SharePoint Modern vs. Classic: Key Differences and Reasons to Migrate
SharePoint has evolved from Classic to Modern, transforming collaboration and content management. Learn the differences, migration challenges, and tools to enhance both.
Organizations today face a choice between two distinct SharePoint experiences: Classic and Modern. SharePoint Classic, the traditional interface that has served businesses for many years, offers a familiar and highly customizable environment. In contrast, SharePoint Modern represents Microsoft’s contemporary vision, featuring a responsive, mobile-friendly design that aligns with current web standards and user expectations.
As organizations evaluate their SharePoint strategy, understanding the distinctions between these two experiences becomes crucial for making informed decisions about their digital workplace. This article delves into the key differences between SharePoint Classic and Modern, exploring their respective advantages and limitations. We’ll examine why many organizations are choosing to migrate to the Modern experience and provide insights into the migration process itself.
Additionally, we’ll explore how solutions like VirtoSoftware SharePoint On-Premise Web Parts and VirtoSoftware Microsoft 365 & SharePoint Online Apps can enhance both experiences, offering additional functionality and improved user experience.
Understanding Classic and Modern SharePoint
SharePoint’s evolution from Classic to Modern represents a significant shift in Microsoft’s approach to enterprise collaboration and content management. This section explores the fundamental characteristics of both versions, their architectural differences, and their respective strengths.
Classic SharePoint highlights
Classic SharePoint represents the platform’s traditional implementation, built on legacy technologies that have served organizations for many years. At its core, it utilizes Master Pages and SharePoint Designer Workflows 2010, technologies that while powerful, have inherent limitations.
One of Classic SharePoint’s defining characteristics is its hierarchical subsite architecture. In this model, all sites exist within a site collection, functioning much like a traditional folder structure where new sites are created as subsites within the hierarchy. This architecture, while organized and familiar, can become complex to manage as organizations grow.
Classic SharePoint excels in scenarios requiring deep customization of portal designs. Organizations can create sophisticated intranet portals with highly customized layouts and functionality. However, this flexibility comes at a cost—implementing such customizations typically requires significant technical expertise and development resources.
Is Classic SharePoint going away?
While you can still use Classic SharePoint, Microsoft strongly advises migrating to the Modern SharePoint experience. Classic SharePoint is now considered outdated, with no active development or enhancements for its features. As a result, businesses that continue to rely on it will likely face increasing challenges as support and functionality begin to phase out.
Microsoft has announced that Classic SharePoint will be fully deprecated, with key features and support being gradually phased out by 2026. This timeline makes it essential for organizations to start planning their migration to Modern SharePoint now. Although Classic SharePoint remains functional for the time being, it is not a sustainable option for the future. Businesses that stick with Classic risk falling behind, especially as Microsoft’s latest tools, updates, and innovations are designed exclusively for Modern SharePoint.
By transitioning to Modern SharePoint, organizations can gain access to cutting-edge features, stronger security, a more intuitive user experience, and ongoing support from Microsoft. Starting the migration process early will help ensure a smooth transition and minimize the risk of disruptions as Classic SharePoint approaches the end of its lifecycle.
Modern SharePoint highlights
Modern SharePoint represents Microsoft’s vision for the future of collaboration and content management within Office 365. This reimagined platform prioritizes user experience and simplicity while incorporating contemporary web design principles and functionality.
The SharePoint Modern experience delivers significant improvements in performance and usability. Pages load faster, the interface is more intuitive, and the responsive design ensures a consistent experience across devices—from desktop computers to mobile phones. This optimization for mobile devices reflects the modern workplace’s increasingly mobile nature.
Perhaps the most significant architectural change in Modern SharePoint is its shift from hierarchical subsites to a flat, hub-based structure. Instead of creating deep hierarchies of subsites, Modern SharePoint employs independent site collections that can be connected through hub sites. This flat architecture offers greater flexibility in how content is organized and shared, while simplifying site management and improving scalability.
The hub-based approach allows organizations to create logical groupings of sites based on departments, projects, or other organizational structures without the rigid hierarchical constraints of the Classic model. Sites can be easily associated with or removed from hubs as needs change, providing the agility required in today’s business environment.
Key Differences between Modern SharePoint and Classic SharePoint
As mentioned, SharePoint has undergone an extensive evolution from its traditional Classic interface to the new streamlined Modern platform. This transition aims to enhance usability, speed, and seamless work with complementary Microsoft 365 apps. Yet key questions persist—what are the core differentiators between legacy and next-generation SharePoint? How do the critical dimensions of user experience, customization, and infrastructure contrast across the platforms? We will explore the modern transformation by comparing and contrasting foundational capabilities below.
Differences in key parameters between Classic & Modern experiences
The below comparison between Classic and Modern SharePoint experiences focuses on key parameters that directly impact usability, customization, performance, and flexibility. These parameters highlight how Modern SharePoint addresses the limitations of Classic SharePoint by providing a more user-friendly, responsive, and integrated platform. Below, we delve into specific areas such as interface design, usability, automation, and overall performance to illustrate the fundamental differences.
Interface
SharePoint Classic view reflects its legacy origins, requiring technical expertise for setup and customization. The navigation can be complex and unintuitive, and its lack of mobile responsiveness limits accessibility. Any structural changes necessitate editing Master Page code, making even minor modifications a technical endeavor.
