Microsoft Teams External Users: Collaboration Guide, Tips & Limitations
Discover how Microsoft Teams enhances collaboration with external users through federated and guest access. Learn the key differences and how to effectively manage external participation in your Teams environment.
With over 300 million monthly active users (1), Microsoft Teams has firmly established itself as the world’s most popular business collaboration platform. This runaway success stems from Microsoft Teams providing a hub for workplace chat, meetings, file sharing and application integration under one roof, empowering productivity within organizations. Yet, enabling collaboration beyond company walls can unlock even greater potential.
This brings us to the concept of external user access. Separate from guest access for partners, external user capabilities in Microsoft Teams allow employees to collaborate with customers, vendors and other outside entities.
There are myriad benefits from facilitating real-time communication, event planning, and more across organization boundaries. However, prudent configuration is vital to balance security and control.
In this article, we will leverage VirtoSoftware’s expertise in Microsoft app development and implementation to explore Microsoft Teams’ external user capabilities. We will review differences from guest access, walk through user management, outline restrictions that apply, and provide best practices for configuration—including specific examples around our Virto Calendar integration.
Understanding Microsoft Teams External Users
Seamless collaboration with outside contacts is critical for any robust work platform. As mentioned, Microsoft Teams facilitates this through its external access capabilities, enabling users to add non-organization members to channels, chats and meetings for fluid teamwork. This differs from guest access, which we’ve covered in one of our previous pieces and which we’ll revisit briefly later in this article.
What is external access in Microsoft Teams?
External access in Microsoft Teams (also referred to as ‘federation’) is designed to bridge the gap between different organizations, enabling users to make calls, chat, and set up meetings with colleagues who are not part of the same company but use Microsoft Teams. This type of access essentially expands the reach of an organization’s communication capabilities beyond its own borders, promoting an inclusive environment for collaboration with clients, suppliers, partners, and freelancers.
Key features of external user access include:
- Chat and calling: External users can participate in one-on-one or group chats and can make voice and video calls.
- Meeting participation: External users can join scheduled meetings in Teams, enhancing collaboration on shared projects or ongoing partnerships.
- Presence information: You can see the online status of external users, which helps in determining the best times to contact them.
External user access does not require adding a user to your organization’s directory. Instead, it operates through the Microsoft Teams federation, allowing users from different Teams-enabled organizations to communicate as long as the respective admins have allowed external access.
👉Can you use Microsoft Teams with external users? Yes, you can use Microsoft Teams with both federated external users and guest users. The key difference lies in the level of access and integration. Federated external users are part of organizations that have a trusted relationship with your organization, allowing them to communicate and collaborate using their own Teams accounts. They can chat, call, and join meetings but usually cannot access channels directly. Guest users, on the other hand, are invited to join your Teams environment and can access channels, participate in meetings, and collaborate on documents, depending on the permissions granted.
Typical use cases for external users
The use of external user access in Microsoft Teams is particularly prevalent in several common business scenarios:
- Project collaboration: For projects that involve multiple stakeholders, including external consultants or contractors, external access allows all parties to communicate and collaborate in real-time, ensuring that everyone is aligned and can contribute effectively to the project goals.
- Client management: Businesses frequently use external access to enhance client relationships. By allowing clients to communicate directly through Microsoft Teams, companies can provide superior service, quicker responses, and a more personalized interaction, all of which contribute to increased client satisfaction and loyalty.
- Supply chain coordination: In industries where supply chain management is crucial, external access enables more efficient coordination between suppliers, distributors, and retailers. Real-time communication and sharing of documents facilitate smoother operations and quicker decision-making processes.
- Educational workshops and seminars: Educational institutions and training providers often use external access to conduct workshops, seminars, and classes that include participants from outside the organization. This makes the educational content more accessible and interactive for a broader audience.
- Cross-company initiatives: For initiatives that span multiple companies, such as joint ventures or industry-wide collaborations, external access in Microsoft Teams provides a common platform where all participants can meet, share resources, and drive initiatives forward without the hassle of multiple communication tools.
Onboarding external users creates value within and beyond an organization’s walls. Internally, it streamlines cross-company collaboration to bolster productivity. Externally, integrating clients, vendors and partners forges an interconnected ecosystem united by shared channels of communication and transparency. In the next section below, we’ll go over these and other myriad benefits of having external users on board in more detail.
👉 What is the difference between external and guest access in Teams? External access (federation) lets Teams users from other domains find, call, chat, and set up meetings with you. Guest access allows individuals to join your Teams as full members, participating in chats, meetings, and collaborations. To learn more about the difference, explore the dedicated section further down below in this article.
