To the untrained eye, Microsoft Teams can seem like a sprawling labyrinth of digital corridors—overwhelming and disorienting. But to daily users, it’s a bustling metropolitan transit system, connecting cross-functional teams with ease. No wonder Microsoft Teams has seen explosive growth since the pandemic. In fact, according to the latest reports, 320 million users actively engage with Teams (1). As flexible work models have become the norm, businesses worldwide have embraced Teams as a core part of their digital transformation. And that makes perfect sense—after all, Microsoft Teams exceeds basic messaging by integrating powerful collaborative features, especially when linked with other Microsoft and third-party services. Precisely, this versatility has fueled Teams’ meteoric rise to over a quarter billion users.
With that said, Microsoft Teams has some limitations. Usage caps, limited storage, strict compatibility requirements, and security constraints can create certain challenges. Even with numerous integrations available, Teams still may not mesh perfectly with every platform and system. Even with all its bells and whistles, Teams isn’t perfect. But that doesn’t mean you’re stuck. In fact, quite the opposite—knowing those roadblocks and planning ahead can help you stay productive within the constraints. This is also where having a partner like VirtoSoftware pays off. With over 15 years specializing in Microsoft integrations, we have the know-how to optimize Teams, solve these challenges, and transform any obstacle into an opportunity.
In this article, we’ll tackle key Microsoft Teams limitations and give you actionable tips to optimize Teams within these boundaries. So, whether you’re searching for info on how many people can be on a Teams call or Teams meeting max participants, you’ll have the answers. Moreover, you’ll also learn how to maximize storage, meet technical prerequisites smoothly, tighten security, and enhance integrations. Limitations won’t stand in your way. Instead, you’ll learn to adapt Teams to its full potential.
What Are the Limitations of Microsoft Teams?
Before we get started, let’s answer one of the most frequently asked questions: “What is the maximum limit for Microsoft Teams?” The thing is, the maximum limit for Microsoft Teams can refer to various aspects, such as the Teams meeting limits, storage restrictions, or even the Microsoft Teams file size limit.
Below, you’ll find a list of the Microsoft Teams limitations as of early 2024 that cover all major areas, from chat to live events. Please note that these limits can evolve over time. For the most up-to-date specifics, refer to the official Microsoft Teams Limits and Specifications page. Consider it the definitive source, as bounds may adjust based on Microsoft’s roadmap.
Limits on the number of participants & Teams meeting limits
Microsoft Teams chat caps at 250 participants per conversation. Video and audio calls from chats are capped at 20 participants. These caps may require an organization to conduct multiple smaller meetings instead of larger, more inclusive discussions.
Some Microsoft 365 plans enable more participants for online meetings and video calls within Teams. Business Basic, Business Standard, Business Premium, and A1 plans allow meetings for up to 300 people. E3/E5, A3/A5, and Government G3/G5 plans increase the Teams meeting capacity to 1,000 participants.
So, if you wonder “how many people can join a teams meeting,” then, as mentioned above, it depends on your plan, as Teams meetings can potentially accommodate up to 1,000 active participants using chat, audio, and video. For meetings that reach the 1,000 person limit, up to 10,000 additional attendees can join in a view-only mode.
For larger scale events, Microsoft outlines other options, like:
- Teams Webinar: Structured event with controlled interaction, ideal for big audiences. Registration may be required.
- Teams Live Event: Broadcast-style event for very large audiences who are primarily viewers. Best for productions with teams.
Presenters should use the desktop app for the best experience with any presentation. Refer to the “Get started with Teams webinars” and “Get started with Teams live events” sections for details on large-scale events. The “Best practices” section also provides production tips.
So, two more frequently asked questions and a recap before we move to the next section:
- Can Teams handle 1,000 participants? Yes, it can, though this depends on the specifics of your subscription plan. In theory, Microsoft Teams is designed to support up to 1,000 participants in a single meeting with full interactive features, including video, audio, and content sharing.
- How many people can join a Teams meeting? A regular Teams meeting supports up to 1,000 attendees with interactive features. Should the number of participants exceed 1,000 but stay within 10,000, the meeting will automatically switch to a view-only broadcast mode.
And a recap on recommendations: Organizations can circumvent limitations on the maximum number of participants in teams video calls by using Microsoft Teams webinars for substantial gatherings and, for even larger audiences, live events. For instance, Teams max participants for live events are limited to 20,000 attendees, and Teams webinar limit is 1,000. Integrating third-party webinar tools with Teams is another workaround.