In contrast, Modern SharePoint offers an intuitive, contemporary interface that automatically adapts to any device size. Its user-friendly design allows even newcomers to navigate and manage sites effectively, significantly reducing the learning curve.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| The interface is outdated and relies on the classic ribbon for commands, which can feel cluttered and unintuitive.Changes to the site structure require editing the Master Page code, which demands advanced technical skills.Mobile responsiveness is absent, making it difficult to use on smartphones or tablets. | Introduces a clean, intuitive command bar that simplifies navigation and actions like creating folders, moving files, and uploading documents.Designed with mobile-first principles, ensuring that pages and libraries are beautifully responsive on all devices.The interface is optimized for speed and accessibility, making it easier to use even for beginners. |
Usability
Modern SharePoint dramatically improves usability compared to its classic predecessor. Its intuitive interface empowers users, even those without web development expertise, to quickly create effective workflows and manage content. Common tasks like copying, moving, grouping, and filtering items are streamlined for efficiency, directly boosting productivity. This contrasts sharply with Classic SharePoint, where these same tasks often proved cumbersome and time-consuming. Further enhancing the user experience are robust collaboration features, including co-authoring, simplified sharing, seamless integration with Microsoft Teams, and streamlined permission management through Microsoft 365 Groups.
Automation
Modern SharePoint integrates Power Automate (formerly Microsoft Flow), a powerful tool for automating business processes and workflows. This modern alternative to SharePoint 2010 Workflows (used in Classic SharePoint) allows users to connect data sources, create sophisticated automated workflows, and share them seamlessly across teams with minimal developer intervention.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Automation relies on SharePoint Designer workflows or Visual Studio workflows, which are complex and resource-intensive.Limited integration with other Microsoft 365 tools and third-party apps. | Power Automate is integrated by default, allowing users to automate processes with an intuitive graphical interface.Integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 apps like Outlook, Teams, and third-party services such as Dropbox and X.Modern workflows are faster to build, require less developer intervention, and are optimized for mobile devices. |
Flexibility
Modern SharePoint’s Hub Site architecture provides greater adaptability to organizational changes compared to the rigid structure of Classic Site Collections. Linking and detaching existing and new SharePoint sites within a Hub is a simple two-click process. Classic Site Collections, on the other hand, are notoriously difficult to restructure, often requiring significant time and resources.
Ease of customization
Classic SharePoint relied heavily on developer expertise, requiring custom code and master pages for modifications. Modern SharePoint, however, empowers users with a no-code approach through web parts. This allows anyone to easily add, modify, and arrange interactive elements on pages without writing any code, democratizing site customization across the organization. While simpler customization options like themes, site designs, and out-of-the-box web parts cater to most needs, the SharePoint Framework still provides a robust platform for developers to build custom modern web parts and extensions when more specialized functionality is required. This blended approach combines ease of use for everyday users with the flexibility of custom development for more complex scenarios.
Integration
Classic SharePoint’s limited integration restricts its effectiveness. Modern SharePoint, conversely, seamlessly integrates with the broader Microsoft 365 ecosystem, including key services like Teams, Outlook, Power Automate, Power Apps, Microsoft Graph, and Delve. This comprehensive integration fosters a more cohesive and productive digital workplace experience by streamlining workflows, centralizing information access, and enabling cross-platform collaboration. Users can leverage the power of multiple applications within a unified environment, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Performance
Modern SharePoint’s optimized loading algorithms deliver notably faster page load times. This improved performance enhances user experience and productivity, particularly when accessing content remotely or on mobile devices.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Performance is slower due to outdated algorithms and less efficient page load mechanisms. | Modern SharePoint provides faster page load times, thanks to improved algorithms, optimized layouts, and modern infrastructure. |
Mobile responsiveness
Modern SharePoint’s responsive design ensures consistent functionality across all devices. Lists, libraries, and site features automatically adjust to different screen sizes, providing a seamless mobile experience that Classic SharePoint cannot match.
Design
Modern SharePoint significantly simplifies site customization and branding compared to its classic counterpart. Users can easily personalize site design elements like logos, colors, and navigation through intuitive point-and-click interfaces, eliminating the need for custom coding. Changing the theme or color scheme to match organizational branding is now a straightforward process. Furthermore, Modern SharePoint prioritizes accessibility, adhering to WCAG guidelines to ensure inclusivity for users with disabilities. Classic SharePoint, in contrast, often demanded extensive coding efforts for even minor design adjustments, creating a barrier for users without technical expertise.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Common branding requires custom Master Pages and CSS, which are time-consuming and require technical expertise. | Sites automatically inherit branding and themes from associated hub sites. Customization can be done with just a few clicks, eliminating the need for coding. |
👉What is the difference between modern and classic SharePoint? The primary distinction lies in their approach to user experience, architecture, and customization. Modern SharePoint prioritizes intuitive design, mobile responsiveness, and integration with current technologies, while Classic SharePoint offers deeper technical customization but requires more expertise to manage.
Differences between elements in Classic vs Modern SharePoint
In addition to overarching parameters, there are significant differences in how core elements—such as the start page, team sites, libraries, and pages—are designed and function in Classic and Modern SharePoint. These differences showcase the shift from rigid, hierarchical structures in Classic SharePoint to the dynamic, flexible, and mobile-ready capabilities of Modern SharePoint. Below, we explore how these elements have evolved to enhance collaboration, accessibility, and overall user experience.
