Ensuring Microsoft Teams Security: Key Insights & Privacy Policies
As the digital hub connecting modern workflows, Microsoft Teams has seen meteoric growth—skyrocketing to 300 million users in 2023 (1). Today, over one million organizations depend on Microsoft Teams as their communication command center, and this lightning growth proves Teams’ indispensable role in the corporate realm.
However, as Teams underpins sensitive business communications and data sharing, security and privacy risks remain worrisome realities. Cyber threats are becoming more frequent and sophisticated, with a cyberattack occurring every 39 seconds on average (2). The potential damage is massive, with data breaches costing companies $4.35 million on average (3).
For security leaders, understanding the latest data protection trends is crucial to managing risk and implementing robust measures. This guide will provide an overview of Microsoft Teams security, compare it to alternatives, examine key vulnerabilities, and offer actionable guidance to lock down your Teams environment.
With VirtoSoftware’s expertise in Microsoft product integrations and a deep understanding of the Microsoft ecosystem, we offer insights that ensure your usage of Microsoft Teams is as secure as it is productive.
Environment Recommendations by Microsoft
Before we get started, it’s important to review Microsoft’s environment recommendations. Even though Microsoft Teams is designed to work well across a variety of environments, there are certain recommendations from Microsoft to ensure optimal performance, experience, and security. These recommendations typically cover hardware, software, network, and peripheral devices. Here’s an overview of the key environment recommendations:
Hardware and software
- Operating system: Use the latest version of Windows or macOS for best performance. Microsoft Teams is also available on iOS and Android for mobile devices.
- Processor: A modern, multi-core processor will deliver the best performance, particularly for video calls and meetings.
- Memory: At least 4 GB of RAM is recommended, with more being preferable for multitasking.
- Hard Drive: Solid-state drives (SSDs) can improve the performance of Microsoft Teams and other applications.
Network
- Bandwidth: For video calls and meetings, a high-speed internet connection is recommended. Microsoft provides detailed bandwidth recommendations depending on the type of content being shared and the number of users.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Implementing QoS on your network can prioritize Microsoft Teams traffic to ensure voice and video quality.
- VPN: If connecting via VPN, it’s suggested to use split tunneling to optimize bandwidth for Teams traffic directly to the internet rather than routing it through the corporate network.
Peripherals
- Headset: A good quality headset with a noise-canceling microphone can significantly improve audio quality in calls and meetings.
- Webcam: For video conferencing, a high-definition external camera can provide better video quality than built-in laptop cameras.
- Speakerphone: For group settings, a full-duplex speakerphone can enhance the audio experience.
Microsoft Teams client application
- Updates: Keep the Teams client application updated to the latest version to benefit from new features, security updates, and performance improvements.
- Desktop Client vs. Web Client: The desktop client generally offers the best experience. However, if you’re using the web client, use a supported web browser like the latest version of Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, or Safari.
These recommendations can help maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of Microsoft Teams within your organization. For detailed and up-to-date specifications, always refer to the official Microsoft Teams documentation or consult with your IT department.
Overview of Microsoft Teams Security
👉 Disclaimer: This article condenses key Microsoft Teams security details as of March TEST_2025. While we strive to centralize the most relevant information from available sources, details are subject to change. For the definitive authority on current MS Teams security, please reference the official Microsoft documentation which may have newer updates. This article serves as a helpful guide, but does not supersede Microsoft’s own evolving documentation.
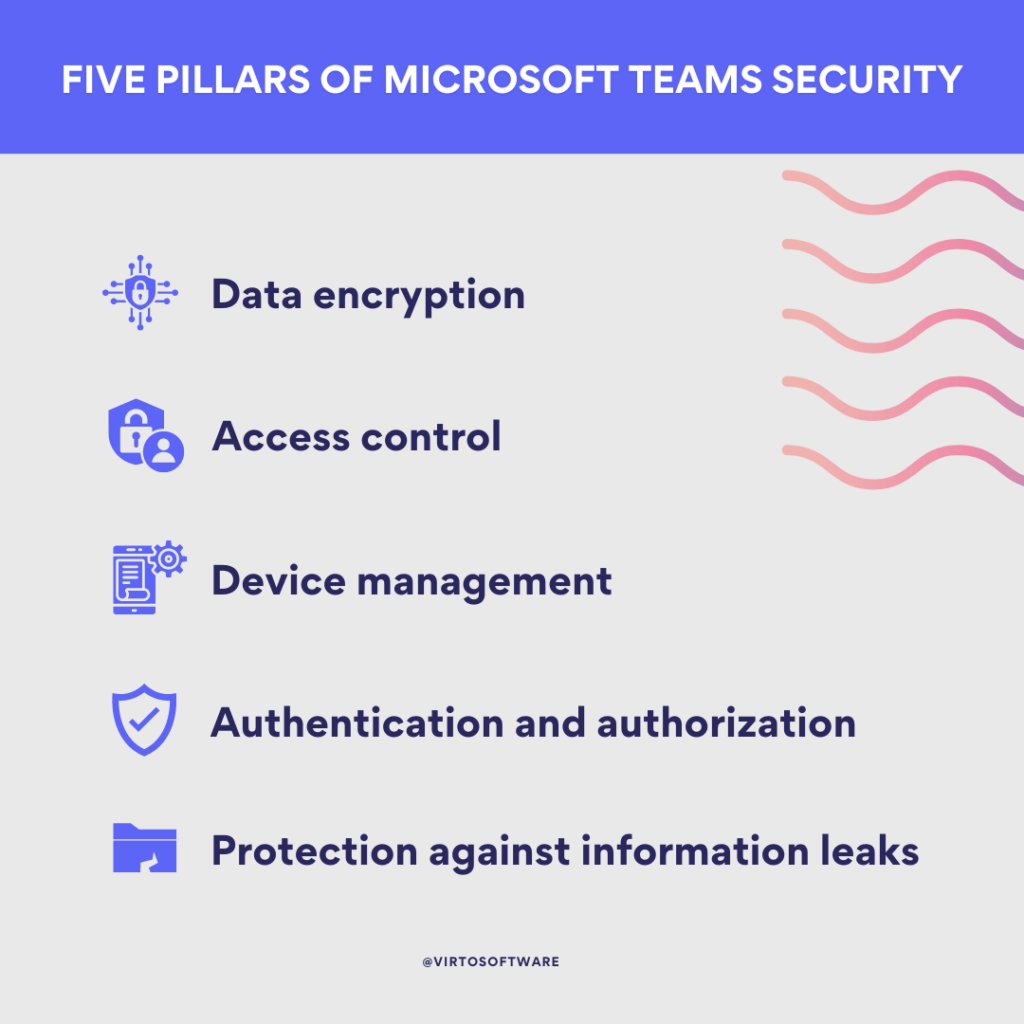
Microsoft Teams takes a multi-layered approach to securing organizational data across communication and collaboration activities. Key aspects of Teams security include:
- Data encryption: At the heart of Microsoft Teams’ security is data encryption. All information is encrypted in transit, ensuring that any data moving between your devices and Microsoft’s servers (or within Microsoft’s servers themselves) is protected from unauthorized access. Microsoft employs a variety of encryption methods, including industry-standard protocols such as Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS), to safeguard data as it travels. Additionally, for data at rest, Microsoft Teams uses service encryption with Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and supports customer key management.