Benefits of working with external users in Microsoft Teams

Federation, or external user access, in Microsoft Teams offers several strategic benefits that can significantly enhance organizational effectiveness and collaboration. Here’s an exploration of the key advantages:
- Seamless communication across organizations: External user access allows users from different organizations to communicate directly within Microsoft Teams. This capability facilitates seamless interactions, making it easier to manage cross-organizational projects, negotiate deals, or provide support without the need for third-party communication tools. The direct communication channel helps in maintaining clear, consistent, and real-time exchanges, improving response times and decision-making processes.
- Enhanced productivity and collaboration: By enabling federation, organizations can collaborate more effectively with partners, vendors, and customers. This type of access supports various forms of communication including chats, calls, and meeting participations. It allows external partners to quickly ask questions, provide updates, and make decisions, all within the same platform used internally. This integration reduces the friction and delays often associated with switching between different communication tools.
- Cost efficiency: External user access can reduce costs associated with multiple communication platforms. By using Microsoft Teams as a unified communication tool for both internal and external interactions, organizations can minimize the need for additional software licenses and reduce overhead associated with managing multiple platforms. This consolidation not only simplifies IT infrastructure but also reduces training requirements as users need to be familiar with only one system.
- Maintain control and security: While federation opens up lines of communication, it does so without compromising security. Organizations can control how and when external users can communicate with their Teams environment. Microsoft Teams provides robust security features that ensure compliance and protect sensitive information, even when interacting with external entities. The ability to monitor and manage these interactions helps in mitigating potential security risks.
- Flexibility and scalability: External user access in Microsoft Teams is highly scalable, accommodating the needs of both small interactions and large-scale collaborations. Whether it’s a one-on-one discussion with a supplier or a broad cooperative effort across multiple organizations, federation scales to meet the demand. This ability to readily adapt is exceptionally important in settings where an organization’s internal priorities and external alliances regularly overlap.
- Improved stakeholder engagement: By facilitating easier and more efficient communication, federation helps in building and maintaining stronger relationships with external stakeholders. When stakeholders such as clients, consultants, and vendors can communicate easily and effectively, they are more likely to feel engaged and integral to the organizational processes. This enhanced engagement can lead to better service delivery, increased customer satisfaction, and stronger business relationships.
- Rapid onboarding and offboarding: Federation allows for quick onboarding of external users to communicate on necessary projects and topics without the need to go through extensive setup processes typical of guest access. Similarly, external users can be easily disconnected once the collaboration is no longer needed, simplifying the management of external contacts.
In summary, the ability to federate in Microsoft Teams boosts day-to-day efficiency while also aiding important business goals by facilitating communication, fortifying collaborations, and streamlining technical needs.
How to Set Up Access for External Users in Microsoft Teams
In this section, we’ll explore the process of setting up access for external users in Microsoft Teams. We’ll examine this from two critical perspectives: the end-user and the administrator responsible for configuring and managing access settings. Understanding both sides will help ensure a smooth and secure collaboration experience for everyone involved.
👉 How do I enable external users in my team? Microsoft Teams giving access to external users involves enabling either external federated access or guest access in the Microsoft Teams admin center.
For users: Joining as an external user (federation)
Can I invite external users to Microsoft Teams? Joining a Microsoft Teams environment as an external user through federation does not typically involve an invitation process similar to guest access. Instead, it operates under the premise that both organizations have allowed external or federated access between their Microsoft Teams setup. Here’s how you can communicate as an external user once federation is enabled:
- Prerequisites:
- Ensure that both your organization and the external organization have enabled external access (federation) in Microsoft Teams.
- Verify that there are no domain restrictions that might block the communication.
- Initiate contact:
- From the Teams chat: Simply start a new chat and type the full email address of the person in the external organization you wish to contact. Microsoft Teams will recognize this if federation is properly set up and allowed.
- Direct call/meeting: You can also directly call or invite the external user to a meeting using their email address. Again, this is contingent upon the proper setup of federation settings by both organizations.
- Communicate as usual:
- Once you initiate the contact and it is recognized, you can chat, share files, and call as you would with an internal team member, depending on the permissions granted by both organizations.
- Joining meetings:
- If an external user sends you a meeting invite, you can join the meeting through the link provided. Ensure you have the appropriate meeting client installed or access it via a web browser.
👉 Can external users access Microsoft Teams? Federated external users can participate in Teams meetings and communicate via chats if federation is properly configured between the organizations.
For administrators: Setting up external user access (federation)
For clarity, let’s touch upon how administrators can set up federation, allowing such external communications:
- Microsoft Teams admin center:
- Log into the Teams admin center.
- Navigate to “External access”:
- Go to “Org-wide settings” > “External access”.