Start page
The Modern Team site home page provides a central hub for news, quick links, and recent site activity, automatically displaying updates such as uploaded files, changes made, and newly created lists and libraries. This dynamic home page significantly enhances the user experience compared to the static home pages of Classic Team sites.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Limited functionality and static design. | Dynamic and personalized, showing frequently visited sites, suggested news, and quick links to create sites or posts. |
Team sites
Modern Team sites integrate with Microsoft 365 Groups, enabling streamlined customization of calendars, task lists, announcements, and more. Creating, navigating, and using Modern Team sites is faster and more responsive than in Classic SharePoint.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Classic team sites rely on SharePoint groups for permissions and include static web parts like Announcements, Calendar, and Links.Branding customization requires themes, alternate CSS, and Master Pages, which need developer expertise.Team sites are slower to provision and lack responsiveness for mobile devices. | Modern team sites are integrated with Microsoft 365 Groups, providing a simpler permissions model and seamless collaboration tools like shared Outlook inboxes, calendars, and document libraries.Modern sites come pre-populated with dynamic features like News, Quick Links, Site Activity, and Document Libraries.Branding is easier with built-in themes that can be changed with just a few clicks, without requiring coding.Modern team sites are faster to create and include in-line editing for navigation elements like the Quick Start menu. |
Document lists and libraries
Modern SharePoint’s streamlined interface for lists and libraries offers improved usability and navigation. Users benefit from enhanced filtering, sorting, and viewing options that make content management more intuitive.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Relies on a classic list and library experience, which lacks modern features like column formatting and inline editing.Tasks like copying, moving, filtering, and grouping items are more time-consuming and require multiple steps.Customizations are limited, and advanced changes often require developer intervention. | Offers advanced column formatting and list view formatting to improve the display of data.Drag-and-drop functionality and an easy-to-use command bar simplify file management.Users can pin important documents to the top of libraries, add files as links, and quickly preview file details without additional steps.Rich location data integration with Bing Maps and organizational directories is supported.Modern lists and libraries provide personalized search suggestions and faster navigation, enhancing user productivity. |
👉 What is the difference between classic and new SharePoint list experience? The new SharePoint list experience in Modern SharePoint offers a more visually appealing and user-friendly interface compared to the classic experience. It includes features like inline editing, quick filtering, and improved mobile responsiveness, making it easier to manage and interact with list data.
Pages and web parts
Modern SharePoint pages offer a quick and easy way to create responsive pages using modern web parts. Creating page templates is straightforward, and the web parts themselves are designed for ease of use and enhanced performance. Classic SharePoint’s wiki and blog pages, while functional, lack the seamless user experience and responsiveness of their modern counterparts.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Classic pages rely on classic web parts, like wiki and blog pages, which require customization for even basic changes.Web part zones are static, and layouts cannot be changed once created.Custom web parts often require code, and many are not mobile-friendly. | Modern pages use modern web parts designed to be faster, easier to use, and highly responsive.Layouts are flexible and customizable, allowing users to change them anytime without coding.Modern web parts support dynamic features like embedding Power BI reports, videos, and news feeds.Developers can use the SharePoint Framework (SPFx) to create custom modern web parts integrated with the web part toolbox.Modern pages are mobile-ready, ensuring a seamless experience across devices. |
Hub sites and site collections
Classic SharePoint relies on hierarchical site collections consisting of a top-level site and related subsites. Modern SharePoint, while still supporting site collections and subsites, encourages the use of hub sites to link related sites together, maintaining consistent branding and navigation in a flatter, more flexible structure.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Classic site collections are hierarchical and rigid, with a parent-child relationship between sites.Reorganizing sites within a collection requires significant time and resources. | Hub sites use a flat architecture, allowing for greater flexibility in linking and detaching sites.Hub sites automatically apply common branding and navigation across associated sites, simplifying consistency.Users can search across all sites within a hub, improving discoverability. |
Communication and publishing sites
Classic SharePoint’s Publishing sites, which required significant developer effort to create and maintain, have been replaced by Modern Communication sites. These offer easy-to-use publishing tools for creating dynamic, mobile-friendly pages with minimal coding.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Classic publishing sites rely on Master Pages and publishing site infrastructure, which require significant developer resources.These sites are more structured but less flexible, making them harder to manage without advanced technical expertise. | Communication sites replace publishing sites with an easy-to-use, mobile-friendly experience.They use modern web parts and dynamic layouts to create visually compelling pages for sharing news, status updates, and reports.Predefined templates like Topic, Showcase, and Blank simplify the page creation process.Communication sites don’t rely on sub-sites, making them less complex and easier to maintain. |
Search
Modern SharePoint provides personalized search results based on user preferences and recent activity. Suggested results appear as you type, streamlining the process of finding information. Classic SharePoint’s search, while customizable, lacks the personalization and predictive capabilities of the modern experience.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Search functionality is static and shows the same results for all users, with limited ability to personalize or refine searches.Search results are less visually appealing and harder to navigate. | Search is personalized, showing results based on user preferences and recent activity.Real-time suggestions appear as users type, making search faster and more intuitive.Modern search is integrated across Start Pages, Team Sites, and Communication Sites, offering a consistent experience. |
News
The News feature in Modern SharePoint allows for easy creation and publishing of various types of posts, from announcements to status updates, enriched with attractive visuals. This streamlined publishing capability simplifies content dissemination and engagement.
| Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Lacks a dedicated feature for creating or sharing news updates. | Includes a News feature that allows users to quickly create and publish updates with rich layouts and graphics. |
By migrating to Modern SharePoint, organizations can accelerate their workflows through improved automation capabilities, enhance team collaboration with integrated communication tools, and adapt more readily to evolving business needs. The platform’s focus on user experience and mobile responsiveness ensures that employees can work effectively from any device, making it a more versatile solution for modern professionals.
Pros and Cons of SharePoint Classic and SharePoint Modern
When deciding between Classic SharePoint and Modern SharePoint, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of each experience. While Classic SharePoint has been a reliable solution for years, it comes with certain limitations that Modern SharePoint has been designed to address. This section explores the strengths and weaknesses of both versions, helping you understand which might be the better fit for your organization’s needs.
Pros and cons of Classic SharePoint
Classic SharePoint is best suited for organizations with deeply ingrained custom solutions and legacy systems that require a high degree of control and specialized configurations. However, this flexibility comes at the cost of complexity and a steeper learning curve.