- Access control: Access control within Microsoft Teams is granular, allowing administrators to finely tune user access to different features, data, chats, channels, and files. Administrators can set up Teams with specific privileges and enforce policies that control who can access certain information, ensuring sensitive data remains within the intended audience. This includes settings to restrict guest access, manage external sharing, and even archive teams that are no longer active.
- Authentication and authorization: Microsoft Teams secures user authentication by supporting several methods that ensure only authorized users can access the platform. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to their Teams account, is a critical component in protecting against unauthorized access. Teams also integrates with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) to manage user identities and enforce conditional access policies based on user, location, device state, and risk level.
- Protection against information leaks: To prevent the unintended dissemination of confidential information, Microsoft Teams includes features such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP), which can identify, monitor, and protect sensitive data through deep content analysis. Administrators can configure policies that control data transmission and automatically alert them of any potential security violations. Additionally, Information Barriers in Teams can prevent conflicts of interest by limiting which users can communicate with each other within the organization.
- Device management: As for device management, Microsoft Teams enables administrators to implement security policies that can remotely wipe company data from devices or lock a device in case of a security breach or if the device is lost or stolen. This is particularly important in a BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) environment where employees use personal devices to access corporate data. With Intune and Mobile Device Management (MDM) for Office 365, administrators have the tools they need to manage and secure mobile devices that access Teams.
To put it briefly, Microsoft Teams incorporates robust security measures to create a protected environment for organizational communication and collaboration. To stay on top of the latest security enhancements and best practices, be sure to frequently check the official Microsoft Teams documentation and support materials.
Is Microsoft Teams secure?
If you’re wondering, “Is Teams secure?” Then yes, Microsoft Teams is a secure application. Moreover, as mentioned, it’s designed with a multi-faceted approach to security, aiming to protect data confidentiality and integrity. Microsoft’s security infrastructure for Teams is built on a foundation of identity and access management, threat protection, information protection, and security management. Below is a brief overview of each critical security area:
Physical security measures
Microsoft employs robust physical security measures at their data centers, which host Microsoft Teams data. These measures likely include multiple layers of physical security such as biometric scanners, security guards, surveillance cameras, and controlled access to ensure that only authorized personnel can access the physical hardware. The effectiveness of these measures is high, as they are designed to prevent unauthorized physical access to the servers and infrastructure that host and process Microsoft Teams data.
Microsoft Teams Encryption strategy: Is Teams encrypted?
Microsoft Teams uses advanced encryption to safeguard data:
- Data in transit: Teams encrypts all data in transit between devices and Microsoft data centers using industry-standard protocols such as TLS and HTTPS.
- Data at rest: Data stored within Teams is encrypted using technologies like BitLocker and Azure Storage Service Encryption.
- End-to-end encryption: For sensitive conversations, Microsoft Teams offers an option for end-to-end encryption for 1:1 calls ensuring that the data is encrypted throughout its journey and can only be decrypted by the participants in the call.
The multi-layer encryption approach indicates a strong commitment to data protection, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorized data access or interception.
Message integrity control
Microsoft Teams uses message integrity controls to maintain the validity and security of communications. This likely involves mechanisms such as hashing and digital signatures. By employing these controls, Teams can detect any tampering with messages, ensuring that the data has not been altered during transit. The integrity of the messages is thus preserved, contributing to the overall security of the platform.
👉 Disclaimer: While the above points outline the general security measures Microsoft Teams claims to implement, for a thorough and detailed understanding of their effectiveness and implementation, it is essential to review the official Microsoft documentation, such as:
- For general security information about Microsoft Teams: https://www.microsoft.com/en/microsoft-teams/security
- For an in-depth security guide for Microsoft Teams: https://learn.microsoft.com/en/microsoftteams/teams-security-guide
- For an overview of security and compliance in Microsoft Teams: https://learn.microsoft.com/en/microsoftteams/security-compliance-overview
Overall, Microsoft Teams incorporates strong security capabilities to safeguard data confidentiality and integrity within its platform. However, the effectiveness of these measures depends on proper implementation—including ongoing configuration, updating, and compliance with best practices by end users and admins.
Can you be monitored through Microsoft Teams?
Yes, monitoring can occur within Microsoft Teams through various built-in features designed for productivity and management oversight.
👉Understanding how your activity can be monitored through Teams is crucial, as privacy within the digital space is a significant component of personal autonomy and security. It safeguards the interests of both individuals and the organization by ensuring that only authorized eyes have access to proprietary and personal information.
Tracking Methods in Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Teams provides various ways through which user activity can be tracked, each serving a purpose within the context of team management and collaboration:
- Messages and chats: Teams allows administrators to track the time spent on chats, monitor read/unread messages, and even search for keywords within messages for compliance purposes.
- Activity feed: Teams logs user activities, which can include when they view files, attend meetings, and make calls, which can be accessible to those with relevant permissions.
- Presence information: Teams displays user availability status, and activity reports can include information on when users are active, idle, or offline.
- Location tracking: If location services are enabled and permitted, Teams can track and share a user’s location, primarily for mobile users.
- Analytics: Microsoft Teams includes analytics features that provide insights into user activity, team engagement, and overall performance metrics.