- Enable federation:
- Toggle the setting to “On” to allow your Teams users to communicate with users in other organizations.
- Configure federation settings:
- You can decide to allow all domains or block/allow specific domains. This helps to manage which external organizations your users can communicate with.
👉 Why am I unable to add external users to Teams channel? Federated external users cannot be directly added to a Teams channel because federation primarily allows for communication via chats and meetings. Federation does not extend to Teams channel membership, which requires a higher level of access typically reserved for full team members or guest users. If you are unable to add guest external users to a Teams channel, it could be due to several reasons. For instance, your Teams administrator might not have enabled guest access, or the guest access settings might restrict particular behaviors, such as engaging in channels, among others.
Although we’re going to explore the differences between guest and federation access in more detail in a later section, it’s worth highlighting the main distinction between the two here for ease of understanding and reference:
- Federation acts as a bridge between Teams domains, allowing users from different organizations to find and contact one another for communication and meetings. It facilitates user-to-user collaboration across company boundaries.
- Guest access goes a step further for more integrated teamwork with people outside your organization. By adding external users as guests directly into your Teams environment, they can be granted access beyond just chatting and meetings. As guests, external collaborators can be given access to view or edit internal files and documents, join private channels, and participate in wider company conversations.
The distinction in what federation users and guest users can access underscores the importance of correctly setting up Teams according to the collaboration needs of your organization.
👉 Learn more about managing external user communications in the following official guides by Microsoft:
- Manage external meetings and chat with people and organizations using Microsoft identities
- Plan for meetings with external participants in Microsoft Teams
Microsoft Teams Connect with External Users: Working with External Users in Microsoft Teams
In this section, we’ll explore the various functionalities and best practices for working with external users within the Microsoft Teams environment. Whether you’re communicating through chat or conducting meetings, Microsoft Teams offers several options to ensure seamless collaboration with partners, clients, and other stakeholders outside your organization.
Communication
Here’s how you can communicate effectively with external users:
Microsoft Teams chat with external users: how to chat on Microsoft Teams with external users
- Enable external access: Make sure that external access (federation) is enabled in your Microsoft Teams settings. This allows users from other organizations to communicate with your team.
- Start a chat: To chat with an external user, simply enter their email address in the search bar at the top of the Teams interface and start a conversation. This is contingent on both organizations allowing federation.
👉Microsoft Teams shared channel external users? No, external federated users cannot be directly invited to participate in a shared channel within Microsoft Teams. Federated external users are typically limited to participating in one-on-one chats, group chats, and joining meetings. However, you can invite them as guests, having enabled guest access before that.
How to create group chats with external users
- Create a new group chat: Click on the chat icon in Microsoft Teams, then select the ‘New chat’ button. Click on the pencil icon to add participants.
- Add external users: Type the full email addresses of the external users you wish to include in the group chat. Ensure these users are from organizations that allow federation with your Teams environment.
- Name and start chatting: Give your group chat a name to make it recognizable, and start your discussion.
Meetings
Meetings with external participants are straightforward to arrange and can be highly productive with the proper setup:
How to set up a conference call in Microsoft Teams with external users in federation:
Before you can invite federated users to a meeting, ensure that both your organization and the external organization have federation enabled and configured to allow mutual communication. This is typically managed by IT administrators within the Microsoft Teams admin center under Org-wide settings > External access. Then, follow the steps:
- Schedule the meeting: Go to the Calendar in Microsoft Teams, click on “New Meeting,” and fill in the meeting details.
- Set meeting options: After creating the meeting, select it in the calendar, click on “Meeting Options” to configure access settings.
- Send invitations: Microsoft Teams automatically sends an email invitation to all listed participants. Federated users will receive this invitation in their own Teams or associated email, with a link to join the meeting.
- Join the meeting: At the scheduled time, all participants can join using the link provided in their invitation. Participants from federated organizations can join directly through their own Teams client, facilitating seamless integration
- Manage the meeting: As the organizer, you maintain control over the meeting, so you can mute/unmute participants, change roles during the meeting, share content, and use other collaborative features.
👉 How to send Microsoft Teams invite to external users? To invite external users to a Teams meeting, simply add their email associated with their federated account to the meeting invite, and they can join using the link provided.
How to schedule meetings with external participants:
- Create a new meeting: Go to the Calendar in Microsoft Teams, click on “New Meeting,” and add the meeting details.
- Invite external participants: Add the email addresses of the external participants under the ‘Add required attendees’ section. They will receive an invitation via email.