Pros:
- Granular customization: Offers extensive customization options through custom code, master pages, and web part development, allowing for highly tailored solutions. This is particularly beneficial for organizations with unique branding requirements or complex business processes.
- Legacy system compatibility: Supports older solutions and workflows, ensuring business continuity for organizations that haven’t yet transitioned to newer technologies.
- Familiar interface (for long-term users): Users accustomed to Classic SharePoint may find the interface familiar and comfortable, minimizing the initial learning curve.
Cons:
- Complexity: Requires significant technical expertise for administration and customization. Managing custom code, master pages, and deployments can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Limited mobile support: Lacks responsive design, resulting in a suboptimal mobile experience. Users accessing SharePoint on mobile devices may encounter difficulties navigating and interacting with content.
- Dated user interface: The user interface appears outdated compared to modern web applications, potentially impacting user adoption and satisfaction.
- Integration challenges: Integrating with modern tools and platforms can be difficult due to its reliance on older technologies. Connecting with cloud-based services and newer APIs might require custom development work.
- Accessibility limitations: Meeting modern accessibility standards can be challenging, requiring manual adjustments and custom code.
Pros and cons of Modern SharePoint
Modern SharePoint prioritizes ease of use, collaboration, and integration with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. It offers a more intuitive and accessible experience, but may not provide the same level of granular customization as Classic SharePoint.
Pros:
- Intuitive user interface: Features a modern, user-friendly interface that simplifies navigation and content management, reducing the need for extensive training.
- Enhanced performance: Offers faster page load times and improved overall performance compared to Classic SharePoint, leading to a more responsive and productive user experience.
- Mobile-responsive design: Provides a seamless experience across devices, allowing users to access and interact with SharePoint content from anywhere, on any device.
- Simplified customization: Offers easy customization options through themes, site designs, and out-of-the-box web parts, empowering users to personalize their sites without coding.
- Seamless Microsoft 365 integration: Integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft 365 tools like Teams, Outlook, Power Automate, and Power Apps, fostering a more cohesive and collaborative digital workplace.
- Improved accessibility: Built with accessibility in mind, adhering to WCAG guidelines to ensure a more inclusive experience for users with disabilities.
👉 What are the benefits of modern SharePoint? Modern SharePoint offers several benefits that cater to today’s dynamic and collaborative work environments. Its seamless integration with Microsoft 365 tools allows teams to work more efficiently, whether through Teams, Outlook, or Power Automate. The mobile-responsive design ensures that users can stay productive from anywhere, while the intuitive interface reduces the learning curve, making it accessible to employees of all skill levels. Additionally, the ability to customize pages and web parts without coding encourages a more agile approach to site management.
Cons:
- Limited deep customization: While offering simpler customization options, Modern SharePoint may lack the deep customization capabilities of Classic SharePoint, potentially requiring custom development for highly specialized requirements. This can be a limitation for organizations with complex branding needs or highly customized workflows.
- Dependence on Microsoft 365: Modern SharePoint’s reliance on the Microsoft 365 ecosystem might be a constraint for organizations not fully invested in the cloud.
- Evolving feature set: As a continuously evolving platform, some features available in Classic SharePoint might not have direct equivalents in Modern SharePoint, requiring alternative solutions or workarounds.
By carefully evaluating these pros and cons in the context of your organization’s specific requirements, you can make an informed decision about whether to stay with Classic SharePoint, transition to Modern SharePoint, or adopt a hybrid approach. It’s crucial to consider factors like user needs, technical capabilities, integration requirements, and long-term goals when making this decision.
The table below spotlights the key differences spanning traditional and modern SharePoint platforms across a few pivotal aspects:
| Feature | Classic SharePoint | Modern SharePoint |
| Customization | Highly customizable but requires technical expertise. | Easy customization without coding but lacks deep customization options. |
| Interface | Outdated and complex. | Modern, clean, and user-friendly. |
| Mobile support | Limited, not mobile-responsive. | Fully mobile-responsive for seamless access on any device. |
| Performance | Slower page load times. | Optimized for faster performance. |
| Integration | Limited integration with modern tools. | Full integration with Microsoft 365 apps like Teams and Outlook. |
| Ease of use | Difficult to use and configure without technical skills. | Simple and intuitive, suitable for all users. |
| Support for legacy Solutions | Strong support for older workflows and systems. | Better suited for modern workflows and technologies but less support for legacy systems. |
Overall, Modern SharePoint provides the tools and flexibility needed to support modern business processes, making it the preferred choice for organizations looking to optimize collaboration and productivity.
Using Classic and Modern SharePoint and Versioning Tips
Navigating the SharePoint landscape can feel complex with the coexistence of Classic and Modern experiences. This section provides practical guidance on when to use each version, how to manage them effectively within a hybrid environment, and tips for optimizing your overall SharePoint strategy. Understanding the strengths of each version empowers you to tailor your approach and maximize the benefits of this powerful platform.
When to use Classic vs Modern SharePoint
Classic SharePoint is best suited for scenarios that require complex customizations and unique solutions. For example, if your organization needs to deeply customize the interface, such as creating a highly tailored intranet or implementing specific business processes, Classic SharePoint is the ideal choice.
Example: A company builds a custom intranet with unique web parts to manage internal workflows, such as an internal corporate portal for handling employee requests or proprietary operations.
Modern SharePoint, on the other hand, excels in ease of use, quick deployment, and seamless integration with Microsoft 365 tools. It is the go-to option for everyday collaboration, document sharing, and creating team or project sites.
Example: A team sets up a Modern SharePoint site to collaborate on a project. Employees can quickly share documents, track progress, and work together in real time, all while integrating seamlessly with Teams and Outlook.