Teams file size limit
MS Teams file size limit for uploads is 250GB per file. Exceeding this limit will prevent users from sharing files, which can obstruct workflows involving large datasets, videos, presentations, etc.
To work within this boundary, compress file sizes or utilize file splitting tools for larger assets. For the biggest files, external storage services with shared links offer a better solution than direct uploads. With some adaptation, the 250GB cap doesn’t have to limit collaboration.
Microsoft Teams limits on storage
Microsoft Teams doesn’t have standalone storage – its limits are inherited from SharePoint Online and OneDrive for Business. These boundaries restrict the total space for files, recordings, and other assets stored in Teams.
Additionally, organizations often implement retention policies that dictate how long different Teams content gets preserved before being deleted automatically. For example, chats may only persist for 30 days versus 1 year for recordings.
If storage caps are exceeded, users may lose the ability to upload files or create new Teams until additional capacity is purchased. To avoid disruptions, regularly review and prune unnecessary files and content.
Move any “cold” data that’s accessed infrequently to external cloud storage solutions. This offloads assets that are still needed but not actively used. Ongoing audits, archiving and clean-up are key to operate within defined storage allowances.
MS Teams limitations private channel
Microsoft Teams caps private channels at 30 per team. Each private channel can have up to 250 members. However, access is restricted—not all team members may be granted entry to a private channel.
These limits create challenges for larger teams. The 250 member limit may preclude wider groups from collaborating in a single private channel. And because file permissions differ from standard channels, certain assets may have tighter access controls.
For big teams, these restrictions can obstruct broader information sharing and group discussions in private channels. Workarounds involve creating multiple smaller private channels based on function or workstreams. For the most sensitive conversations, alternative communication methods outside Teams may be preferable.
Teams Limit for chat and email
Microsoft Teams caps chats at 250 members for 1:1, group, and meeting conversations. This creates challenges when coordinating larger teams or communities. Messages are also restricted to 28KB, limiting the length and media able to be included in a single post. When emailing a channel in Teams, there are throttling limits in place, as well as limits on message size (28KB), number of attachments (20), and use of inline images (50).
These chat and email boundaries mean communication requires more brevity. Discussions with hundreds of participants will be fragmented across multiple chats. Media files and detailed content may need to be posted externally and shared via link instead.
Solutions include leveraging alternative platforms for very large groups. For big Teams communities, you can create smaller chat segments of 250 members around specific topics or workstreams. Get creative with threads, tabs, and external file sharing to collaborate broadly despite the restrictions.
Microsoft Teams time limit: Does Microsoft Teams have a time limit?
When it comes to the Teams meeting limit, it’s capped at 30 hours, and once a meeting hits that mark, it’ll get disconnected. Live events are even shorter and capped at a maximum of 16 hours. Going over these numbers results in the event ending and needing a restart. Actual meeting and call limits also depend on other factors like organization policies, event types, and conference call settings.
If certain talks require uninterrupted sessions beyond the Teams meeting time limit of 30 hours, explore third-party video services with higher limits, ensuring compliance with security policies. Otherwise, carefully schedule meetings based on anticipated needs. Use agendas to keep sessions focused and designate a timekeeper to alert when nearing any potential cutoffs. For lengthy training events or conferences, build in breaks to pause and reset the session.
Finally, testing to find organization-specific maximums for critical meetings can help based on meeting type and policies. Agendas and incremental breaks provide structure for extended sessions.
Please refer to the following table for a more structured and concise overview of the points discussed above:
| Category | Limitations | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Participants in Chat | 250 participants in private chat; 20 in audio/video call from chat | Use live events or third-party tools |
| File Size | 250 GB per file via SharePoint/OneDrive | File compression, cloud storage links |
| Storage | Tied to SharePoint/OneDrive storage limits | Regular clean-up, archiving |
| Private Channels | 30 per team; 250 members per private channel | Additional channels, alternative tools |
| Chat & Email | 28 KB message size; throttling limits on email to channel | Use other communication or email solutions |
| Duration of Sessions | Not specified; to 16-hour meetings | Plan meetings within time constraints |
Before we get started with technical specs, let’s answer another frequently asked question: “What are the limitations of external users in Teams?” External users, or guests, on Teams have more restrictions compared to internal members. For example, guests may have limited access to organizational resources and files. They are also typically unable to initiate calls or meetings on their own. Certain administrative features and privacy controls are not accessible to guests. Additionally, guests cannot actively search and join teams; they must receive invitations in order to gain access. Overall, Microsoft imposes more limitations on guests versus internal team members when it comes to functionality, access, and privacy.