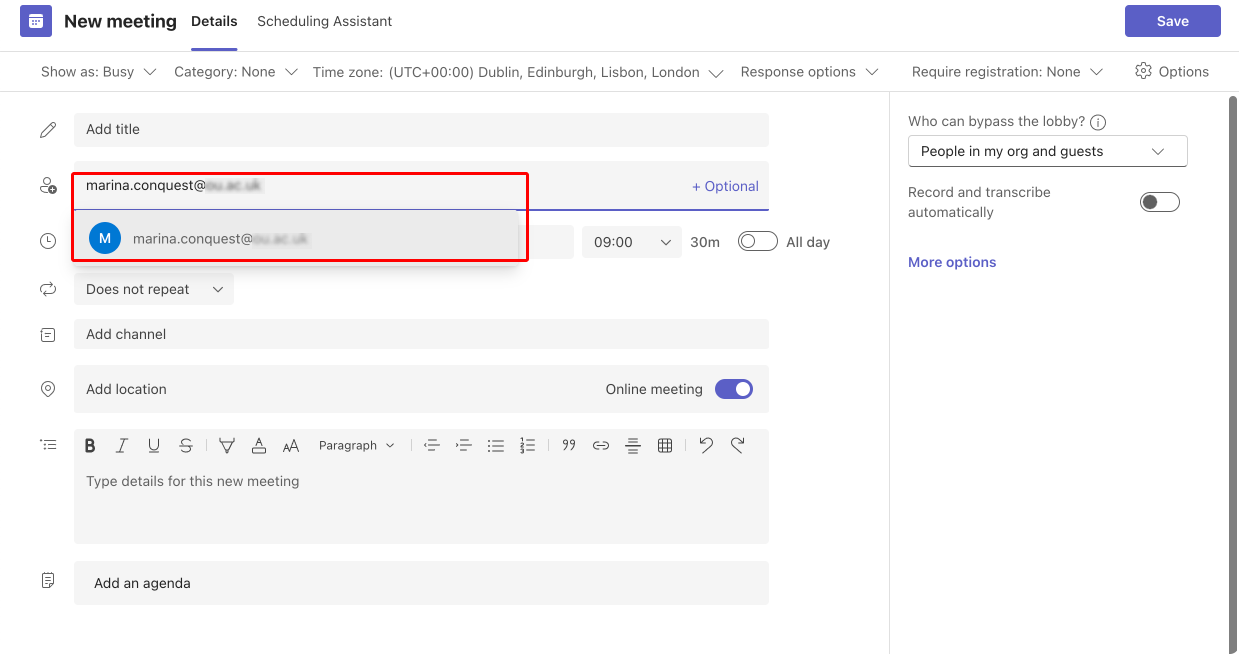
Pic. 1. Adding external participants to your meeting.
- Set permissions: Adjust meeting options if necessary, such as who can bypass the lobby or present during the meeting.
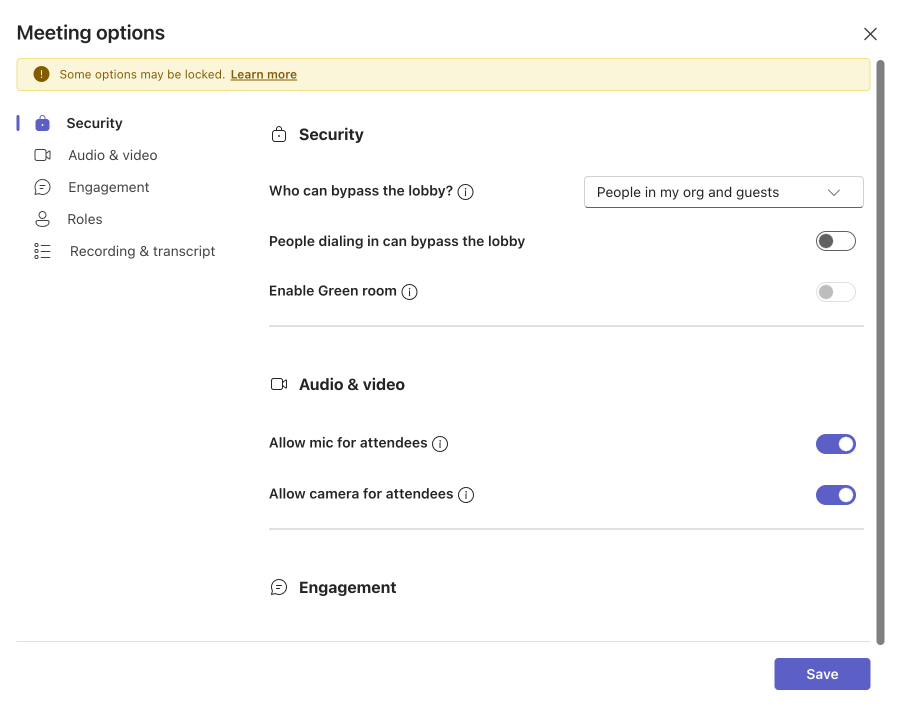
Pic. 2. Click on “More options” to open up the “Meeting options” window and adjust permissions.