Tips for managing classic and modern SharePoint in a hybrid environment
Many organizations operate in a hybrid environment, leveraging both Classic and Modern SharePoint. Here’s how to effectively manage this coexistence:
- Establish consistent governance: Implement uniform rules for data structure, access control, and content management across both versions to ensure consistency and maintainability.
- Leverage management tools: Utilize the SharePoint Admin Center and other management tools to oversee both Classic and Modern sites, monitor usage, and manage permissions.
- Implement redirects: Set up redirects from classic sites to their modern equivalents (where applicable) to facilitate a smooth transition for users and avoid confusion.
- Connect classic sites to groups: Site collection administrators can connect existing classic sites to Microsoft 365 Groups to enhance collaboration and simplify permission management. They can also update the home page of the classic site to the modern home page experience.
- Modernize classic home pages: Even without migrating an entire classic site, you can create a modern page with desired web parts and set it as the home page for the classic site, providing a more modern entry point.
Tips for managing the two experiences
Successfully managing a hybrid SharePoint environment requires a strategic approach. The following tips offer guidance on upgrading, optimizing, and training, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the benefits of both Classic and Modern SharePoint.
- Gradual upgrade of classic sites: Don’t attempt a “big bang” migration. Instead, gradually upgrade legacy Classic SharePoint elements to be compatible with Modern SharePoint. Prioritize high-impact areas and migrate incrementally.
- Modernization assessment: Use tools like the SharePoint Modernization Scanner to analyze your existing Classic SharePoint environment and identify which elements can be easily migrated to Modern SharePoint. This helps prioritize your modernization efforts.
- Optimize information architecture: Develop a plan to consolidate data, optimize site structure, and improve navigation across both Classic and Modern SharePoint. This ensures a cohesive and user-friendly experience regardless of the version being used.
- Create hub sites: Establish a common “hub site” in Modern SharePoint to connect related classic and modern sites, creating a central navigation point and fostering a more unified experience.
- User training: Provide comprehensive training to employees on how to effectively use Modern SharePoint for their daily tasks. Focus on the benefits and new features to encourage adoption.
- Performance monitoring: Regularly monitor the performance of both Classic and Modern SharePoint environments using analytics tools like Microsoft 365 Usage Analytics to identify areas for improvement and optimize resource allocation.
Use cases for Classic and Modern SharePoint
Organizations often use Classic and Modern SharePoint for different purposes based on their specific requirements:
- Classic SharePoint for complex customizations: A company’s legal team uses Classic SharePoint to access secure documents stored in a highly customized corporate portal designed to meet strict compliance and workflow requirements.
- Modern SharePoint for everyday collaboration: The marketing and sales teams use Modern SharePoint to collaborate on campaign materials, share documents, and manage projects in real-time, leveraging its mobile-friendly interface and integration with Teams.
- Hybrid use: An organization maintains a Classic SharePoint intranet for internal workflows and corporate announcements, while using Modern SharePoint for project-specific collaboration and team sites.
By understanding when and how to use each version, organizations can maximize the strengths of both Classic and Modern SharePoint, ensuring a tailored solution that meets both legacy requirements and modern workplace demands.
Best Practices for Migrating from Classic to Modern SharePoint (and Back): How to Switch between Classic and Modern View in SharePoint
Migrating from Classic to Modern SharePoint can significantly improve usability, performance, and integration with other Microsoft 365 tools. However, the migration process requires careful planning to ensure a smooth transition while maintaining the organization’s data integrity and structure. This section outlines best practices for migrating to Modern SharePoint, highlights key considerations, and explains why some users may want to revert to the Classic experience.
Understanding the limitations of migration
Migrating from Classic to Modern SharePoint is not as simple as flipping a switch. While some elements, such as lists and libraries, can be easily transitioned to Modern views, the underlying site and its core components often remain rooted in the Classic framework unless additional steps are taken. This creates a hybrid environment where users may experience a mix of Modern and Classic interfaces, which can be confusing and inconsistent.
Modernizing lists and libraries vs. entire sites
SharePoint allows lists and libraries to adopt the Modern experience relatively easily. This can be done by enabling the Modern view for these components in the SharePoint Admin Center or via PowerShell. Once activated, users benefit from the sleek Modern interface for these particular elements, including:
- A responsive design optimized for mobile devices.
- Improved performance with faster loading times.
- Enhanced features such as grouped views, column formatting, and the ability to pin documents.
However, while these individual elements can be modernized, the site itself—including its home page, navigation, and overall structure—remains in the Classic experience unless more substantial changes are made.
Challenges in transforming entire sites
Achieving a fully Modern SharePoint site requires transforming the foundational components of the Classic site, including site pages, customization, and navigation. These transformations are complex due to the following limitations:
- No direct page conversion: Classic pages (wiki pages, web part pages) cannot be automatically converted to modern pages. While tools like the SharePoint Page Transformation tool can analyze classic pages and offer recommendations, they do not perform automatic conversion. The differences in web parts, layouts, and the underlying framework necessitate a manual rebuilding process. For example, a heavily customized Classic page with custom scripts or third-party web parts might require significant redevelopment to achieve similar functionality in Modern SharePoint.
- Requires manual effort and expertise: Transforming Classic pages to Modern pages demands manual effort and expertise from IT administrators and developers. They must assess each page, determine the compatibility of its components with modern web parts, and often rebuild the page from scratch using modern page elements and the SharePoint Framework (SPFx) for custom development.
- Compatibility issues with customizations: Classic SharePoint often relies on customizations like custom master pages, alternate CSS, and custom JavaScript for branding and functionality. These customizations are incompatible with Modern SharePoint, which uses tenant-controlled theming and the SharePoint Framework (SPFx) for client-side development. Organizations must either redesign these customizations using modern tools or abandon them.
