides actionable recommendations for implementing robust security measures. Understanding these security principles ensures that your SharePoint environment enables collaboration while protecting your organization’s most valuable information assets.
Why security is critical when working with documents
SharePoint environments typically house an organization’s most sensitive information assets, making security considerations essential rather than optional. These platforms often store internal documents containing trade secrets, proprietary methodologies, personal information subject to privacy regulations, financial reports with material business implications, and strategic planning documents that could provide competitive advantages to unauthorized parties.
The collaborative nature of modern business means that both external and internal file sharing must be managed transparently and remain fully trackable. Organizations need clear visibility into who accesses what information, when access occurs, and what actions users take with shared documents. This transparency supports both security monitoring and regulatory compliance requirements.
Perhaps most concerning is how easily user errors can compromise document security. A single mistake—such as copying a link incorrectly, granting overly broad access permissions, or sharing with unintended recipients—can provide unauthorized third parties with access to sensitive information. These errors often occur with the best intentions, making them particularly difficult to prevent through policy alone.
Potential risks when sharing files
Understanding the specific security risks associated with SharePoint file sharing helps organizations develop targeted protection strategies and make informed decisions about access controls. These risks range from accidental exposure due to user error to sophisticated attacks targeting shared document repositories. Each risk category presents unique challenges and requires different mitigation approaches.
Unauthorized access scenarios
Unauthorized access frequently results from configuration errors rather than malicious intent. Common scenarios include sending links to incorrect recipients due to similar email addresses or names, configuring overly broad permissions such as “anyone with the link” for sensitive documents, and failing to remove access when project relationships or employment status changes.
Loss of document control
Without proper tracking mechanisms, organizations lose visibility into how their shared documents are being used. This includes inability to identify who currently has access to specific files, lack of awareness when documents are downloaded or copied locally, and missing audit trails when access permissions are modified or expanded by recipients.
Data leakage vulnerabilities
Data leakage can occur through multiple pathways, particularly when external access lacks appropriate restrictions. Compromised user accounts can provide attackers with legitimate-appearing access to shared documents. Additionally, recipients may inadvertently share access further than intended, creating access chains that extend beyond the original sharing intent.
Reputational consequences
Data breaches involving shared documents can severely damage organizational reputation. Customer trust erodes when personal information is mishandled, partner relationships suffer when confidential collaborative documents are exposed, and competitive positioning weakens when strategic information becomes publicly available.
Legal and regulatory implications
Modern regulatory frameworks impose significant penalties for data handling failures. GDPR violations can result in fines up to 4% of annual global revenue, HIPAA breaches carry penalties reaching $1.5 million per incident, and industry-specific regulations often include additional compliance requirements that affect how documents can be shared and stored.
Financial impact
Beyond regulatory penalties, document security failures can generate substantial financial losses. Trade secret exposure can eliminate competitive advantages that took years to develop, customer churn following privacy breaches reduces revenue, and incident response costs including legal fees, forensic analysis, and remediation efforts can reach millions of dollars.
Security recommendations for file sharing in SharePoint
Implementing effective security measures for SharePoint file sharing requires a multi-layered approach that combines technical controls, user education, and ongoing monitoring. The following recommendations provide practical steps for reducing security risks while maintaining the collaborative capabilities that make SharePoint valuable. These measures should be adapted to your organization’s specific risk profile, compliance requirements, and operational needs.

Always verify permissions carefully
Before granting access to any document or folder, conduct thorough permission reviews to ensure appropriate access levels. Implement the principle of least privilege by granting only the minimum access necessary for recipients to complete their intended tasks. This means choosing view-only permissions when editing isn’t required, limiting access to specific files rather than entire folders when possible, and regularly reviewing existing permissions to remove unnecessary access.
Permission verification should include confirming recipient identities, especially when dealing with similar names or email addresses, and double-checking that access levels match the sensitivity of shared content and the recipient’s legitimate business need.
Implement time-limited access controls
SharePoint’s link expiration functionality provides essential security controls for temporary collaborations. Configure expiration dates that align with project timelines, business relationships, and content sensitivity levels. For contractor relationships, set expiration dates that match contract periods. For document reviews, use shorter timeframes such as 30 days for sensitive materials or 7 days for highly confidential content.
The SharePoint interface allows you to set expiration dates during the sharing process by selecting the calendar icon in the sharing dialog and choosing your desired expiration timeframe. This automatic access revocation ensures that temporary sharing arrangements don’t inadvertently become permanent access grants.
Avoid anonymous links for confidential content
Reserve “anyone with the link” sharing exclusively for non-sensitive materials such as public announcements, marketing collateral, or general reference documents. For confidential documents, always require recipient authentication through specific user invitations, which enables tracking, audit trails, and granular access control.
Enable comprehensive activity auditing
SharePoint’s built-in auditing capabilities track detailed user activities including file access, downloads, modifications, and sharing actions. Configure audit logging to capture who accessed specific files, when access occurred, what actions were performed, and from which locations or devices access originated.
These audit logs serve multiple purposes: identifying suspicious access patterns, supporting compliance reporting requirements, and providing forensic evidence when security incidents occur. Regular review of audit logs helps detect unauthorized access attempts and ensures that shared documents are being used appropriately.
Require two-factor authentication
Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly reduces risks associated with compromised user credentials. This protection is particularly crucial for external users who may use less secure personal devices or networks, and for administrators who have elevated access to SharePoint configuration settings.
2FA requirements should apply to all users accessing sensitive documents, with particular attention to external collaborators who represent higher risk profiles due to reduced organizational control over their security practices.
Deploy data loss prevention policies
Microsoft 365’s DLP capabilities provide automated protection against inadvertent sharing of sensitive information. Configure DLP policies to detect and block sharing of documents containing credit card numbers, social security numbers, medical record identifiers, or other personally identifiable information.
DLP policies can automatically prevent sharing when sensitive data patterns are detected, alert administrators when policy violations occur, and provide user education when inappropriate sharing is attempted. These automated controls supplement human judgment with consistent, scalable protection.
Implement sensitivity-based access controls
Sensitivity labels enable automatic application of security policies based on document classification. Documents labeled as “Confidential” can automatically restrict printing, prevent forwarding, require authentication for access, and limit availability to specific organizational groups.
This approach ensures that security controls scale with your document volume and reduces reliance on manual security decisions. Sensitivity labels can be applied automatically based on content analysis or manually by document creators, providing flexible protection that adapts to different content types and collaboration scenarios.
Labels such as “Internal Use Only” might prevent external sharing entirely, while “Partner Confidential” could allow limited external access with enhanced monitoring. This classification-based approach provides consistent security application across your entire SharePoint environment while supporting diverse collaboration requirements.
Additional Features and Advanced Settings
While SharePoint’s basic file sharing capabilities meet the needs of most day-to-day collaboration scenarios, the platform offers sophisticated features and advanced configurations that can streamline team workflows and automate access management. This section explores tools that go beyond simple file sharing to create structured, scalable collaboration environments. These advanced features become particularly valuable for organizations managing complex project teams, standardized processes, or large-scale collaborative initiatives.
The basic file sharing features in SharePoint are suitable for most users, but for enhanced team collaboration and automated access management, you can leverage advanced tools and automated scripts that reduce administrative overhead while improving security and consistency.
Advanced file sharing features in SharePoint
These advanced capabilities build upon SharePoint’s standard sharing functionality to provide more sophisticated collaboration environments. Each feature addresses specific organizational needs, from streamlining repetitive permission tasks to enabling seamless integration with other Microsoft 365 tools. Understanding these options helps you design SharePoint environments that scale with your team’s complexity and collaboration requirements.
Create libraries with access templates
SharePoint enables you to establish separate document libraries configured for specific purposes with pre-defined access levels. This approach standardizes collaboration patterns and eliminates the need to manually configure permissions for individual files within structured environments.
For example, you can create a read-only library specifically designed for external contractors, ensuring they can access necessary reference materials without editing capabilities. Similarly, you might establish a library with full edit rights for your marketing team, enabling seamless collaboration on campaigns and content development.
This templated approach proves especially valuable for organizations with repeating collaboration patterns or standardized project structures. Rather than configuring access permissions for each document individually, the library-level permissions automatically apply to all content within that space, ensuring consistency and reducing configuration errors.
Use Microsoft 365 Groups to manage access
Instead of assigning permissions individually to each user, Microsoft 365 Groups provide a centralized approach to access management. When you add users to a Microsoft 365 group, SharePoint access automatically aligns with the permissions assigned to that group, dramatically simplifying permission management for teams of any size.
This group-based approach becomes particularly powerful when managing dozens of users across multiple projects or departments. When new employees join your organization or existing team members change roles, adding them to the appropriate groups instantly grants the necessary SharePoint permissions without requiring individual configuration.
Group management also improves security oversight, as administrators can review group memberships rather than tracking individual permissions across numerous SharePoint sites and libraries. This centralized approach reduces the likelihood of orphaned permissions when employees leave or change positions.
Microsoft Teams integration: files and channels
The deep integration between Microsoft Teams and SharePoint creates seamless collaboration workflows that leverage the strengths of both platforms. All files uploaded to Teams channels automatically save to associated SharePoint libraries, creating a unified storage and collaboration environment.
This integration enables several powerful collaboration scenarios:
Automatic team access: Documents shared in Teams channels become immediately available to all team members without requiring additional permission configuration. Team membership automatically determines SharePoint access levels.
Teams tabs for quick access: You can create Teams tabs that provide direct access to SharePoint libraries, enabling team members to work with documents without leaving their primary collaboration environment.
Integrated notifications: Configure Teams notifications about SharePoint document changes through associated channels, ensuring team members stay informed about relevant updates without managing separate notification systems.
This integrated approach proves especially valuable for permanent work groups that maintain dedicated Teams channels, as it creates a single collaborative workspace that combines communication, file sharing, and project coordination.
Concurrent editing of documents
One of SharePoint’s most powerful collaboration features is real-time co-authoring, which enables multiple users to edit the same document simultaneously. SharePoint supports concurrent editing through Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, both in web browsers and desktop Office applications.
Real-time co-authoring eliminates the version control challenges that plague email-based collaboration, as all contributors work on the same document instance. Users can see each other’s changes as they occur, enabling dynamic collaboration that would be impossible with traditional file sharing methods.
The platform automatically manages conflict resolution when multiple users edit the same sections, and maintains comprehensive version history that enables recovery of previous document states if needed. This functionality transforms document collaboration from a sequential process into a truly collaborative experience.
Can multiple users edit a SharePoint document at the same time?
Yes, SharePoint fully supports simultaneous document editing by multiple users. The platform’s co-authoring capabilities enable real-time collaboration where contributors can see each other’s changes as they work, facilitating dynamic teamwork on documents, spreadsheets, and presentations. This functionality works seamlessly across both web-based and desktop Office applications.
Streamlined access distribution without email notifications
For scenarios where you need to provide access to multiple users without sending individual email invitations, SharePoint offers efficient bulk access methods:
Link-based sharing with parameters: Use SharePoint’s link sharing feature with specific parameters such as “only for team members” or “anyone with this link,” depending on your security requirements and recipient group composition.
Disable automatic email invitations: In the sharing settings, turn off the option to automatically send email invitations to recipients. This prevents inbox clutter while still generating the necessary access permissions.
Manual link distribution: Copy the generated sharing link and distribute it through your preferred channels—Teams conversations, instant messaging platforms, internal portals, or project management systems.
This approach proves particularly convenient for internal portals where you want to embed document access or when working with large groups where individual email invitations would create unnecessary communication overhead. Manual distribution also provides greater control over how and when recipients receive access information, enabling you to include additional context or instructions that automated emails might not accommodate.
The flexibility of manual link distribution supports diverse organizational communication patterns while maintaining the security and tracking benefits of SharePoint’s permission system. Recipients still receive appropriate access levels, and administrators retain full visibility into who has accessed shared documents, but without the communication complexity that individual invitations can create.

How to Manage Files and Access After Publishing
Effective SharePoint management extends far beyond the initial sharing process—it requires ongoing oversight to maintain security, ensure appropriate access levels, and track document usage patterns. This section covers the essential post-sharing management tasks that help organizations maintain control over their shared content. From monitoring who has access to revoking permissions when projects conclude, these management capabilities ensure that your SharePoint environment remains secure and aligned with evolving business needs.
After you have shared a file or folder in SharePoint, it becomes crucial not to lose control over that content. Organizations must maintain awareness of who has access, revoke rights when circumstances change, and modify settings as project requirements evolve. This ongoing management prevents security drift and ensures that access permissions remain aligned with current business relationships and project status.
Checking current access permissions
Understanding who currently has access to your shared files provides the foundation for effective ongoing management. SharePoint’s access review tools give you comprehensive visibility into current permission structures.
To review existing access permissions, begin by opening the file or folder within your SharePoint library. Click the three dots menu (“…”) next to the item name, or alternatively use the command options in the top toolbar. From the available options, select “Manage access” or “Share”—both options will open a window displaying current permission configurations.
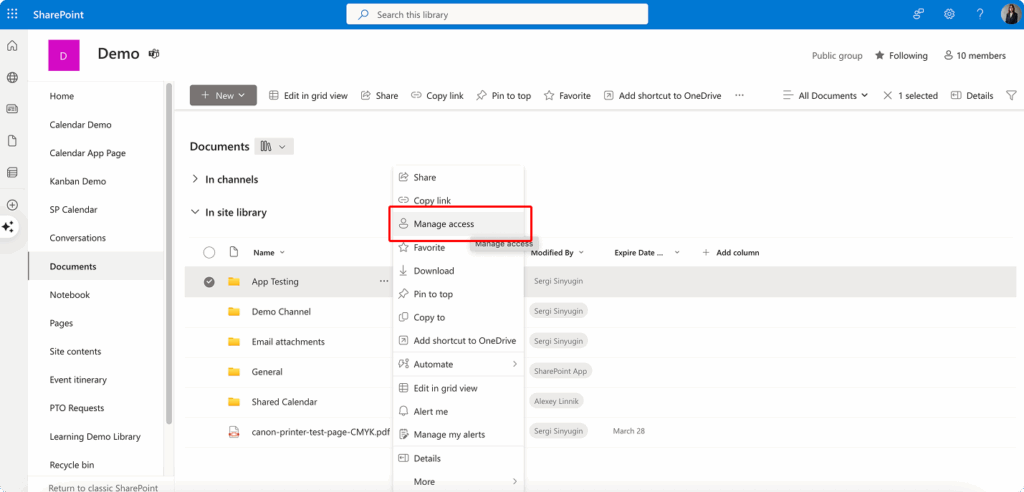
This access management window provides detailed information about all current access arrangements, including individual users who have been granted specific permissions, groups that have been given access with their respective permission levels, active shared links along with their access parameters, and the specific rights associated with each access method (view-only, edit, full control, etc.).
The interface clearly distinguishes between different types of access, making it easy to understand whether permissions were granted through direct user invitations, group memberships, or shared links. This visibility helps you assess whether current access arrangements still align with your intentions and security requirements.
Modifying and revoking access permissions
SharePoint provides flexible tools for adjusting access permissions as circumstances change. Within the same “Access Management” window used for reviewing permissions, you can make several types of modifications to existing access arrangements.
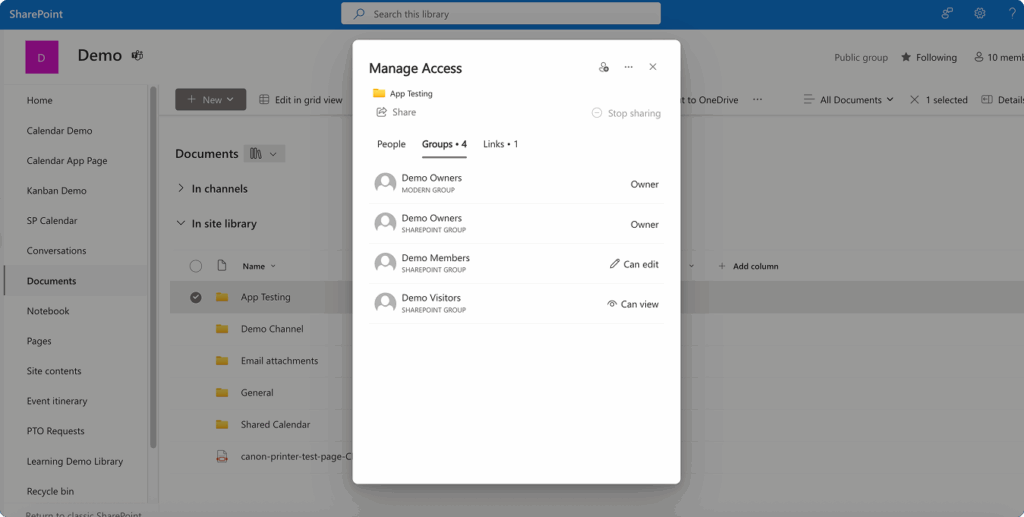
For individual users and groups, you can change access levels by selecting different permission options. For example, you might reduce a user’s access from editing rights to view-only permissions when their role in a project changes, or escalate permissions when additional collaboration becomes necessary.
To completely remove access, you can delete users from the access list or disable group permissions entirely. This capability proves essential when projects conclude, when external contractors complete their work, or when internal team members change roles and no longer require access to specific documents.
For shared links, the management process involves additional considerations. You can click the “…” menu next to any active link and select “Remove link” to completely eliminate that access pathway. This action immediately prevents anyone from using that specific link to access your content, regardless of whether they previously bookmarked or saved the link.
SharePoint also enables you to modify link parameters without completely removing access. You can adjust expiration dates, change permission levels, or add password protection to existing links, providing flexible control over ongoing access arrangements.
Setting access expiration dates proves particularly valuable for temporary collaborations. Rather than relying on manual permission revocation, you can configure automatic access termination that aligns with project timelines, contract periods, or other predetermined endpoints.

Tracking file activity and usage patterns
Monitoring how shared files are being used provides valuable insights for both security oversight and collaboration effectiveness. SharePoint’s activity tracking capabilities help you understand engagement patterns and identify potential security concerns.
To access basic activity information, navigate to your target file or library and click the “Details” button or the “i” icon typically located in the upper right corner of the interface. This action opens a details panel that displays recent activity information.
The activity panel shows several types of useful information, including when and by whom the file was last modified, which users have recently viewed the document, what specific actions have occurred such as downloads, deletions, or permission changes, and the timestamps associated with each recorded activity.
This basic activity tracking helps you understand whether shared documents are being used as intended and can alert you to unexpected access patterns that might warrant investigation.
Advanced auditing for comprehensive oversight
For organizations requiring more detailed analysis—particularly larger companies with complex collaboration requirements—SharePoint integrates with Microsoft 365’s comprehensive auditing system. Administrators can access extensive audit logs through the Microsoft 365 admin center, where complete records of user actions are maintained.
These advanced audit logs capture detailed information about every interaction with shared documents, including successful and failed access attempts, permission modifications made by any user, document downloads and exports, sharing activities initiated by recipients, and access from unusual locations or devices.
The comprehensive audit trail supports compliance requirements, security investigations, and usage analysis that informs future sharing policies. This level of detail proves particularly valuable for organizations in regulated industries or those handling sensitive information that requires detailed access documentation.
Advanced auditing also enables administrators to identify trends in collaboration patterns, detect potential security risks, and optimize SharePoint configurations based on actual usage data rather than assumptions about how the platform is being used.
Regular review of these audit logs helps organizations maintain security posture while ensuring that SharePoint continues to support effective collaboration across their teams and external partnerships.
Using Additional Solutions from VirtoSoftware to Optimize File Sharing
While SharePoint’s native file sharing capabilities serve most organizational needs effectively, standard SharePoint can sometimes prove inconvenient for bulk operations or present navigation challenges when managing large volumes of files. Complex document hierarchies, repetitive upload tasks, and the need for enhanced monitoring can create bottlenecks in otherwise efficient workflows. This section explores how VirtoSoftware’s specialized solutions address these limitations and significantly enhance SharePoint’s file management capabilities.