👉Microsoft teams allow remote control external users? No, Microsoft Teams does not allow external users to control a shared screen remotely during Teams meetings or in any other scenario. However, guest users can use the remote control feature during Teams meetings, provided certain conditions are met. For a guest user to take control of another user’s screen during a meeting, both the guest user and the host must have the necessary permissions enabled, and their respective organizations must allow this feature in their Teams settings.
How to join meetings with external participants:
- Accepting an invitation: External participants will receive an invitation with a link to join the meeting. They can join via their Teams account or use a web browser if they do not have Teams installed.
- Joining the meeting: Click on the link provided in the invitation when it’s time for the meeting. External users may need to wait in the lobby based on your meeting settings until a host admits them.
👉 Can you invite external users to a Microsoft Teams channel? Federated external users cannot be directly added to a Teams channel; they need to be invited as guests for channel access. The same applies for the following—Can you add external users to a Microsoft Teams group—as external federated users need guest access for group collaboration.
How to share Microsoft Teams recording with external users:
- Record the meeting: During the meeting, click on “More options” (three dots) and select “Start recording.” Make sure all participants are aware that the meeting is being recorded.
- Access the recording: Once the meeting concludes, the recording will be available in the chat or meeting thread. It may take some time to process.
- Share the recording: To share the recording with external users, you can either share the link directly from the chat or download the recording and send it via email or another secure method. Ensure you comply with your organization’s data security policies when sharing recordings.
👉 How to send a Microsoft Teams recording to external users? To send a Teams recording to federated external users, upload it to a mutually accessible cloud platform and share the link with them.
Limitations and Security Issues When Working with External Users
In this section, we will outline the limitations and potential security issues that can arise when working with external users in Microsoft Teams. This discussion includes perspectives both from the viewpoint of external users themselves and from administrators who manage these interactions. It is crucial to comply with established safety measures and understand that these restrictions are primarily dictated by organizational policies and the settings configured by administrators.
Restrictions for external users in federation
- Chat and call access: External users can engage in one-on-one chats and VoIP calls with members of your organization. However, their ability to see organizational details or access broader internal communications is restricted.
- Meeting participation: External users can join meetings if invited and can participate in the meeting through chat and voice. Video participation and other advanced features might be limited based on the meeting settings established by the host.
- Access to files and internal resources: External users generally cannot access files, detailed team data, or other resources unless these are explicitly shared during a meeting or in a chat.
👉 How to share files in Microsoft Teams with external users? Sharing files directly in Teams with federated external users is not supported, but files can be shared via linked cloud storage solutions like OneDrive or SharePoint.
Restrictions for administrators in federation
- Domain management: Administrators can manage which external domains their organization is allowed to communicate with. This includes permitting or blocking entire domains.
- Feature restrictions: Administrators can enable or disable certain features for federated users, such as allowing calls and meetings but disabling the ability to initiate chats.
- Security settings: Security policies can be applied to control how and when external users can interact with your organization through federation. This includes settings like authentication requirements and data sharing controls.
Other Limitations in Federations
- Number of participants: There may be limits on how many external users can be added to meetings or group chats. These limits are generally set by Microsoft and can vary based on the organization’s licensing agreement with Microsoft.
- Integration with third-party apps: The use of third-party applications by external users is typically restricted unless specific permissions are set up. These applications might also have their own separate limitations and restrictions for external users.
Disclaimer: Please note that these limitations are subject to change as Microsoft continuously updates the functionalities and policies governing external user interactions in Teams. Additionally, third-party applications integrated within Microsoft Teams might enforce additional limitations for external users, which requires careful consideration and compliance checks.
Security considerations when working with external users
When engaging in federation, or external collaboration, with users from other organizations, it’s crucial to prioritize security to protect sensitive information and maintain organizational integrity. Before granting access to external users, a thorough review of security considerations is essential. Here are several recommendations to ensure that your engagements with external users are both productive and secure:
- Grant external users only the necessary permissions
- Principle of least privilege: Apply the principle of least privilege by only granting external users the permissions they absolutely need to fulfill their collaboration goals. For instance, if the external collaboration requires only communication via chat, there is no need to enable additional permissions such as video calls or access to organizational files.
- Limit access to confidential information
- Access controls: Use strict access controls to ensure that confidential information remains secure. Configure settings so that sensitive documents, financial details, and strategic plans are not accessible to external users unless absolutely necessary and explicitly approved.