- Hybrid experience during transition: During migration, users will likely experience a hybrid environment where some elements are modern while others remain classic. This inconsistency can confuse and frustrate users, especially those less familiar with SharePoint. Clear communication, training, and a well-defined migration plan are crucial to mitigate these challenges.
The role of page transformation tools
Transforming classic site pages into modern pages is crucial for a complete modern SharePoint experience. However, this process requires careful planning and execution due to the inherent differences between classic and modern page architectures.
- SharePoint Page Transformation Tool: The SharePoint Page Transformation tool (formerly known as the Modernization scanner and now integrated into the PnP framework) is not a tool that automatically converts classic pages to modern pages. Its primary function is assessment. It analyzes classic pages, identifies the complexity of their components, and provides recommendations for modernization. It helps determine whether a page can be easily transformed, requires significant modification, or is best rebuilt from scratch.
Key functionalities include:- Analyzes classic pages: Scans classic pages to identify the web parts, layouts, and customizations used.
- Assesses complexity: Determines the level of effort required to modernize a page based on its components.
- Provides recommendations: Suggests appropriate actions, such as using specific modern web parts or rebuilding the page manually.
- Reports and insights: Generates reports that help prioritize page transformation efforts.
- Manual Rebuilds: Due to the limitations of direct conversion, manual rebuilding is often the most effective approach for transforming classic pages to modern pages. Developers use modern web parts and the SharePoint Framework (SPFx) to recreate the functionality and design of classic pages within the modern framework. This ensures compatibility and leverages the full potential of modern SharePoint.
Key aspects of manual rebuilds:
- Recreating functionality: Developers use modern web parts and SPFx to replicate the functionality of classic web parts.
- Redesigning layouts: Modern pages use a responsive design approach. Developers need to redesign page layouts to ensure they adapt to different screen sizes.
- Preserving content: Content from classic pages is migrated to the new modern pages.
- Addressing customizations: Any custom code or solutions used in classic pages need to be rewritten or adapted for the modern framework.
By understanding the true role of the Page Transformation tool as an assessment tool and recognizing the importance of manual rebuilds, organizations can approach page transformation with realistic expectations and a more effective strategy. The key is to analyze first, then rebuild using modern techniques.
👉 Deepen your understanding of modernizing SharePoint experiences with these official Microsoft resources:
Why IT expertise is essential
Because transforming a SharePoint site to a fully modern experience can be complex and has limitations, successful modernization often requires a joint effort. IT administrators, developers, and business stakeholders each play a vital role. Specifically, IT teams are essential for:
- Assessing compatibility between Classic and Modern components.
- Using migration tools effectively to convert pages and elements.
- Resolving issues related to customizations and workflows.
- Training end users to navigate and use the Modern interface.
While lists and libraries can be easily transitioned to Modern views, migrating an entire Classic site to a Modern experience is a more complex undertaking. It requires advanced tools, technical expertise, and thoughtful planning to address compatibility issues, preserve functionality, and ensure a smooth user experience. Organizations should view this process as an opportunity to not only modernize their SharePoint environment but also optimize their workflows, content, and branding for future growth.
When migration makes sense: Why move to Modern SharePoint?
Migrating from Classic to Modern SharePoint is most beneficial in situations where usability, mobility, and integration with Microsoft 365 tools are a priority. Modern SharePoint offers a more intuitive, mobile-responsive interface, better performance, and seamless integration with applications like Teams, Outlook, and Planner. Migration makes the most sense when:
- Users need an easier way to collaborate and share documents.
- Mobile access and responsiveness are crucial for productivity.
- Teams require integration with Microsoft 365 tools to streamline workflows.
- The organization wants to adopt modern, future-proof technologies to improve business processes.
- Accessibility is a priority for ensuring inclusivity and compliance.
Key considerations for migration
Migrating from Classic to Modern SharePoint requires careful planning and execution. Organizations should thoroughly evaluate their needs, existing infrastructure, and user requirements before initiating a migration. Key considerations include:
- Compatibility: Not all Classic customizations and workflows will seamlessly transition to Modern SharePoint. Custom master pages and alternate CSS used in Classic sites are incompatible with Modern SharePoint’s theming system. Modern customizations should be built using the SharePoint Framework (SPFx).
- User adoption: Employees accustomed to the Classic interface may require training and support to adapt to the Modern experience. Strategies for promoting user adoption include providing training materials, conducting workshops, setting up demo sites, and establishing champions within the organization.
- Content relevance: Review existing content and determine what should be migrated, archived, or discarded. Migration presents an opportunity to reorganize and restructure content, improving information architecture and findability.
Stages of migration
Migrating to Modern SharePoint involves several distinct stages. Below is a roadmap to guide organizations through the process:
- Assess your current infrastructure: Begin with a comprehensive audit of your existing SharePoint environment. This assessment helps identify compatibility issues, prioritize migration efforts, and plan for necessary modifications. Key activities include:
- Inventory and analysis: Review site structures, lists, libraries, pages, and content. Analyze usage patterns to understand how users interact with the current environment.
- Content cleanup: Identify outdated or unused content for archiving or removal. This streamlines the migration process and improves information architecture.
- Customization evaluation: Assess existing customizations (e.g., master pages, CSS, custom code) and determine their compatibility with Modern SharePoint. Recognize that many classic customizations will need to be rebuilt using the SharePoint Framework (SPFx).
- Technical assessment: Utilize the SharePoint Online Management Shell and the page transformation assessment capabilities of the PnP framework to analyze your environment and identify potential challenges.
- Plan your migration: Develop a detailed migration plan that outlines the steps, timeline, and resources required for a successful transition. This stage involves:
- Data preparation: Organize and clean up content, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
- Phased approach: Develop a phased migration plan to minimize disruption to users and allow for iterative testing and adjustments.