Technical Specifications
A stable internet connection is crucial for the smooth operation of Microsoft Teams, especially for high-quality video meetings and calls. While specific speed requirements are not provided, individual users typically need a minimum of 1.5-3 Mbps broadband connection for decent performance in Teams video conferences. However, faster speeds above 3 Mbps are recommended for optimal quality, particularly for group video calls and live events. By prioritizing network stability and adequate bandwidth, organizations can enable Teams to deliver seamless, lag-free communication and teamwork. The better the internet connection quality, the better the Teams experience.
When using Microsoft Teams, a broadband internet connection like DSL, cable, or fiber is typically recommended for the most reliable performance. Mobile network connections via 3G, 4G/LTE, or 5G can be utilized but may face limitations that impact the Teams experience. For example, mobile data often provides reduced video quality, higher latency, and data caps that could constrain Teams usage, especially in areas with poor reception. Organizations should try to provide employees with robust wired broadband whenever possible, and educate them on potential mobile network limitations when using Teams remotely.
For a comprehensive look at the hardware requirements for Microsoft Teams, reviewing the official Microsoft documentation would prove helpful. In the meantime, you may refer to the following brief summary for easier and faster reference.
The list of operating systems compatible with Microsoft Teams includes:
- Windows: Windows 11, Windows 10 (excluding Windows 10 LTSC for Teams desktop app), Windows 10 on ARM, Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2012 R2.
- macOS: One of the three most recent versions of macOS.
- iOS: Compatible with iPhone, iPad, and iPod touch, limited to the two most recent major versions.
- Android: Compatible with Android phones and tablets, support limited to the last four major versions.
The supported device types for Microsoft Teams are:
- Computers: Desktops and laptops with the minimum technical characteristics outlined in the document.
- Smartphones and tablets: Devices running compatible versions of iOS or Android.
Minimum technical characteristics for computers include:
- Processor: Minimum 1.1 GHz or faster, two-core processor. For Intel processors, the maximum speed achieved using Intel Turbo Boost Technology must be considered.
- Memory (RAM): 4.0 GB RAM.
- Hard disk: At least 1.5 GB (Mac) or 3.0 GB (Windows) of available disk space.
- Display: Minimum resolution of 1024 x 768 (Windows) or 1280 x 800 (Mac).
- Graphics hardware: For Windows, DirectX 9 or later, with WDDM 2.0 or higher for Windows 10 (WDDM 1.3 or higher for Windows 10 Fall Creators Update).
- Operating system: Compatible OS as listed above.
- Video: USB 2.0 video camera.
- Devices: Standard laptop camera, microphone, and speakers.
Recommended settings for optimal performance include:
- Processor: A four-core processor or better is recommended for higher video/screen share resolution and frame rate.
- Memory (RAM): 4.0 GB RAM or higher, with 8 GB recommended if using features like avatars in the Teams app.
- Video: Hardware encoder for producing Teams live events.
- Devices: For joining a meeting using proximity detection in Microsoft Teams Rooms, Bluetooth LE is required, and the 64-bit version of the Teams client is necessary for Bluetooth features.
To achieve optimal performance from Microsoft Teams, organizations should always run the latest available version of the Teams desktop and mobile apps. Regularly upgrading to the most recent release allows access to the newest features and fixes. Additionally, it’s important to keep the operating systems on devices updated with the latest patches and upgrades. Staying current on OS updates provides critical security protections and potential performance improvements.
Security and Data Protection Policies in Teams
As per the Microsoft Teams security and compliance overview, Microsoft Teams is designed to provide robust security measures to protect user data and ensure compliance with various regulatory requirements.
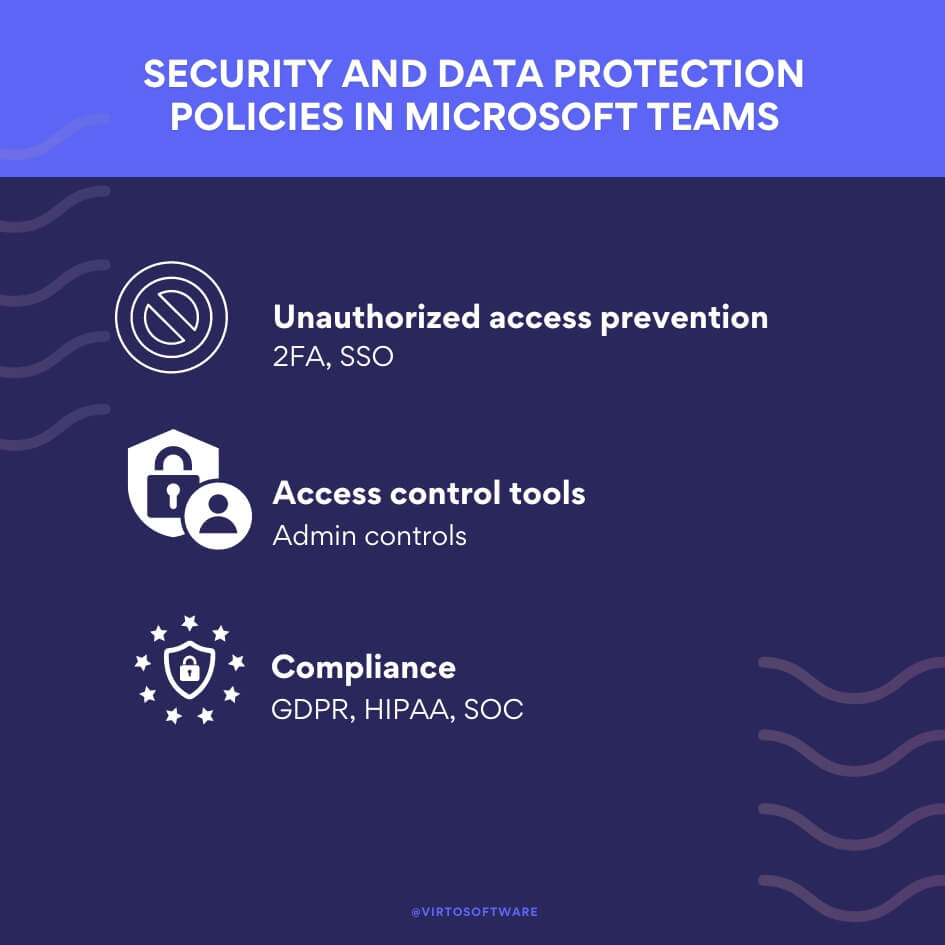
Here’s an overview of the key security policies and features in place:
Unauthorized access prevention and confidentiality:
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Teams enforces organization-wide 2FA, which requires users to provide a second form of identification beyond just a password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Single sign-on (SSO): Integration with Active Directory allows for secure and convenient SSO, using the same set of credentials across various services.
- Encryption: Data in transit and at rest are encrypted. Files are stored in SharePoint and benefit from SharePoint encryption, whereas notes in OneNote have similar security measures.
Access control tools:
- Administrator controls: Teams provides granular access controls that allow administrators to define who can access what data and features within Teams. This includes the ability to set user permissions and create policies for handling potentially malicious content.
- Private channels: While currently offering limited security and compliance features, enhanced support for a full set of security and compliance capabilities in private channels is anticipated.
Compliance with regulatory requirements:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): Microsoft Teams adheres to GDPR requirements, ensuring that personal data is handled according to stringent EU privacy laws.
- Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): Teams is compliant with HIPAA, which is critical for healthcare organizations in protecting sensitive patient health information.
- Service Organization Control (SOC) reports: Teams complies with SOC requirements, providing assurance through external audits of Microsoft’s control over information security and privacy.
Compliance with data regulations and standards is critically important for many organizations, especially those operating in regulated industries like healthcare and finance. For these companies, adhering to frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC is often legally required in order to handle sensitive customer data appropriately.
Beyond legal obligations, compliance helps boost an organization’s ability to securely manage sensitive information and maintain customer trust. Implementing compliant governance controls and procedures enables organizations to avoid substantial fines and reputation damage by protecting data in line with regulations.
While not always legally mandated, all companies can benefit from following best practices for data security and privacy.
Third-party data transfer and components:
- Third-party components: While Teams allows integration with third-party services, it is crucial for organizations to understand the security implications of these integrations. Microsoft does not transfer company data to third parties; however, if an organization installs a third-party component, it must ensure that the component complies with its security policies and does not bypass Teams’ restrictions.
- Data storage: All customer data in Teams, including content from OneDrive and SharePoint, remains within the tenant’s control, adhering to Microsoft’s principle that they “do not use your data for anything other than providing you with the service you have subscribed to.”
To summarize—Microsoft Teams provides security and compliance capabilities to safeguard against unauthorized access, maintain data confidentiality, and adhere to strict industry regulations. Organizations handling sensitive information are advised to leverage these baked-in protections to uphold security and compliance standards. Teams’ offerings like encryption, access controls, and auditing help secure proprietary data and meet legal requirements, especially for regulated industries like healthcare and finance.
However, when integrating third-party apps and services with Teams, vigilance is required to ensure these add-ons do not create security holes or compliance risks. Companies should thoroughly vet external tools to guarantee they align with internal data policies before embedding them in Teams.
For instance, Microsoft’s native add-ons like Virto Calendar Overlay and Virto Kanban Board keep data within the Microsoft ecosystem. However, integrating external, third-party apps like Asana or Trello stores data both on those third-party provider servers as well as Microsoft’s, since they are not natively integrated. For organizations where security is critical and data storage needs to remain on Microsoft servers only, it’s advisable to choose integrations vetted to meet this requirement or built-in Microsoft add-ons. Assessing where and how third-party integrations store data is key to maintaining consistent security standards and avoiding compliance risks.
Limitations on the Number and Type of Available Applications and Integrations
Although Microsoft Teams provides extensive integration capabilities to boost productivity and collaboration, organizations may face limits on how many third-party apps and services can be integrated based on their Microsoft subscription plan and IT-configured policies. Since the number of supported integrations in Teams frequently evolves, refer to Microsoft’s integration article for up-to-date specifics.
For an in-depth exploration of the Microsoft Teams integrations, please browse through relevant articles on our blog:
Factors affecting availability and categories of unavailable apps
The availability of specific applications or integrations for users or organizations within Microsoft Teams can be influenced by several factors, such as:
- Licensing requirements, as some apps require additional licenses;
- Regional availability, since not all apps are available in every region;
- Organizational policies, as companies may restrict certain apps to comply with internal security policies;
- Compliance standards that apps must meet in order to be listed in the Teams app store.
Some types of applications and integrations may have limited availability or be entirely unavailable in Microsoft Teams because of the abovementioned factors. For example, third-party integrations that are not vetted by Microsoft or do not meet Microsoft 365 certification criteria could be restricted. The same applies to custom-built internal applications or niche tools that may not comply with Microsoft’s security and privacy requirements. Additionally, non-standard communications platforms that do not seamlessly integrate with Teams communication protocols could face limitations on availability within Teams.
Recommendations for alternative applications
If your organization needs an app that is unavailable or restricted in Microsoft Teams, explore alternatives on Microsoft AppSource. With apps spanning dozens of categories, you can likely find a suitable substitute. For example, if you cannot integrate an external calendar app, consider Microsoft native add-ons like VirtoSoftware. VirtoSoftware integrations are purpose-built to work within Teams, filling capability gaps while meeting Microsoft’s strict security protocols. Our products compensate for limitations you may encounter, providing smooth integration with Microsoft ecosystem apps. For compliant Teams integrations that overcome restrictions, VirtoSoftware solutions are worth exploring.
Importance of security and privacy in Microsoft Teams
Securely managing company data within Microsoft Teams is a top priority. Organizations must adhere to Microsoft’s stringent security and privacy policies, and confirm that any third-party integrations do not improperly share data. External add-ons bring potential privacy risks, as they may not be subject to Microsoft’s internal restrictions and controls. When evaluating integrations beyond Microsoft’s native options, thoroughly vet their security standards to avoid compromising your Teams environment. Staying compliant with Microsoft’s guidelines, and carefully selecting trusted integrations, is crucial for maintaining data protection.
For more specifics on Microsoft’s app certification process and the categories of integrations available for Teams, you can refer to Microsoft’s official certification overview. This provides in-depth details directly from Microsoft about securely expanding Teams with trusted apps.
Conclusion
While Microsoft Teams is a robust platform, it does have some inherent limitations including caps on users, teams, channels, messaging, meetings, and events. However, with careful planning, you can optimize efficiency within these constraints or explore secure third-party add-ons to extend capabilities. For example, structure teams and channels judiciously to stay within creation limits, leverage organization-wide teams to maximize reach, and implement best practices for large meetings to ensure smooth operations.
When integrating external applications that bypass restrictions, prioritize data security and compliance with Microsoft policies to protect sensitive information. Solutions like the Virto Calendar Overlay App for Microsoft Teams, Virto Kanban Board for Teams, and the Virto Notifications App for Teams enhance the experience while adhering to Teams security protocols. So, why not schedule a demo today? We can help you leverage Microsoft Teams experience, enhance its capabilities, while maintaining security and compliance!
If you want to browse first and may have specific questions regarding Microsoft Teams limitations, refer to the following official Microsoft documentation:
- Limits and Specifications for Microsoft Teams
- Overview of App Certification by Microsoft
- Hardware Requirements for the Teams App
References:
(1) Stats from DemandSage.