- Data segmentation: Segment data and use private channels or specific teams where external users do not have access. This minimizes the risk of accidental exposure.
- Be careful when communicating with external users
- Verify identity: Always verify the identity of external users before sharing any information. Phishing or impersonation attempts can occur, especially when dealing with unfamiliar domains.
- Clear communication guidelines: Establish clear guidelines about what information can be shared and what should remain confidential. Educate your team members about these protocols to prevent inadvertent leaks.
- Regularly check the access rights of external users
- Audit and review: Regularly audit the access rights granted to external users. Review these permissions to ensure they are still necessary and adjust them as the collaboration evolves or concludes.
- Automated alerts: Use automated tools to monitor unusual activities, such as accessing high volumes of data or attempting to access restricted areas. These tools can help in quickly identifying and mitigating potential security breaches.
- Monitor and manage external sessions
- Session timeouts: Implement session timeouts for external users to reduce the risk of unauthorized access from unattended sessions.
- Continuous authentication: Consider continuous authentication mechanisms where the identity of the external user is periodically verified throughout their access period, especially during sessions involving sensitive interactions.
- Educate your team
- Security training: Regularly conduct security training for your team to recognize the risks involved with external collaborations. Training should include recognizing phishing attempts, secure sharing practices, and the importance of maintaining operational security.
- Use secure and approved tools
- Approved communication channels: Ensure that all communications with external users occur through approved and secure channels. Avoid using unendorsed applications or services that may not comply with your organization’s security standards.
- Develop an incident response plan
- Prepare for breaches: Develop and maintain an incident response plan that includes scenarios involving external users. Knowing how to respond quickly to a security breach can significantly reduce potential damages.
By adhering to these security considerations, organizations can safely leverage federation for external collaboration while minimizing the risks associated with exposing sensitive information and systems to external entities. Regular updates to security protocols and continuous education on new security threats are essential to maintain a robust defense against potential security breaches.
Understanding external access and guest access
In this section, we’ll review the differences between external access (or federation) and guest access in Microsoft Teams. Both types of access serve to facilitate collaboration with individuals outside your organization, but they do so in different ways and for different purposes. Understanding these differences is crucial for both users and administrators, as it helps in deciding which type should be used and why.
- Available features:
- External access: This type of access is generally used for communication purposes. It allows users from different organizations to communicate via chat, voice, and video calls but restricts access to organizational resources like teams or detailed file repositories.
- Guest access: Guest access allows external users to have deeper integration within your organization’s Teams environment. Guests can be added to teams, participate in channels, collaborate on documents, and even participate in meetings and group chats, assuming they are granted the necessary permissions.
- Permission Levels:
- External access: Users have limited permissions, primarily restricted to initiating and receiving chats and calls. They do not have access to teams or channels unless explicitly invited to a meeting.
- Guest access: Guests can be granted a wide range of permissions, tailored to the needs of the collaboration. This can include access to files, the ability to post messages in channels, participate in chats, and more. Permissions for guests are highly customizable.
- Security considerations:
- External access: Requires careful management of which domains are allowed to federate with your organization. Security policies can be applied specifically to external communications.
- Guest access: Involves a more comprehensive security approach since guests can potentially access more resources. Requires setting up detailed access controls and continuously monitoring guest activities and permissions.
| Feature | External access (federation) | Guest access |
|---|---|---|
| Communication tools | Chat, voice, and video calls | Chat, voice, video calls, team channels, meetings |
| Access to resources | None by default; meeting access if invited | Access to files, applications, and other resources as permitted |
| Permission customization | Limited; mainly controlled at the domain level | Highly customizable at the individual and team level |
| Security management | Domain-based restrictions, basic communication security settings | Detailed access controls, activity monitoring, potential for more granular security policies |
How external/guest users can participate in Microsoft Teams meetings?
Here’s a comparison of how external (federated) users and guest users can participate in Microsoft Teams meetings:
| Feature | Federated users | Guest users |
|---|---|---|
| Access method | Directly through their own Teams environment | Via a specific invitation link to join as a guest |
| Pre-configuration | Requires federation settings enabled between the organizations | Requires enabling guest access in Teams admin settings |
| Invitation process | Invited directly through their email associated with their Teams account | Invited via email, can join through a link in the email |
| Meeting entry | Can join directly if allowed in meeting settings | May need to wait in a lobby if configured so |
| Participation level | Can participate similarly to internal users depending on permissions set | Permissions can be extensive, similar to internal users, controlled by meeting settings |
| Collaboration | Can engage in chats, calls, and meetings, but typically cannot share files | Full collaboration capabilities including chat, calls, meetings, and file sharing (if permissions allow) |
| Security and Compliance | Governed by the federation policies and security settings of both organizations | Governed by the host organization’s guest access policies and security settings |
Recommendations to administrators
When to use federation (external access):
- Sporadic or formal communication: Ideal for scenarios where communication needs are limited to basic interactions like discussions or negotiations without the need for deep resource sharing.
- Security concerns: When interactions should not expose any internal resources beyond necessary communication channels.
When to use guest access:
- Long-term collaboration: Suitable for scenarios involving projects where external users need to work closely with internal teams, require access to specific documents, tools, or need to participate actively in communications.
- High trust environments: When the external individuals or entities involved are trusted partners, like vendors working closely on joint developments, consultants, or freelancers who need broader access to your organization’s resources.
Choosing between external access and guest access depends significantly on the nature of the collaboration, the required level of resource access, and security considerations. Administrators should always weigh the benefits against potential risks and ensure that the appropriate type of access is granted to support both operational efficiency and security requirements.
👉Find out more about external and guest user access in Microsoft’s official documentation: Use guest access and external access to collaborate with people outside your organization
Best Practices for Working with External Access Using Virto Calendar App
Virto Calendar App is not just a tool for scheduling; it’s a comprehensive solution that helps streamline the coordination of meetings, events, and deadlines across various teams and external partners. Its intuitive interface and enhanced features allow for better visibility and management of shared schedules, which is crucial for successful collaboration across disparate groups.
Here are some best practices and tips for optimizing your use of the Virto Calendar App when working with external users:
- Centralize calendar management: Use Virto Calendar App to centralize all scheduling activities. This enables both internal and external users to have a single source of truth for all meeting times and deadlines, reducing confusion and scheduling conflicts.
- Set clear permissions: Clearly define what external users can see and do within the Virto Calendar. You can control whether users can only view events, add events, or even edit details of existing events. This level of control is crucial for maintaining confidentiality while still fostering collaboration.
- Use color coding: Take advantage of Virto Calendar’s color-coding features to differentiate between internal and external meetings, project deadlines, and other types of events. This visual distinction helps users quickly navigate the calendar and understand their commitments at a glance.
- Integrate with existing tools: Virto Calendar App can integrate with other tools used by your organization and various project management software, including Microsoft Planner and SharePoint Lists. This integration ensures that all stakeholders, including external users, have the most up-to-date information.
- Provide adequate training: Ensure that both internal and external users are trained on how to use the Virto Calendar App effectively. This includes understanding how to add events, set reminders, and make use of any custom features specific to your organization’s setup.
- Regularly update and review access rights: As with any tool that involves external users, it’s important to regularly review who has access to what information. Periodically verify that the rights granted are still appropriate for each user’s level of involvement with your organization.
If you’re looking for a step-by-step instruction for granting access to the Virto Calendar for external users, please refer to the “How to grant access to Virto Calendar for external users” article in our Knowledge Center. Alternatively, see below for a condensed set of instructions:
- Navigate to the SharePoint site:
- Begin by going to the SharePoint site where the Virto Calendar is hosted. This is the site you want to share with the external user.
- Add members to the SharePoint site:
- Click on the “Members” button located typically on the top right corner of the SharePoint site page.
- Select “Add members” to start the process of adding a new external user.
Pic. 3. Adding members to SharePoint site.
- Use Outlook for adding members:
- In the pop-up that appears after clicking “Add members”, look for a hint or link that directs you to “go to Outlook” and click on it.
Pic. 4. Follow the prompt to Outlook.
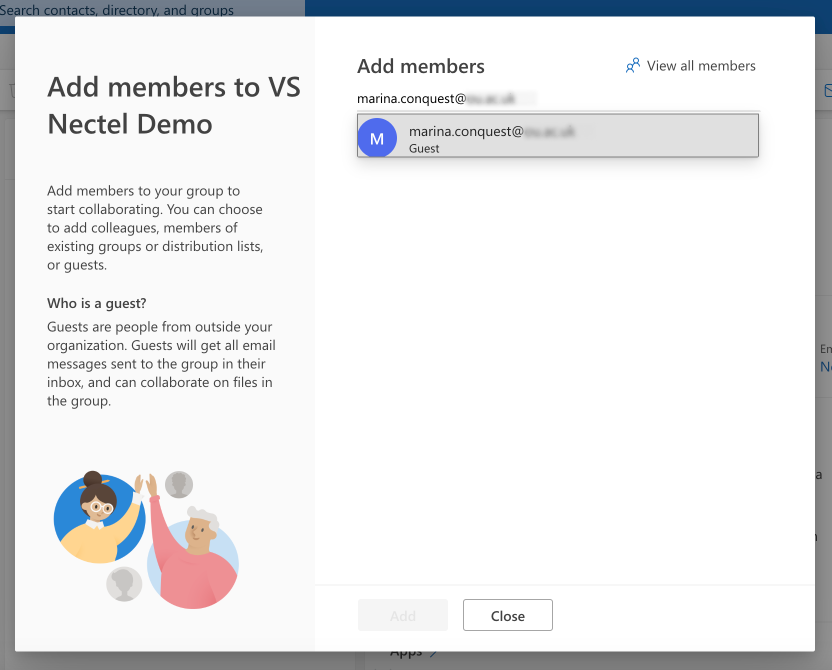
- Outlook will open (ensure you are logged in to the correct account that has admin privileges for the SharePoint site). Click on “See all members”.
Pic. 5. Adding members to your group in Outlook.
- Then, click on “Add members” on the right side of the Outlook screen.
- Enter external user’s email and send invitation:
- Provide the email address of the external user with whom you wish to share the calendar.
Pic. 6. Sending out an invite for a new member.
- Click “Add” to send them an invitation. The external user will receive an email prompting them to access the SharePoint site.
- External user accepts invitation:
- The external user must click “Go to SharePoint” in the email they receive.
Pic. 7. Accepting invitation.
- They will be prompted to log in using their email address and will receive a single-use code from Microsoft via email to authenticate their identity.
- After entering the code, they need to accept the permission request to proceed.
- Access to Virto Calendar:
- Once the external user has successfully logged in and accepted the permissions, they can view the site and its content, including the Virto Calendar.
- The access level (view or edit) to the Virto Calendar depends on the permissions set during the invitation process. Make sure to configure these settings based on the desired level of interaction with the calendar.
👉If you’re looking for a more general “permissions guide,” then be advised that we’ve provided comprehensive details on configuring user permissions in our previous article accessible here: SharePoint Permission Guide. This guide also includes information on setting up permissions in the Virto Calendar App, specifically under the section titled Virto Calendar and SharePoint Calendar Permissions. For complete guidance, we recommend checking that article or visiting our Knowledge Center for a dedicated piece on the topic.
Benefits over standard Teams calendar
When comparing Virto Calendar App to the standard Teams calendar, several benefits stand out:
- Enhanced customization: Virto allows for more extensive customization options than the standard Teams calendar, including custom views, event labels, extensive colour-coding and categorization capabilities, and more precise control over who can view or edit events.
- Better integration capabilities: While the Teams calendar primarily syncs with Outlook and Teams itself, Virto Calendar App can integrate with a wider range of services, providing a more unified view of all schedules and tasks across different platforms.
👉 To learn more about adding iCalendar feeds to your Virto Calendar view, please visit the “Internet calendars (iCalendar feed, Google Calendar)“ article in our Knowledge Center.
- Superior visibility and accessibility: With Virto, it’s easier to handle multiple calendars at once, aggregate them into a single view, and share these views with partners in a controlled manner. This is particularly useful for projects involving multiple stakeholders.
👉 To learn more about how Virto Calendar can assist with your calendar management needs—whether improving practices within your organization or coordinating with external contacts—please schedule a demo or view our contact page to get in touch via your preferred method.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve explored the nuances of external user collaboration within Microsoft Teams, highlighting the distinct features and benefits of both guest access and federation access. Guest access in Microsoft Teams allows external users to become almost like full members of your team, providing them the ability to access resources and participate actively. On the other hand, federation access offers a more controlled interaction, limiting external users to basic communication features without deeper integration into team resources.
Each model carries distinct benefits and restrictions. Guest access can facilitate seamless cooperation vital for intricate projects, yet risks potential data breaches. Federation access delivers straightforward, secure messaging, but likely limits creative cooperation. Ultimately, choosing the appropriate access type involves navigating this balance between functionality and security.
For organizations looking to enhance their Microsoft Teams experience, particularly in managing external users and calendars, the Virto Calendar App provides a compelling solution. Our app integrates seamlessly with Microsoft Teams, offering robust features to streamline scheduling and time management across different teams and external participants.
We encourage you to sign up for a demo call to explore how the Virto Calendar can be set up to accommodate external user access effectively. The demonstration will provide insights into optimizing your collaborative environment securely and efficiently.
Moreover, for those keen on delving deeper into the security aspects and restrictions of using Microsoft Teams, our comprehensive articles offer a wealth of information:
- Microsoft Teams Limitations
- Guide to Microsoft Teams Security & Data Privacy
- Best Microsoft Teams Apps Integrations
- Best Shared Calendars for Microsoft Teams
For detailed insights into managing guest access specifically, refer to our detailed article on guest access.
References:
(1) Stats from Statista.