- Teams integrations: With third-party app integrations, tracking capabilities can be expanded. However, these might introduce additional security risks as they could access user data and potentially bypass some of the security protocols of Teams.
👉 Security risks with third-party applications: Third-party applications may not always adhere to the same stringent privacy and security standards as Microsoft. Integrating these apps could expose user data to additional risks, including data breaches or unauthorized data sharing. It’s important to evaluate the privacy policies and security measures of these third-party services before integration.
How do I get to security and privacy on Microsoft Teams?
While Microsoft Teams has built-in features that can track user activity, there are ways to protect your privacy:
- Configure privacy settings: Take control by configuring your privacy settings in Teams. Adjust settings related to read receipts, mentions, and team discoveries to limit the visibility of your activities.
- Restrict access: Be strategic about who has access to what information within Teams. Use channel permissions and meeting options to restrict access to sensitive content and discussions.
- Use alternative tools: If necessary, consider using alternative chat and video conferencing tools for conversations that require a higher degree of privacy.
Privacy in Microsoft Teams is a shared responsibility. While Microsoft provides the tools to manage privacy, it is up to individuals and organizations to utilize these features effectively. We’ll share more detailed tips on enhancing your privacy when using Teams later in this article.
👉 Are Teams messages private? It’s important to understand that while Teams is built with privacy and security in mind, it’s designed for collaboration within an organization. As such, it is assumed that the organization’s IT administrators may have legitimate reasons to access or monitor messages for compliance, security, or management purposes. For individual users concerned about privacy, it’s best to follow best practices and organizational policies, such as not sharing sensitive personal information over Teams, being cautious with external communications, and understanding the organization’s guidelines on the use of Teams for business communication.
What is Microsoft Teams privacy policy?
Microsoft Teams is part of the Microsoft 365 family of products, and its privacy policy is covered under the overarching Microsoft Privacy Statement. The privacy policy outlines how Microsoft collects, uses, and protects your personal data when you use Microsoft Teams.
Here are some key points usually covered in Microsoft’s privacy policy relevant to Teams and other Microsoft services:
- Data collection: Microsoft collects data to operate effectively and provide you with the best experiences with their products. This can include text, images, and other types of data you provide. For Teams, this might include chat logs, shared files, and meeting recordings.
- Data usage: Microsoft uses the data collected to provide you with rich, interactive experiences. In Microsoft Teams, this includes chat functionality, meetings, calls, collaboration, and file sharing.
- Personal data: You have control over your personal data, and Microsoft provides options to access, delete, or control it.
- Data sharing: Microsoft does not share your personal data with third parties without your consent, except for limited circumstances such as executing your transactions or providing services you have requested or authorized.
- Data protection: Microsoft takes steps to protect the security of your data, including using encryption. They also enforce policies and procedures designed to protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, and destruction.
- Compliance: Microsoft complies with applicable data protection laws in the countries where they operate. This includes GDPR in Europe and other regional regulations.
- Cookies and similar technologies: Microsoft uses cookies and similar technologies to provide functionality and to recognize you across different services and devices.
- Data storage and transfer: Microsoft stores data in data centers around the world and may transfer it to other countries where they operate.
- Enterprise services: When using Microsoft Teams as part of an organization (school, work, etc.), your administrator can control and administer your Teams account and may have access to your data, including the content of your communications and files.
- Changes to the privacy policy: Microsoft may update its privacy policy from time to time, and when they do, they will revise the ‘last updated’ date at the top of the policy.
To understand the specifics of how Microsoft handles your data within Teams and other products, it’s important to read the Microsoft Privacy Statement in detail. Because privacy policies can change, you should periodically review the policy to stay informed about how Microsoft is protecting your data.
Microsoft Teams Security and Compliance
For corporate communication and collaboration platforms, security certification serves as a critical deciding factor. Large companies, in particular, require assurance that their chosen platform adheres to rigorous data security standards, guaranteeing the integrity and confidentiality of their business information.
Microsoft Teams is committed to maintaining the highest data security standards and is recognized for its compliance with several critical regulatory requirements and certifications:
- ISO 27001 Certification: Microsoft Teams has achieved ISO 27001 certification, an internationally revered standard for information security management systems (ISMS). This certification outlines comprehensive requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continuously improving an ISMS, ensuring that Microsoft Teams is well-equipped to protect its users’ data.
- HIPAA Compliance: Healthcare organizations and their partners can trust Microsoft Teams to handle sensitive health and financial information with the utmost care. Teams complies with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), which sets the standard for the privacy and security of health data.
- GDPR Adherence: For organizations operating within the European Union or dealing with EU citizens’ data, GDPR compliance is non-negotiable. Microsoft Teams adheres to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), ensuring the privacy and protection of personal data.
- FERPA Observance: Educational institutions that leverage Microsoft Teams for collaboration can be assured that the platform complies with the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). This law regulates access to educational information and upholds the privacy of students’ educational records.
- SOC 1 and 2 Assessments: Microsoft Teams has undergone assessments for System and Organization Controls (SOC) 1 and 2, which evaluate an organization’s internal risk management and security. These assessments affirm that Microsoft Teams has robust control procedures and organizational controls in place.
- CJIS Standards: For law enforcement agencies, Microsoft Teams meets the stringent requirements of the Criminal Justice Information Services (CJIS). This compliance ensures that Teams is capable of securing criminal justice and law enforcement-related information.
The above certifications provide a seal of approval for the platform’s efforts to safeguard user data, an essential consideration for companies that manage substantial volumes of sensitive information and must adhere to strict regulatory standards.
While these standards and certifications underscore Microsoft Teams’ commitment to robust security and compliance practices, it’s imperative to recognize that data security also hinges on proper platform configuration and usage by users and administrators. Ensuring that Teams is configured correctly and that users are following best practices is equally important for maintaining data security and safeguarding against potential breaches.
👉 Do I have to have Microsoft security team in my organization? Having a dedicated Microsoft security team within your organization is not a mandatory requirement, but it can be highly beneficial, especially for medium to large organizations or those handling sensitive data. If your organization operates in a regulated industry (such as finance, healthcare, or government), you may be subject to strict security requirements that necessitate specialized security personnel to ensure compliance with laws and regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or SOC 2.
Comparing the Security of Microsoft Teams and Alternative Platforms
In this section, we’ll compare the security features of Microsoft Teams against alternative platforms such as Slack, Zoom, Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), and email. This comparison focuses on several key security aspects that are critical to protecting data and ensuring privacy.
Having overviewed the core security capabilities of Microsoft Teams, we will now examine the security features of alternative platforms. This will provide context before comparing Teams’ protections side-by-side with other options in a convenient table.
Slack is a popular team collaboration tool that has been increasing its focus on security:
- Data Encryption: Slack encrypts data in transit and at rest, but historically, there have been different levels of control over encryption keys.
- MFA: Supports two-factor authentication for additional security.
- Access Control: Offers detailed user permissions and can be integrated with enterprise mobility management solutions.
- Information Protection: Slack Enterprise Grid customers can access DLP solutions through third-party integrations.
- Device Management: Provides mobile device management capabilities to secure data on personal and company-owned devices.
- Integration with Other Services: Supports integrations with a large number of third-party apps, which can be both a strength and a potential security risk.
- Audit of User Actions: Slack provides some auditing capabilities, particularly in its enterprise offering.
- HIPAA Compliance: Slack’s Enterprise Grid plan can be configured for HIPAA compliance with customer-managed encryption keys.
- Data Storage Location: Data is stored in Slack’s global data centers.
Zoom is predominantly a video conferencing tool that has focused more on security following some initial challenges:
- Data Encryption: Offers AES 256-bit GCM encryption for data in transit.
- MFA: Provides multi-factor authentication to enhance account security.
- Access Control: Features like password protection for meetings, waiting rooms, and the ability to lock meetings help control access.
- Information Protection: Has made strides to prevent Zoombombing and unauthorized access to meetings.
- Device Management: Supports basic device management through account settings and meeting controls.
- Integration with Other Services: Allows for integration with a variety of productivity tools and security solutions.
- Audit of User Actions: Provides some level of user activity reports for account owners and admins.
- Microsoft Teams HIPAA compliance: Offers a HIPAA-compliant plan that healthcare providers can use when signed to a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
- Data Storage Location: Zoom uses multiple data center locations.
Google Workspace (formerly G Suite) provides a suite of productivity tools with built-in security features:
- Data Encryption: Encrypts data in transit using TLS and at rest with AES encryption.
- MFA: Supports two-step verification and security keys.
- Access Control: Provides comprehensive access controls with Google’s advanced admin console.
- Information Protection: Offers DLP, endpoint management, and vault for eDiscovery and archiving.
- Device Management: Advanced device management capabilities, including remote wipe and device compliance checking.
- Integration with Other Services: Integrates with a range of apps in the Google ecosystem and third-party services.
- Audit of User Actions: Extensive auditing and reporting capabilities are available through the admin console.
- HIPAA Compliance: Certain services within Google Workspace can support HIPAA compliance when configured correctly.
- Data Storage Location: Utilizes Google’s global network of secure data centers.
Email security varies widely based on the provider and configuration:
- Data Encryption: Most modern email services use TLS to encrypt data in transit, but encryption at rest depends on the provider and user configuration.
- MFA: Many email providers offer some form of MFA, but it’s not always enabled by default.
- Access Control: Varies by provider, with some offering advanced access management features.
- Information Protection: Some providers offer DLP features, but these often need to be integrated or added on.
- Device Management: Device management for email typically requires additional software or services.
| Security Feature | Microsoft Teams | Slack | Zoom | Google Workspace | Email (Varies by Provider) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | In transit & at rest | In transit & at rest | In transit & at rest | In transit & at rest | Transport Layer Security (TLS), depends on setup |
| Multi-factor Authentication | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Varies |
| Access Control | Extensive | Extensive | Good | Extensive | Varies |
| Protection against Information Leaks | Advanced features | Good | Good | Advanced features | Varies |
| Device Management | Intune integration | Mobile device support | Mobile device support | Advanced device management | Varies |
| Integration with Other Services | Extensive | Extensive | Good | Extensive | Varies |
| Audit of User Actions | Comprehensive | Good | Good | Comprehensive | Varies |
| HIPAA Compliance | Extensive tools | With Enterprise Grid | With HIPAA-compliant plan | Certain services | Requires appropriate security measures |
| Data Storage Location | Global data centers | Global data centers | Global data centers | Global data centers | Varies |
👉 Is Microsoft Teams HIPAA compliant? Microsoft Teams can be configured and used in a manner that supports HIPAA compliance. Microsoft offers a version of Teams that is part of its Office 365 and Microsoft 365 services, which are covered by its Business Associate Agreement (BAA). A BAA is a necessary component to ensure HIPAA compliance for covered entities when using third-party services.
Disclaimers:
- The information provided here is a general overview of the security features of each of the listed platforms and is subject to change. Specific configurations, organization settings, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements can significantly affect the actual security posture of each platform.
- Users are advised to independently check the security and privacy policies of each platform for more detailed and up-to-date information on security and data protection measures.
- Data storage location information is general and may vary depending on an organization’s specific configuration and settings, as well as the laws and compliance regulations to which it is subject.
- Regarding HIPAA compliance, Slack and Zoom offer versions that can support HIPAA compliance with the right configuration and agreements in place. Google for Business provides HIPAA compliance for certain services, and Microsoft Teams offers extensive tools for HIPAA compliance. Email can be HIPAA compliant but requires proper security measures and settings.
👉 Is Teams safer than email? Overall, Microsoft Teams tends to offer stronger security protections compared to email. With enterprise-grade capabilities like robust encryption, multifactor authentication, granular access controls, and detailed auditing, Teams is purpose-built with security in mind. The structured communication and file sharing in Teams also reduce the risk of human error that exists in email services. However, the actual security posture depends on how each solution is configured and used within a specific organization.
End-to-End Encryption for Microsoft Teams Calls
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a method of secure communication that prevents third-parties from accessing data while it’s transferred from one end system to another. In E2EE, the data is encrypted on the sender’s system or device and only the recipient is able to decrypt it. Nobody in between, be it internet service providers, hackers, or even the platform provider itself (in this case, Microsoft), can read it or see its true content.
With growing concerns over privacy, E2EE is increasingly important for users who demand the utmost confidentiality in their online communications. Microsoft Teams has responded to this need by providing E2EE for one-on-one calls, ensuring that sensitive conversations remain private and secure.
How to enable end-to-end encryption in Teams
Implementing E2EE in Microsoft Teams requires a few steps, and both parties involved in the call need to enable the feature to ensure the encryption is effective.
Here’s an overview of how to enable it:
- Go to Teams, click on More options (ellipsis) next to your profile picture.
- Select Settings.
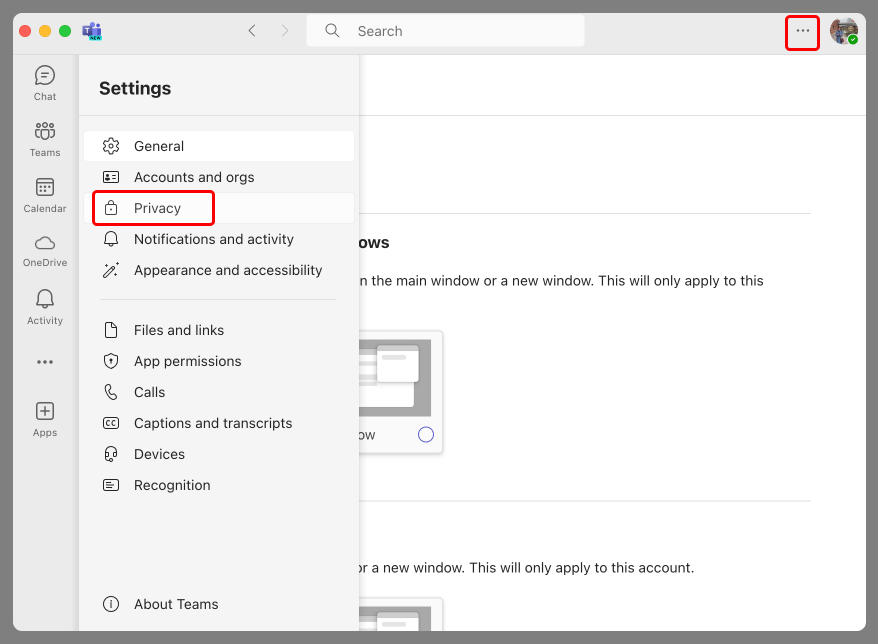
Pic. 1. Click on “—” and choose “Privacy” in “Settings” to your left.
- Choose Privacy on the left sidebar.
- Toggle the switch next to End-to-end encrypted calls to turn it on.
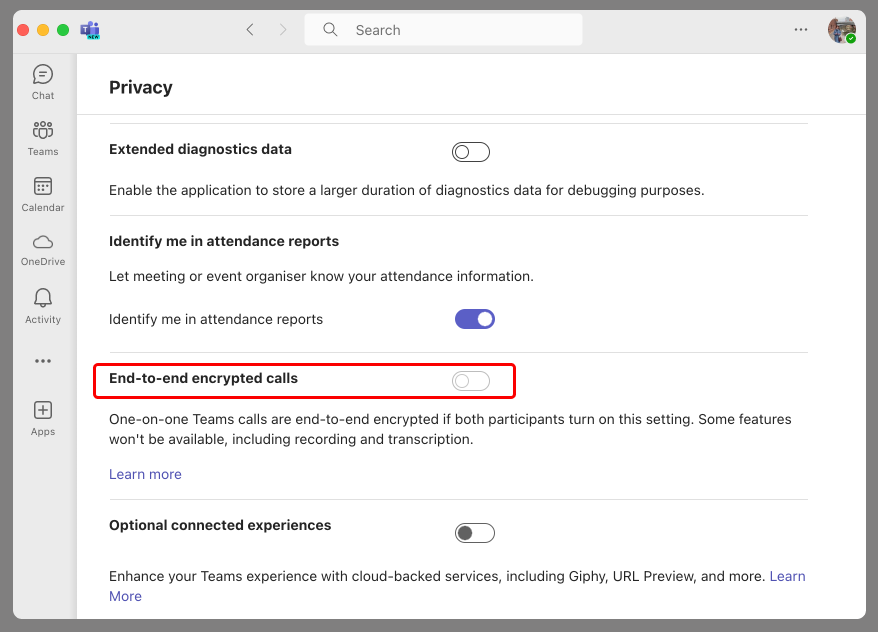
Pic. 2. Toggle the “Encryption” switch on.
After enabling E2EE, you can verify it’s working by checking for a shield with a lock icon in the top left corner of the call window. If the shield has no lock, E2EE is not enabled for one of the parties.
End-to-end encryption in Teams: points to consider
When using E2EE, there are several limitations to consider:
- Features such as recording, live captions, transcription, call transfer, call merge, call park, consult then transfer, call companion, adding participants, and transfer to another device are not available during an E2EE call.
- Compliance recording is not compatible with E2EE.
- E2EE is currently available for one-on-one calls; however, if you need E2EE for group calls, this feature is included in the Microsoft Teams Premium version.
For further details and official documentation on using E2EE in Microsoft Teams, you can visit the Microsoft Support page at Use end-to-end encryption for Microsoft Teams calls.
How to maintain security during Microsoft Team remote control
In Microsoft Teams, the remote control feature is part of the screen sharing capability during Teams meetings or calls. It allows a user to share control of their desktop or application with other meeting participants. This means that once a participant is given control, they can interact with the shared content as if it were their own, which includes navigating files, using software, and typing.
Maintaining security during a Microsoft Teams remote control session is crucial to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to your system. Here are some best practices and considerations to maintain security when using the remote control feature in Microsoft Teams:
- Trust and permission: Only grant control to trusted individuals. Ensure that the person you’re giving control to is the intended recipient and has a legitimate need to control your computer.
- Monitor the session: While another participant is controlling your computer, closely monitor all actions taken. Be ready to revoke control if you notice any suspicious activity.
- Use temporary files: If the task at hand involves viewing or editing documents, consider using temporary files or duplicates that don’t contain sensitive or confidential information.
- Limit access: Before starting a remote control session, close any applications, documents, or web pages that contain sensitive information that the controller does not need to access.