- User training and communication: Prepare users for the Modern experience through training materials, workshops, and ongoing communication. Clearly communicate the benefits of the migration and address any concerns.
- Testing and validation: Test new features and functionalities in a staging environment before deploying to production.
- Success metrics: Define clear metrics to measure the success of the migration, such as user adoption rates, performance improvements, and reduction in support requests.
- Execute the migration: Leverage appropriate tools and techniques to execute the migration efficiently and effectively.
- Built-in Microsoft tools: Utilize resources like the SharePoint Admin Center, the page transformation assessment capabilities of the PnP framework, and the SharePoint Online Management Shell for assessment, migration, and management tasks.
- Third-party migration and management tools: Consider using third-party tools for additional functionality and support, especially for complex migrations. Evaluate the pros and cons of different tools based on your specific needs.
- Migration approach: Determine the most appropriate migration approach (manual vs. automated, phased vs. “big bang”) based on the complexity of your environment and your resources. Recognize that significant manual effort is often required for page transformations.
Summary: So, how do I change SharePoint from Classic to Modern?
The journey from Classic SharePoint to Modern SharePoint is a thoughtful transition with a couple of main paths.
One path involves connecting your existing classic sites to Microsoft 365 groups. This is a relatively quick way to introduce some modern elements. By connecting a classic site to a group, you get a brand new, modern home page for the site, and you gain access to the collaborative power of Microsoft 365 groups, including shared mailboxes, calendars, Planner, and Teams. However, it’s important to understand that this approach doesn’t magically transform the entire site. All the other pages and lists within the site remain in their classic form. This is a good initial step if you want to introduce some modern functionality without undertaking a full-scale migration.
The second, and more comprehensive, path to modernization involves rebuilding your classic site pages as modern pages. This is where the real transformation happens. While there are tools within the PnP framework that can analyze your classic pages and offer helpful recommendations, there’s no automatic conversion tool. Modernizing pages requires a manual process of rebuilding them using modern web parts and the SharePoint Framework. This approach takes more time and effort, but it results in a fully modern experience with improved performance, mobile responsiveness, and access to the latest SharePoint features. So, while connecting to Microsoft 365 groups can be a good starting point, rebuilding your pages is the key to unlocking the full potential of Modern SharePoint.
👉 For step-by-step guidance, refer to resources like Transform classic pages to modern pages & Modernize your classic SharePoint sites
Why some users revert to Classic SharePoint
While Modern SharePoint offers numerous advantages, certain situations might necessitate reverting to the Classic experience, at least temporarily or for specific functionalities. These situations typically arise due to compatibility issues, user experience challenges, or specific business requirements that are not yet fully supported in the modern experience.
Legacy customizations: Organizations with heavily customized Classic SharePoint environments, especially those relying on custom master pages, JavaScript embeddings, or complex web parts, often face compatibility challenges. Modern SharePoint utilizes the SharePoint Framework (SPFx) for customizations, which requires re-engineering existing solutions. Migrating these customizations can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, leading some organizations to retain Classic SharePoint until a suitable modernization strategy is implemented.
Familiarity and user experience: While the Modern SharePoint interface is designed for intuitive use, some users accustomed to the Classic experience may initially find the change disruptive. This can lead to a temporary dip in productivity as users adjust to the new navigation, page layouts, and features. Proper training and change management are crucial for mitigating this challenge. However, in some cases, users might strongly prefer the Classic interface for specific tasks or workflows, leading to a preference for reverting.
Specific business needs and feature gaps: Certain business processes, particularly those involving complex workflows, custom forms, or highly specialized document management requirements, might not have direct equivalents in Modern SharePoint. For example, some third-party integrations or legacy systems might not be compatible with the Modern experience. In such cases, organizations might retain Classic SharePoint for these specific functionalities until modern alternatives are available or developed.
Phased approach and hybrid environments: It’s important to note that reverting to Classic SharePoint doesn’t necessarily mean abandoning the Modern experience altogether. Many organizations adopt a phased approach, migrating certain sites and functionalities to Modern while retaining Classic for others. This creates a hybrid environment where both experiences coexist, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of Modern SharePoint while ensuring business continuity for processes that rely on Classic features.
Example: A legal firm might utilize Modern SharePoint for team collaboration and document sharing but retain Classic SharePoint for a records management system that relies on highly customized workflows and specific metadata schemas not yet supported in the modern experience. This hybrid approach allows the firm to embrace modern features where appropriate while maintaining the integrity of its critical records management processes.
Improving Both Experiences: VirtoSoftware SharePoint On-Premise Web Parts & Online Apps
VirtoSoftware offers a wide range of solutions to enhance both SharePoint On-Premise and SharePoint Online experiences. Whether your organization relies on Classic SharePoint or Modern SharePoint, VirtoSoftware provides tools that improve functionality, streamline workflows, and enhance the user experience. With their comprehensive set of SharePoint web parts and Microsoft 365 apps, VirtoSoftware empowers organizations to optimize task management, scheduling, collaboration, and more.
Enhancing SharePoint with VirtoSoftware solutions
VirtoSoftware’s SharePoint On-Premise Web Parts and Microsoft 365 & SharePoint Online Apps provide versatile tools that seamlessly integrate with your existing environment. These solutions help organizations bridge gaps in functionality, offering additional features that make both Classic and Modern SharePoint more productive and user-friendly.