Standard SharePoint interfaces work well for individual file operations but can become cumbersome when dealing with hundreds of documents, complex folder structures, or requiring detailed oversight of file activities. Organizations often find themselves needing more sophisticated tools to handle enterprise-scale file management while maintaining the security and collaboration benefits that SharePoint provides.
Virto Multiple File Operations solutions
VirtoSoftware offers comprehensive file management solutions designed to streamline bulk operations and enhance user experience across both SharePoint Online and On-Premises environments.
Virto Multiple File Upload App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365

The Virto Multiple File Upload App transforms the standard SharePoint upload experience with advanced bulk capabilities that eliminate time-consuming repetitive tasks. This solution enables users to upload multiple documents and entire folder structures directly to libraries or as attachments to list items, significantly reducing the administrative overhead associated with large-scale content migration.
The app features a user-friendly drag-and-drop interface that simplifies file selection and uploading processes, making it accessible to users regardless of their technical expertise. Additionally, the metadata assignment capability allows users to add custom metadata to files during the upload process, enabling immediate categorization and improved document organization.
Cross-browser compatibility ensures efficient document management across various devices and platforms, supporting diverse organizational technology environments. The solution also provides configurable upload preferences, including file type restrictions and size limitations, helping organizations maintain content governance standards while enabling efficient bulk operations.
Virto Multiple File Operations for SharePoint On-Premises

For organizations using SharePoint On-Premises, the Virto Multiple File Operations web part provides comprehensive bulk file management capabilities that extend far beyond basic upload functionality. This solution supports a wide array of file actions including upload, download, delete, copy, move, check-in, approve, and edit operations, all executable in bulk format.
The advanced file handling capabilities include sophisticated drag-and-drop uploads, bulk downloads for offline work, and the ability to edit multiple metadata fields simultaneously across numerous files. These features prove particularly valuable for organizations managing large document repositories or implementing content lifecycle management processes.
Customizable configurations allow administrators to set file size limits, restrict specific file types, and adjust metadata settings to align with organizational requirements. This flexibility ensures that the solution adapts to existing governance frameworks while providing enhanced operational efficiency.
👉 Learn more about VirtoSoftware’s secure file management & sharing solution here: Secure document management and SharePoint file approval workflow with ease
VirtoSoftware Alerts and notification solutions
Effective file sharing requires ongoing awareness of document activities and changes. VirtoSoftware’s notification solutions ensure that teams remain informed about critical file operations and collaborative activities.
Virto Alerts & Reminder App for SharePoint Online & Microsoft 365

This comprehensive alerting system enables organizations to set up automatic notifications when new files are uploaded or existing documents are modified, which proves invaluable when collaborating on time-sensitive documents or maintaining audit trails for compliance purposes.
The solution supports personalized notifications configured by groups, folders, or document types, ensuring that relevant stakeholders receive appropriate updates without overwhelming users with irrelevant information. Advanced scheduling capabilities allow for both immediate alerts and customized reminder schedules that align with project timelines and business processes.
The app integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Teams and Outlook, delivering notifications through the communication channels that teams already use daily. This integration eliminates the need to monitor multiple systems while ensuring that critical file activities receive appropriate attention.
Virto Notifications & Reminders App for Microsoft Teams
Designed specifically for Teams-centric workflows, this app brings SharePoint file notifications directly into Teams channels, maintaining collaborative momentum without requiring users to switch between applications. The webhook integration capabilities allow for automatic updates from various services, creating a centralized notification hub within Teams.
The solution supports condition-based custom alerts that filter notifications according to specific criteria, ensuring teams receive only relevant updates about file activities that require their attention. This targeted approach prevents notification fatigue while maintaining comprehensive oversight of document collaboration.
Enhanced efficiency and control benefits
Implementing these VirtoSoftware solutions dramatically increases efficiency and control when working with files in SharePoint through several key improvements. Bulk operations that previously required hours of repetitive work can be completed in minutes, freeing staff to focus on higher-value activities. The enhanced notification systems ensure that critical file activities receive timely attention, reducing the risk of missed deadlines or overlooked collaborative contributions.
Improved metadata management capabilities enable better document organization and discovery, while customizable notification filters ensure that teams receive relevant information without being overwhelmed by excessive alerts. The seamless integration with existing Microsoft 365 workflows means that these enhancements complement rather than complicate established business processes.
Organizations using these solutions report significant improvements in document lifecycle management, collaborative efficiency, and governance compliance. The combination of enhanced bulk operations and sophisticated notification systems creates a more responsive and controlled file sharing environment that scales effectively with organizational growth and complexity.
These specialized tools transform SharePoint from a capable but sometimes cumbersome document platform into a highly efficient, enterprise-grade file management system that supports both day-to-day operations and complex, large-scale document initiatives.
Conclusion on How to Use SharePoint to Share Files
SharePoint stands as a powerful tool for secure and flexible file sharing both within organizations and with external partners. Its robust architecture supports everything from simple document sharing between colleagues to complex, multi-stakeholder projects involving external consultants, vendors, and clients. The platform’s ability to adapt to diverse collaboration scenarios while maintaining consistent security standards makes it an invaluable asset for organizations of all sizes.
The platform excels at supporting collaboration through real-time co-authoring, version control, and integrated communication tools that keep teams aligned and productive. Whether team members are working from the office, home, or anywhere in between, SharePoint ensures that everyone has access to the most current versions of documents while maintaining comprehensive audit trails of all activities.
SharePoint’s sophisticated access control mechanisms help organizations maintain security without sacrificing usability. The granular permission system allows administrators to implement precise access policies that align with organizational hierarchies, project requirements, and regulatory compliance needs. From simple view-only access for external reviewers to full collaborative rights for core team members, SharePoint accommodates the full spectrum of access requirements that modern projects demand.
The platform significantly simplifies day-to-day document interactions through intuitive interfaces, seamless integration with familiar Microsoft 365 applications, and automated workflows that reduce manual administrative tasks. Users can focus on their core work rather than struggling with complex file management procedures, leading to improved productivity and user satisfaction.
While SharePoint’s built-in features provide a solid foundation for file sharing and collaboration, combining these capabilities with additional solutions like Virto File Operations and Alerts & Reminders creates a truly enterprise-grade document management environment. These specialized tools increase transparency by providing enhanced monitoring and reporting capabilities, automate routine tasks that would otherwise consume valuable staff time, and minimize risks through proactive notifications and improved governance controls.
VirtoSoftware’s solutions transform SharePoint from a capable platform into a highly efficient, automated system that anticipates organizational needs and responds accordingly. The combination of enhanced bulk operations, intelligent notifications, and streamlined workflows creates an environment where document collaboration becomes effortless and secure.
To make file sharing in SharePoint truly efficient and secure, we encourage you to explore the capabilities of VirtoSoftware’s file management and notification solutions for SharePoint. These tools have been specifically designed to address the real-world challenges that organizations face when scaling their document collaboration initiatives.
Experience the difference firsthand by scheduling a demo with our team to see how these solutions can transform your SharePoint environment. You can also install free trial versions of these apps directly from our website to evaluate their impact on your specific workflows and requirements.
Our experts are ready to work with you to understand your organization’s unique challenges and demonstrate how our solutions can address your specific file sharing and collaboration needs.
To deepen your understanding of SharePoint file sharing capabilities and best practices, we recommend exploring these valuable resources:
Official Microsoft documentation:
- Share SharePoint files or folders
- Share a document using SharePoint or OneDrive
- How to share SharePoint files without an email being sent
- Is it possible to share files externally in SharePoint?
VirtoSoftware blog articles for advanced techniques:
- SharePoint Multiple Files Edit & Share Guide
- SharePoint Multiple Files Delete & Copy Guide
- SharePoint Multiple Files Upload & Download Guide
- How to Delete Multiple Files from SharePoint
These resources provide practical guidance, advanced techniques, and real-world examples that will help you master SharePoint file sharing and make the most of your collaborative workflows.