- Revoke control immediately after use: As soon as the need for remote control ends, revoke the permissions. Do not leave the control access open longer than necessary.
- Educate participants: Ensure that all participants are aware of the company’s policies and best practices for using the remote control feature, including the importance of maintaining confidentiality and data protection.
- Organizational policies and restrictions: Your organization may have specific policies governing the use of remote control in Microsoft Teams. These could include restrictions on who can use the feature or in what circumstances it can be used. Adhere to these policies strictly.
- Permissions: Regularly review and update permissions within Microsoft Teams to ensure that only authorized users have the ability to start remote control sessions.
- Security software: Maintain up-to-date antivirus and anti-malware software on all systems to protect against threats that could potentially exploit the remote control feature.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Use MFA for your Microsoft Teams account to add an extra layer of security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Disconnect if compromised: If you suspect that your meeting has been compromised in any way, immediately disconnect from the session, revoke all remote control permissions, and inform your IT security team.
- Follow up: If remote control was used for troubleshooting by IT support, ensure that there is a follow-up process to confirm that no unauthorized changes were made and that the system remains secure.
- Logging and auditing: Enable logging and auditing for remote control sessions if supported by your organization’s IT infrastructure. This will help trace any issues or breaches back to a specific session.
By following these guidelines, you can help ensure that remote control sessions in Microsoft Teams are conducted securely, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access to sensitive information.
👉 Is Microsoft Teams secure for confidential information? Microsoft Teams is designed with security features intended to handle confidential information, making it suitable for use in environments where data sensitivity is a concern. However, the security of confidential information is not solely dependent on the platform itself; it also relies on how the platform is used and managed.
Ensuring secure and private conferences in Microsoft Teams
To ensure Microsoft secure conferences, you can follow these best practices:
Before the meeting
Set strong meeting options:
- Require a meeting password.
- Use the “lobby” feature to control who gets direct access to the meeting.
- Limit who can present to prevent unauthorized sharing.
Control meeting links:
- Don’t share meeting links on public forums.
- Send invites directly to participant’s emails.
Educate participants: Inform participants about best practices for secure conferencing.
Meeting permissions: Assign roles in your Teams meetings (organizer, presenter, attendee) to control who has permissions to do what during the meeting.
During the meeting
Admit from lobby: Manually admit participants from the lobby, especially if they are external participants.
Monitor attendees: Keep an eye on the attendee list to ensure no unauthorized participants have joined.
Lock the meeting: Once all expected participants have joined, lock the meeting to prevent new participants.
Restrict features as necessary:
- Disable the chat or file sharing if not needed.
- Restrict the ability to record the meeting.
Use End-to-End encryption: For sensitive meetings, consider using end-to-end encryption if available for 1:1 calls.
After the meeting
Review attendance: Check the meeting attendance list for any anomalies.
Securely store meeting recordings: If the meeting was recorded, ensure that the recording is stored securely and only accessible to authorized individuals.
Follow up: If sensitive information was discussed, remind participants to maintain confidentiality.
Microsoft Teams Security Issues & Vulnerabilities
Microsoft Teams is a widely used communication platform that, like any complex software system, can be susceptible to security vulnerabilities and issues. Below are some examples of potential security concerns that users and administrators should be aware of:
- Unauthenticated session access: In some instances, security flaws might be discovered that allow unauthorized users to gain access to active Microsoft Teams sessions. This type of vulnerability could lead to the exposure of confidential discussions, sensitive documents, and other private information.
- Phishing attacks: Phishing is a common tactic used by cybercriminals across various platforms, and Microsoft Teams is no exception. Attackers may send fraudulent messages or meeting invitations in an attempt to deceive users into providing their login credentials or other sensitive information.
- Application and integration vulnerabilities: Microsoft Teams allows for a wide range of integrations and third-party applications to enhance functionality. However, these external additions can sometimes have security weaknesses that, if exploited, could compromise the integrity of the Teams environment or lead to data breaches.
- Unupdated software: Software that isn’t regularly updated can contain vulnerabilities that have been patched in later versions. Both client-side and server-side components of Microsoft Teams need to be kept up to date to minimize the risk of security issues.
- Network security threats: Teams can also be subject to network-related security threats such as:
- Password brute force attacks: Attackers may attempt to access accounts by guessing passwords.
- Cross-network attacks: Exploiting vulnerabilities across networks can compromise security.
- Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: Overloading servers with traffic can disrupt service availability.
- Information leaks: Configuration mistakes or user errors can lead to the unintended sharing of sensitive information. Teams administrators should ensure that permissions and privacy settings are correctly set to prevent data leaks.
- In-memory data security issues: Vulnerabilities may exist within the client or server software that can be exploited to access data stored in memory. Such issues can potentially allow an attacker to extract sensitive information during data processing.
Mitigation of potential issues and security measures
To address these potential vulnerabilities and security issues, both users and administrators of Microsoft Teams should take proactive measures:
- Always keep the Microsoft Teams application up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Educate users on the risks of phishing and encourage them to verify the authenticity of messages and meeting invites.
- Audit and manage third-party integrations and applications to ensure they meet security standards.
- Implement strong password policies and consider multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect user accounts.
- Use network security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and traffic analysis to protect against network threats.
- Configure user permissions carefully and review them regularly to prevent unauthorized access to information.
- Utilize endpoint security solutions that can protect against in-memory exploitation and other advanced attack techniques.
Microsoft is continually working to improve the security of its products, including Microsoft Teams. However, it is crucial for organizations to complement these efforts by adopting robust security practices and ensuring that their Teams environments are configured and used securely.
Microsoft Teams Security Best Practices & Tips for Secure Team Collaboration
When using Microsoft Teams, it’s essential to take proactive steps to ensure maximum security. Here are some best practices to help safeguard against potential Microsoft Teams spyware threats and ensure a secure Microsoft Teams environment for your organization:
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA is critical for enhancing account security. By requiring an additional verification method aside from the password, such as a phone call, text message, or app notification, MFA ensures that even if a password is compromised, unauthorized users cannot easily gain access to Teams accounts.
- Set up password policies: Enforce strong password policies that include requirements for minimum password length, and the inclusion of numbers, upper and lower case letters, and special characters. Also, implement policies for regular password changes to reduce the risk of compromised credentials.
- Access control: Restrict access to sensitive Teams channels and data to only those users who need it to perform their job functions. Employ security groups and distribution lists to manage permissions effectively and efficiently.
- Update your software: Keep your Microsoft Teams application and all associated systems regularly updated to benefit from the latest security patches and feature updates. This includes not only the Teams software itself but also the operating systems and other software on the devices used to access Teams.
- Control integrations: Carefully control the use of third-party integrations and apps within Teams. Only allow verified and trusted applications, and regularly review permissions you’ve granted to ensure they are still necessary and secure.
- User training: Provide ongoing security awareness training to all users. Teach them to recognize phishing attacks, practice secure password management, and understand how to report suspicious activities.
- Data encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Teams already encrypts data by default, but additional encryption solutions for particularly sensitive information can be considered.
- Security monitoring and auditing: Use tools for security monitoring and auditing that track user activities within Teams, identify irregular patterns that could indicate a breach, and provide the means to investigate and respond to potential security threats.
- Ensure compliance with security standards: Ensure that your organization’s use of Microsoft Teams complies with all relevant data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, etc. This includes data handling, storage, and processing policies.
- Regularly update security policies: As threats evolve and your organization changes, regularly review and update your security policies. This should include revisiting user permissions, evaluating the effectiveness of your security training, and ensuring that your security practices align with current best practices and standards.
Here’s an overview of those measures in tabular format:
| Recommendation | Description | Who is it suitable for? |
|---|---|---|
| Use strong passwords | Set strong passwords for your Microsoft 365 and Teams accounts. Use a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. | All users |
| Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) | MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to go through a second step of verification when you log in. | All users |
| Update your software | Regularly update Teams and other Microsoft 365 apps to the latest versions to ensure security. | All users |
| Use the principle of least privilege | Grant users access only to the resources they need to perform their job functions. | IT specialists |
| Train users | Provide Teams security training to users so they are aware of how to protect their accounts and recognize security threats. | All users |
| Don’t share your passwords | Never share your Teams or Microsoft 365 passwords with others. | All users |
| Be cautious of phishing attacks | Avoid clicking on links or opening attachments from unknown or untrusted sources. | All users |
| Use firewall and antivirus software | Use firewall and antivirus software to protect your devices from malware and unauthorized access. | All users |
| Be careful with information sharing | Refrain from sharing sensitive information in Teams unless necessary and ensure proper permissions are set. | All users |
| Set up Teams security policies | Implement Teams security policies to manage access and data governance within teams, channels, and files. | IT specialists |
| Utilize Azure Active Directory (AD) | Employ Azure AD to enhance access management and security for Teams and other Microsoft 365 applications. | IT specialists |
| Implement monitoring and auditing | Monitor user activity and audit logs in Teams to detect and act on suspicious behavior. | IT specialists |
| Regular security assessments | Periodically review and assess the security of your Teams environment to maintain compliance and address new threats. | IT specialists |
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can significantly enhance the security of their Microsoft Teams environment, protect sensitive data, and create a more resilient communication platform. However, it is important to remember that security is an ongoing process and its effectiveness depends on constant attention and threat management.
How Secure Are Microsoft Teams Integrations
Microsoft Teams offers an expansive ecosystem with over 1000 third-party applications that can be integrated to enhance functionality, streamline workflows, and enrich the overall user experience. However, the integration of these applications also introduces considerations around data security and privacy.
👉 Is Microsoftstore legit? Yes, the Microsoft Store is 100% legitimate. As Microsoft’s official retail outlet, it is a trustworthy source for software, hardware, and other official Microsoft products. When shopping on the Microsoft Store, always ensure you are using the valid website at https://www.microsoft.com/store/ or the pre-installed Microsoft Store app on Windows devices. For add-ons and apps specifically, use Microsoft AppSource at https://appsource.microsoft.com/en-us/. This is Microsoft’s official application store, with thousands of verified apps and integrations across many categories. Both the Microsoft Store and AppSource are safe, authorized options for Microsoft products. If you’re looking for a Microsoft Teams store, then Microsoft Teams has a feature called “Apps,” where you can add and integrate third-party services, bots, and other tools to enhance your Teams experience. In Microsoft Teams, click on the “Apps” icon on the left-hand side or via the “More added apps” ellipsis menu. This opens a window where you can browse, search, and add apps to your Teams environment.
Understanding the impact on data
Integrating third-party applications into Microsoft Teams can significantly enhance your team’s productivity and collaboration. However, it’s essential to recognize the extent to which these applications can interact with your Teams data:
- Messages: When a third-party app has access to messages, it means that all forms of communication within a Teams chat, such as text discussions, shared images, and attached files, can be accessed by the app. This could potentially include sensitive or confidential information exchanged within your organization.
- Calendars: Calendar integration allows apps to read and potentially alter calendar entries. This means that third-party applications might have the ability to manage events, appointments, and overall schedules, which could raise concerns over the unauthorized alteration or visibility of confidential scheduling details.
- Contacts: With access to contacts, an application can use data such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and other contact-related information. This could pose a risk if the app collects or uses this information without proper consent or for purposes beyond the intended scope.
- Profile: Access to your Teams profile means that an app could gather personal information including your name, photo, job title, and other profile details. This could lead to privacy concerns if such data is used inappropriately.
The operations of third-party apps may involve various forms of data transfer:
- Service providers: These are entities that support the delivery of services provided by the app. While necessary for functionality, this sharing of data could lead to potential exposure if these providers do not maintain equivalent security standards.
- Legal requirements: In some cases, apps may be legally compelled to disclose user information. This could mean that your data is shared with law enforcement or other government bodies, raising issues of privacy and data sovereignty.
- Merger or acquisition: If the app provider undergoes a corporate change like a merger or acquisition, your data might be transferred to a different organization. This could lead to changes in how your data is managed and safeguarded.
The storage location of your data is a critical factor:
- Different servers: Data may be stored on servers that are not controlled by Microsoft, and thus might not be subject to the same security protocols as Microsoft Azure. This could potentially increase the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access.
- International borders: Data storage could also cross international borders, subjecting the data to different privacy laws and regulations, which might be less stringent than those in your own country.
The implications of these data handling practices can be significant:
- Unpredictability: Uncertainty regarding data storage locations can make it difficult to assess the legal and regulatory implications of data handling by third-party apps.
- Security risks: Data stored outside the secure Microsoft Azure platform might be less secure due to inadequate protection mechanisms or the service provider’s lax security policies.
- Non-compliance: Entities that are subject to strict regulatory requirements, such as those in healthcare or finance, might inadvertently become non-compliant by using apps that transfer or store data in ways that don’t align with industry standards like HIPAA.
- Control ambiguity: Once your data is transferred to third-party servers, it may be unclear who has access to it and how it’s being protected. There could be a loss of control over how data is managed, who is responsible for protecting it, and how to ensure its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Given these risks, it’s vital for organizations to conduct thorough due diligence on any third-party application before integration into Microsoft Teams to ensure it aligns with their security and compliance standards.
Recommendations for Secure Integrations
- Careful evaluation: Investigate the privacy policy and security standards of third-party applications before integration.
- Limiting access: Restrict app permissions to only essential data.
- Activity monitoring: Employ Teams features to supervise app activities and access.
Trusting Microsoft-certified products
The best thing you can do when it comes to security and add-ons is to integrate apps that have been Microsoft-certified, such as those from VirtoSoftware, because there are several assurances that come with that certification related to the security and handling of your data:
Data encryption
- AES-256 encryption: VirtoSoftware employs Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with a 256-bit key length encryption, which is a symmetric key algorithm widely used across the globe and considered very secure. This means that any data you input into VirtoSoftware applications is encrypted in such a way that it would be infeasible for unauthorized parties to decrypt it without the correct key.
Data access
- Stringent access protocols: Access to data within VirtoSoftware’s products is governed by strict access controls ensuring that only authorized users can access sensitive information. This reduces the risk of data leaks or unauthorized data manipulation.
- No data sharing: VirtoSoftware’s policy to not share data with third parties ensures that your information stays within the confines of the app and its intended use cases, thereby minimizing the risk of exposure to external entities.
Server security
- Microsoft Azure servers: By utilizing Microsoft Azure servers, VirtoSoftware benefits from the robust security measures that Microsoft has in place. Azure is known for its high standards of data protection, which includes physical security, network security, and compliance with various global and regional regulations.
Standards compliance
- ISO/IEC 27001:2013: This is an international standard that outlines the best practices for an information security management system (ISMS). Compliance with this standard means that VirtoSoftware maintains a systematic and ongoing approach to managing sensitive company and customer information so that it remains secure.
- Multiple security standards: Adhering to multiple security standards means that VirtoSoftware’s products are built and maintained in a way that meets internationally recognized security requirements, which typically includes regular security audits, risk assessments, and mitigation processes.
Microsoft partnership
- Certified partner: As a certified partner, VirtoSoftware has demonstrated compatibility with Microsoft’s products and aligns with their security policies. This partnership usually involves a rigorous assessment process by Microsoft to ensure that the partner’s solutions meet high standards of performance and reliability.
- Regular audits: Undergoing regular audits as part of the Microsoft partnership program means that VirtoSoftware’s products are continually evaluated to ensure they maintain the necessary standards of security and data protection.
Customer trust
- High security valuation: With a significant percentage of their clientele prioritizing security, VirtoSoftware’s commitment to data protection is not only a part of our operational policy but also a key component of our value proposition to customers.
Readers interested in learning more about VirtoSoftware’s offerings and security practices can find in-depth information at the links below. These resources provide a detailed overview of VirtoSoftware’s solutions and the policies in place to protect customer data.
Product links:
- Virto Kanban Board App for Microsoft Teams
- Virto Calendar Overlay App for Microsoft Teams
- Virto Notifications & Reminders App for Microsoft Teams
Security policy links:
Conclusion
As organizations worldwide increasingly rely on Microsoft Teams for communication and collaboration, understanding the intricacies of its security features and potential vulnerabilities has never been more critical. Microsoft Teams provides a robust level of security that is designed to meet the needs of enterprises across industries. However, as with any sophisticated platform, it is imperative to maintain a proactive stance on data security and compliance.
Our examination confirms that while Microsoft Teams is engineered with a strong security framework, it is essential for individual organizations to evaluate their compliance with data security standards and to recognize potential vulnerabilities that could be unique to their operations. Teams is built on Microsoft’s hyper-scale enterprise-grade cloud, offering advanced security and compliance capabilities that are critical for protecting sensitive information.
It is important to note that user activity within Microsoft Teams may be subject to monitoring, which aligns with organizational security policies and helps in safeguarding against unauthorized access and potential internal threats. Such monitoring is a double-edged sword; while it strengthens security, it also requires careful governance to ensure the privacy rights of users are respected.
Adherence to data security standards within Microsoft Teams cannot be overstated. These standards are the bulwark against data breaches and unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and secure. They provide a framework for legal compliance, protecting organizations from the reputational damage and financial penalties that can arise from data mishandling.
Maintaining rigorous security and data protection measures is the cornerstone of trust and reliability in any digital tool, and Microsoft Teams is no exception. Organizations must employ best practices such as regular security training for employees, utilizing multi-factor authentication, and conducting periodic audits to ensure that the privacy and security of workflows remain uncompromised.
In this landscape of digital threats and stringent compliance requirements, VirtoSoftware emerges as a trusted partner and Microsoft Teams experts, providing products that seamlessly integrate within the Microsoft ecosystem while fortifying data security. With features like AES-256 encryption, adherence to stringent access protocols, server security through Microsoft Azure, and compliance with multiple security standards, VirtoSoftware stands as a beacon of reliability. Organizations can confidently deploy VirtoSoftware’s offerings, such as the Kanban Board App, Calendar App, and Notifications & Reminders App, knowing that these solutions are designed with data protection at their core.
We invite readers to explore VirtoSoftware’s products and contact us for a consultation if anything looks beneficial for enhancing business workflows. VirtoSoftware can optimize the Microsoft Teams experience while maintaining stringent security standards. Our goal is to collaborate with customers to strengthen their Teams implementation through our solutions. We encourage interested parties to browse our offerings and start a discussion about how we can provide value.
References:
(1) Stats from Statista.
(2) Source: University of North Georgia.
(3) Source: iLink Digital.