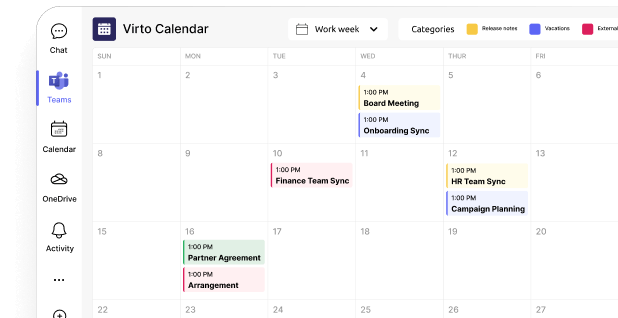
Virto Calendar App
The Virto Calendar App is a powerful tool for centralizing and simplifying scheduling across multiple calendars and platforms. Designed for both SharePoint On-Premise and Online, this app overlays calendars from various sources, helping teams efficiently plan and organize their schedules.
Key features:
- Overlay multiple calendars
- Combine Exchange Online calendars with other Microsoft 365 calendars in a single view.
- Use SharePoint lists as data sources to display events or tasks in the calendar.
- Merge calendars from SharePoint lists, Outlook, meeting rooms, and external sources like Google Calendar using iCal links.
- Flexible views
- Effortlessly switch between day, week, month, year, or task views to organize events based on your team’s preferences.
- Color-coded events
- Assign colors to different event categories for a well-structured and visually clear calendar overlay.
- Compact mini calendar
- Incorporate a mini calendar for a quick and compact overview of all scheduled events.
Why it stands out:
- Comprehensive integration: Merge multiple calendars (SharePoint lists, Outlook, Planner, Google Calendar, iCal) into a central scheduling hub, simplifying planning and coordination.
- Microsoft 365 native: Fully integrated with M365, ensuring consistency in security and user experience.
- Versatile and adaptive: Designed to handle all calendar-related scenarios, from project management to simple scheduling.
Virto Kanban Board App
The Virto Kanban Board App brings visual task management to SharePoint and Microsoft Teams. By transforming SharePoint lists into dynamic Kanban boards, this tool allows teams to organize tasks, track project progress, and quickly identify bottlenecks.
Key Features:
- Agile task management
- Visualize tasks as individual cards and organize them into columns based on their status (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done).
- Use a backlog column to manage tasks that are yet to be started.
- Highly customizable
- Tailor boards with swimlanes, color-coded cards, subtasks, and categorization to fit your workflow.
- Seamless integration
- Fully integrates with the Microsoft 365 ecosystem for consistent user experience across tools like Teams and SharePoint.
Why it stands out:
- Quick Start: Get started immediately with predefined Quick Board templates.
- Manage and collaborate: Assign roles, set permissions, and configure notifications for efficient teamwork.
- Analyze and optimize: Use filters, WIP (Work In Progress) limits, and flexible charts to analyze workflows and improve productivity.
Additional VirtoSoftware apps
VirtoSoftware offers additional apps to further enhance both SharePoint On-Premise and Online environments:
- Virto Alerts & Reminder App
- Automate notifications and reminders for tasks, events, or deadlines.
- Set up custom alerts to ensure important activities are never missed.
- Virto Multiple File Upload App
- Streamline the process of uploading files to SharePoint by enabling bulk uploads.
- Supports drag-and-drop functionality and customizable upload settings.
All VirtoSoftware apps are available for both SharePoint On-Premises and SharePoint Online, making them suitable for organizations with hybrid environments.
How VirtoSoftware enhances SharePoint experiences
VirtoSoftware solutions are designed to address common challenges in both Classic and Modern SharePoint environments, delivering:
- Central scheduling hub
- The Virto Calendar App consolidates multiple calendars, simplifying planning and scheduling across teams and projects.
- Diverse data source integration
- VirtoSoftware apps integrate with various data sources such as SharePoint lists, Outlook, Planner, Google Calendar, iCal, and Apple Calendars.
- High-level security
- All VirtoSoftware apps are built with enterprise-grade security and privacy features, ensuring they can be safely deployed across industries.
- Dynamic task management
- The Virto Kanban Board App provides teams with an agile and customizable task management solution that adapts to their workflow.
VirtoSoftware’s SharePoint On-Premise Web Parts and Microsoft 365 & SharePoint Online Apps are valuable tools for improving both Classic and Modern SharePoint experiences. From powerful scheduling with the Virto Calendar App to dynamic task management with the Virto Kanban Board App, these solutions enable efficient workflows, better collaboration, and enhanced productivity. We encourage you to check out those apps by scheduling a quick demo or browsing through the website and installing free versions of each app to test their functionality.
Conclusion on SharePoint Modern vs Classic
The evolution of SharePoint from Classic to Modern experiences marks a significant stride toward usability, responsiveness, and integration with Microsoft 365 tools. While Classic SharePoint has served as a reliable platform for years, it comes with limitations such as an outdated interface, complex customizations, and limited mobile support. Modern SharePoint, on the other hand, delivers a more intuitive, flexible, and mobile-friendly experience that enhances collaboration and productivity.
For businesses aiming to improve efficiency, streamline workflows, or adopt future-proof technologies, migrating to Modern SharePoint is a logical next step. However, the decision to migrate should be guided by careful assessment of your organization’s needs, infrastructure, and user readiness. Thoughtful planning, combined with proper training and the use of migration tools, can ensure a smooth transition while preserving the functionality of legacy systems.
Additionally, tools like VirtoSoftware SharePoint On-Premise Web Parts and VirtoSoftware Microsoft 365 & SharePoint Online Apps further enhance both Classic and Modern SharePoint. By introducing new and improved capabilities—such as managing calendars, tasks, and files—VirtoSoftware provides users with powerful solutions to tackle day-to-day challenges. Whether you’re leveraging Classic SharePoint or Modern SharePoint, these tools empower businesses to maximize their SharePoint investment.
To dive deeper into the topic and make an informed decision about your SharePoint environment, explore these additional resources:
- Official Microsoft resources:
- Our blog articles: