In project management, success hinges on the collective effort of a well-organized team. A project team is a group of individuals carefully selected and assembled to tackle specific project tasks, each bringing unique skills and expertise to the table. These teams are the driving force behind turning project goals into tangible results.
At the heart of any effective project team lies a clear definition of roles. When each team member understands their responsibilities and how they fit into the larger picture, it creates a synergy that propels the project forward. Clear roles not only prevent overlap and confusion but also ensure that all aspects of the project are covered, from planning and execution to monitoring and closure.
The structure of a project team is equally crucial. A well-designed team structure acts as the backbone of project management, facilitating smooth communication channels and enabling efficient decision-making processes. It creates a framework where information flows freely, tasks are delegated effectively, and potential issues are identified and addressed promptly.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of project management teams, including:
- The fundamental structure of a project team
- Key roles within a project team and their responsibilities
- Strategies for effective team management and collaboration
- Tools and technologies that enhance project team performance
We’ll also introduce you to powerful tools that can transform your project management approach. These include the Virto Calendar App, which streamlines scheduling and time management; the Virto Kanban Board App, which provides visual task management and workflow optimization; and the Virto Gantt Chart App, offering intuitive project timeline visualization and progress tracking.
What Is a Project Management Team, Its Functions, and Structure?
This section provides a complete overview of project management teams and their importance for successful projects. We’ll start with the basics: what a project management team is and why a well-structured team is essential. Then, we’ll dive into the various types and structures of these teams, looking at what influences structural choices and how the team’s role changes throughout a project’s life.
What is a project management team?: Definition of a project team
A project management team is a group of individuals brought together to achieve specific project objectives. This team is typically composed of professionals with diverse skills and expertise, all working collaboratively towards a common goal. The team is responsible for planning, executing, and closing projects, ensuring that all deliverables are met within the specified time, budget, and quality constraints.
The Importance of a clearly structured team

A well-structured project team is crucial for several reasons:
- Efficient task allocation: Clear team structures ensure that tasks are appropriately assigned based on individual strengths and expertise.
- Improved communication: Defined roles and reporting lines facilitate smoother information flow within the team.
- Accountability: A structured team makes it easier to track progress and hold members accountable for their responsibilities.
- Faster decision-making: Clear hierarchies or decision-making processes enable quicker resolution of issues and approval of changes.
- Goal alignment: A structured team ensures that all members are working towards the same objectives, reducing conflicts and misunderstandings.
👉What is management project team? A management project team is a group of professionals assembled to oversee and execute a specific project, with a clear project team structure roles and responsibilities defined for each member. This team typically includes a project manager who leads the group, along with various specialists and team members who contribute their expertise to different aspects of the project.
Types of project teams and structures
Project teams can be organized in various ways, depending on the project’s scope and objectives. Some common types include:
- Functional teams: Organized by department or specialization (e.g., marketing team, development team).
- Advantages: Expertise concentration, clear career paths
- Disadvantages: Potential for silos, slower cross-functional communication
- Cross-functional teams: Composed of members from different functional areas.
- Advantages: Diverse perspectives, holistic problem-solving
- Disadvantages: Potential conflicts due to different working styles
- Matrix teams: Team members report to both a functional manager and a project manager.
- Advantages: Efficient resource utilization, flexibility
- Disadvantages: Potential for conflicting priorities, complex reporting structures
- Virtual teams: Members work remotely, often across different time zones.
- Advantages: Access to global talent, reduced overhead costs
- Disadvantages: Communication challenges, potential for isolation
- Self-organizing teams: Teams with high autonomy in decision-making and task allocation.
- Advantages: High motivation, rapid adaptability
- Disadvantages: Requires mature team members, potential lack of direction
| Team type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Functional teams | Organized by department or specialization | ✅ Expertise concentration ✅ Clear career paths | ❌ Potential for silos ❌ Slower cross-functional communication |
| Cross-functional teams | Members from different functional areas | ✅ Diverse perspectives ✅ Holistic problem-solving | ❌ Potential conflicts ❌ Different working styles |
| Matrix teams | Dual reporting to functional and project managers | ✅ Efficient resource use ✅ Flexibility | ❌ Conflicting priorities ❌ Complex reporting structures |
| Virtual teams | Members work remotely across time zones | ✅ Access to global talent ✅ Reduced overhead costs | ❌ Communication challenges ❌ Potential for isolation |
| Self-organizing teams | High autonomy in decisions and tasks | ✅ High motivation ✅ Rapid adaptability | ❌ Requires mature members ❌ Potential lack of direction |
👉What is project management team structure? A project management team structure refers to the organizational framework that defines how project team members are arranged, how they interact, and how they report within the context of a project. It encompasses both the type of team (e.g., functional, cross-functional, virtual) and the overall organizational structure (e.g., matrix, project-oriented).
Factors influencing team structure choice
Several factors can influence the choice of team structure:
- Project size: Larger projects may require more complex structures with multiple sub-teams.
- Project complexity: Highly complex projects might benefit from cross-functional or matrix structures.
- Industry: Some industries have specific regulatory requirements that influence team structure.
- Organizational culture: The existing company culture can impact the effectiveness of different team structures.
- Geographic distribution: Teams spread across different locations may require a virtual or matrix structure.
- Project duration: Long-term projects might benefit from more stable team structures, while short-term projects could use more flexible arrangements.
- Available resources: The skills and number of available team members can dictate the possible team structures.
- Stakeholder requirements: Key stakeholders may have preferences or requirements for how the team is structured.
👉What’s the difference between team project management and project management team? Team project management refers to the collaborative process and methodologies used to manage a project, emphasizing shared decision-making and collective problem-solving. It’s about how a project is managed using a team-based approach. On the other hand, a project management team is the actual group of individuals responsible for overseeing and executing the project. This team typically includes a project manager, team leads, and specialists with defined roles and responsibilities. In essence, team project management is the “how”—the approach and methods used, while the project management team is the “who”—the people tasked with implementing these methods and driving the project to completion.
Impact on project management
The choice of team type and structure significantly affects how project managers approach their role:
- Authority and decision-making: In functional structures, project managers may have limited authority, while in project-oriented or self-organizing teams, they have more direct control.
- Communication: Cross-functional and virtual teams require more deliberate communication strategies, while functional teams may need to focus on breaking down silos.
- Resource allocation: Matrix structures offer flexibility in resource allocation but require careful balancing of priorities.
- Team development: Self-organizing teams need facilitation rather than direct management, while functional teams may require more focus on cross-functional skill development.
👉Regardless of the chosen team type and structure, effective coordination is crucial for project success. Tools like the Virto Calendar App can significantly improve team coordination, especially in complex structures like matrix or virtual teams. The Virto Calendar App offers features such as shared team calendars, automated scheduling, and integration with other project management tools. These capabilities can help bridge communication gaps, manage multiple priorities, and align team members across different functional areas or geographic locations.
The role of the project management team
The project management team serves as the backbone of any successful project, orchestrating various elements to ensure smooth execution and delivery. This team is responsible for guiding the project from inception to completion, employing a wide range of skills and expertise along the way. Let’s delve into the core functions of the project management team:
- Planning: The project management team’s primary role begins with comprehensive planning. This involves:
- Defining project scope and objectives;
- Creating detailed project schedules;
- Estimating and allocating resources;
- Identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies;
- Establishing communication protocols.
Effective planning sets the foundation for project success, providing a roadmap for all stakeholders to follow.
- Task execution: Once the plan is in place, the project management team oversees its execution:
- Assigning tasks to team members based on their skills and availability;
- Coordinating activities across different project areas;
- Facilitating collaboration between team members and stakeholders;
- Managing project resources efficiently;
- Adapting the plan as necessary to address unforeseen challenges.
- Performance control: Monitoring and controlling project performance is crucial to keep the project on track:
- Tracking progress against the project schedule;
- Managing the project budget and monitoring expenses;
- Identifying and addressing performance issues promptly;
- Implementing corrective actions when necessary;
- Reporting project status to stakeholders regularly.
- Quality assurance: Ensuring the project delivers high-quality outcomes is a key responsibility:
- Establishing quality standards and criteria;
- Implementing quality control processes;
- Conducting regular reviews and audits;
- Managing change requests to maintain project integrity;
- Ensuring deliverables meet or exceed stakeholder expectations.
- Stakeholder management: Effective communication and stakeholder management are vital:
- Identifying and analyzing stakeholder needs and expectations;
- Developing and implementing a stakeholder communication plan;
- Managing stakeholder expectations throughout the project lifecycle;
- Resolving conflicts and addressing concerns;
- Ensuring stakeholder satisfaction with project outcomes.
👉 So, what is the function of the project management team? The primary function of the project management team is to oversee and coordinate all aspects of a project to ensure its successful completion. This includes planning the project, executing tasks, controlling performance, assuring quality, and managing stakeholders. The team acts as a central hub, bringing together various resources, skills, and stakeholders to achieve the project’s objectives within the specified constraints of time, budget, and scope.
Key Project Roles and Their Responsibilities in a Project Team
This section will provide a comprehensive overview of the key players in a project team and how they contribute to the overall project success.
What are the roles in a team project?
Effective project management hinges on the proper assignment and execution of roles within the project team. Each role contributes uniquely to the project’s success, and understanding these roles is crucial for smooth project execution. Let’s explore the key roles in a project and how they interact to drive project success.
The Importance of proper role assignment
Assigning the right people to the right roles is fundamental to effective project work. Proper role assignment:
- Ensures that tasks are performed by those with the appropriate skills and experience
- Clarifies responsibilities and accountability
- Facilitates efficient communication and decision-making
- Minimizes conflicts and overlaps in responsibilities
- Maximizes the use of team members’ strengths
Key project management roles and responsibilities
Project management team roles encompass a diverse range of positions, each contributing uniquely to the project’s progress and ultimate success. From the visionary project manager to specialized team members, each role plays a vital part in the project team organization:
- Project manager
The project manager is the linchpin of the project team, responsible for:
- Planning and defining the project scope
- Creating and managing the project schedule
- Coordinating team activities and resources
- Monitoring progress and ensuring deadlines are met
- Managing the project budget
- Ensuring quality standards are maintained
- Communicating with stakeholders
- Identifying and mitigating risks
Interactions: The project manager interacts with all team members and stakeholders, acting as the central point of communication and decision-making.
- Project sponsor
The project sponsor provides high-level support and guidance:
- Securing funding and resources for the project
- Providing strategic direction aligned with organizational goals
- Making key decisions, especially those beyond the project manager’s authority
- Championing the project within the organization
- Resolving high-level issues and conflicts
Interactions: The sponsor primarily interacts with the project manager and other high-level stakeholders, providing support and removing organizational obstacles.
- Resource manager
The resource manager ensures the project has the necessary resources:
- Allocating personnel, equipment, and materials to the project
- Balancing resource needs across multiple projects
- Managing resource conflicts and prioritization
- Ensuring team members have the necessary skills and training
- Monitoring resource utilization and efficiency
Interactions: The resource manager works closely with the project manager to ensure resource needs are met, and with team members to understand their capabilities and workload.
- Business analyst
The business analyst bridges the gap between business needs and project execution:
- Analyzing and documenting business requirements
- Helping to formulate project goals and objectives
- Ensuring project deliverables align with business needs
- Facilitating communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders
- Assisting in change management processes
Interactions: The business analyst works closely with stakeholders to understand their needs, with the project manager to align these needs with project goals, and with team members to ensure requirements are understood and met.
- Team members
Team members are the doers of the project, responsible for:
- Executing assigned tasks within their area of expertise (e.g., development, testing, design)
- Collaborating with other team members
- Reporting progress and issues to the project manager
- Contributing to problem-solving and innovation
- Maintaining quality standards in their work
Interactions: Team members interact with each other, the project manager, and sometimes directly with stakeholders, depending on the project structure.
- Stakeholders
Stakeholders have a vested interest in the project’s outcome:
- Providing input on project requirements and expectations
- Reviewing and approving project deliverables
- Making decisions that impact the project’s direction
- Providing feedback throughout the project lifecycle
- Potentially using or being affected by the project’s output
Interactions: Stakeholders typically interact with the project manager and project sponsor, and sometimes directly with team members for specific inputs or reviews.
Role allocation and project success
The allocation of these roles significantly impacts project success:
- Clear role definition prevents task overlap and ensures comprehensive coverage of all project aspects.
- Proper allocation allows team members to focus on their areas of expertise, improving efficiency and quality.
- Well-defined roles facilitate better communication and reduce conflicts.
- Understanding of roles helps in identifying skill gaps and training needs.
- Clarity in roles and responsibilities aids in performance evaluation and project audits.
So, as you can see, each role contributes uniquely to the project, and the synergy between these roles is crucial for project success. Effective collaboration and clear communication among these roles help in achieving project objectives efficiently and effectively.
👉What are the positions in project management? Project management encompasses a variety of project team roles, each crucial to the successful execution of a project. At the helm is the Project Manager, who oversees the entire project and is responsible for its planning, execution, and closure. Supporting the Project Manager are roles such as Project Coordinator, who assists with administrative tasks, and Team Leads, who manage specific aspects or phases of the project. Specialized positions within project management may include Risk Manager, Quality Assurance Specialist, Resource Manager, and Scheduler, each focusing on critical aspects of project delivery.
👉Interested in learning more about project management? Consider browsing through the following articles:
- Efficient Multiple Project Management with Kanban: An Expert Guide
- Master Project Management with Office 365 Software and Tools
- Mastering Project Management in Microsoft Teams: Key Features, Best Practices, Integrations
- How to Manage Multiple Projects: Expert Advice & Software Tools
- Project Calendar Mastery: Tools Comparison & Expert Guide for 2024
Project manager, their functions, and responsibilities
A project manager is the person responsible for leading a project from its initiation to its closure. They are responsible for planning, executing, and monitoring the project to ensure it’s completed on time, within budget, and meets the specified requirements. Let’s delve into the multifaceted responsibilities of their responsibilities and understand how they drive project success:
- Developing and maintaining project schedules
- Setting realistic deadlines for tasks and milestones
- Monitoring progress and ensuring timely completion of deliverables
- Identifying and mitigating schedule risks
- Adjusting timelines as needed while keeping stakeholders informed
- Identifying and allocating necessary resources (human, material, and financial)
- Ensuring optimal utilization of resources across the project lifecycle
- Balancing workloads to prevent burnout and maintain productivity
- Identifying skill gaps and arranging for training or additional resources
- Collaborating with the Resource Manager to secure and manage project resources
- Budget management
- Developing and maintaining the project budget
- Tracking expenses and ensuring they align with the budget
- Forecasting future costs and identifying potential overruns
- Implementing cost-control measures when necessary
- Reporting financial status to stakeholders and justifying expenditures
- Team management
- Building and leading a cohesive project team
- Defining roles and responsibilities within the team
- Facilitating effective communication among team members
- Providing guidance and support to team members
- Conducting regular team meetings and status updates
- Evaluating team performance and providing constructive feedback
- Scope management
- Defining and documenting the project scope
- Ensuring all stakeholders understand and agree on the project scope
- Managing change requests and their impact on the project
- Preventing scope creep while remaining flexible to necessary changes
- Balancing project constraints (time, cost, quality) with scope
- Risk management
- Identifying potential risks that could impact the project
- Developing risk mitigation strategies
- Monitoring and reassessing risks throughout the project lifecycle
- Implementing contingency plans when risks materialize
- Communicating risk status to stakeholders
- Stakeholder management
- Identifying all project stakeholders and their interests
- Developing and implementing a stakeholder communication plan
- Managing stakeholder expectations throughout the project
- Resolving conflicts between stakeholders
- Ensuring stakeholder satisfaction with project progress and outcomes
👉PM team meaning? A PM team, short for project management team, refers to a group of individuals collectively responsible for planning, executing, and completing a project. This team typically consists of project management team members with diverse skills and roles, including a project manager, team leads, and specialists in areas such as risk management, quality assurance, and scheduling. The PM team works collaboratively to define project goals, allocate resources, manage timelines, and overcome challenges throughout the project lifecycle.
Conflict resolution and team motivation
Beyond these core responsibilities, a Project Manager plays a crucial role in maintaining team harmony and motivation:
- Conflict resolution
- Identifying conflicts early through active listening and observation
- Addressing conflicts promptly and impartially
- Facilitating open communication to resolve disagreements
- Finding win-win solutions that benefit the project and maintain team cohesion
- Using conflicts as opportunities for team growth and improved processes
- Team motivation
- Setting clear goals and helping team members understand their importance
- Recognizing and celebrating team and individual achievements
- Providing opportunities for professional growth and skill development
- Creating a positive work environment that fosters creativity and innovation
- Shielding the team from unnecessary external pressures
- Leading by example, demonstrating enthusiasm and commitment to the project
👉 So, what does a project manager team do? A project manager plans, executes, and oversees projects from start to finish. They coordinate resources, manage budgets and schedules, and ensure project goals are met. Project managers facilitate communication among team members and stakeholders, resolve conflicts, and make critical decisions to keep the project on track. They’re responsible for risk management, quality control, and adapting to changes while guiding the team to successfully complete the project within defined constraints.
How to define roles and responsibilities in a project?
Clearly defining roles and responsibilities ensures that every team member understands their part in the project and how they contribute to its overall goals. Let’s explore how to effectively define and manage roles and responsibilities in your project.
- Defining roles based on skills, experience, and project needs:
- Assess the project requirements: Start by breaking down the project into specific tasks and identifying the skills needed for each.
- Evaluate team members: Consider each team member’s skills, experience, and strengths.
- Match skills to tasks: Align team members’ capabilities with project requirements.
- Consider workload: Ensure a balanced distribution of tasks among team members.
- Account for development opportunities: Assign roles that allow team members to grow and develop new skills.
- Creating role profiles: Detailed role profiles help clarify expectations and requirements for each position. A typical role profile should include:
- Job title
- Main responsibilities
- Required skills and qualifications
- Experience level
- Key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Reporting relationships
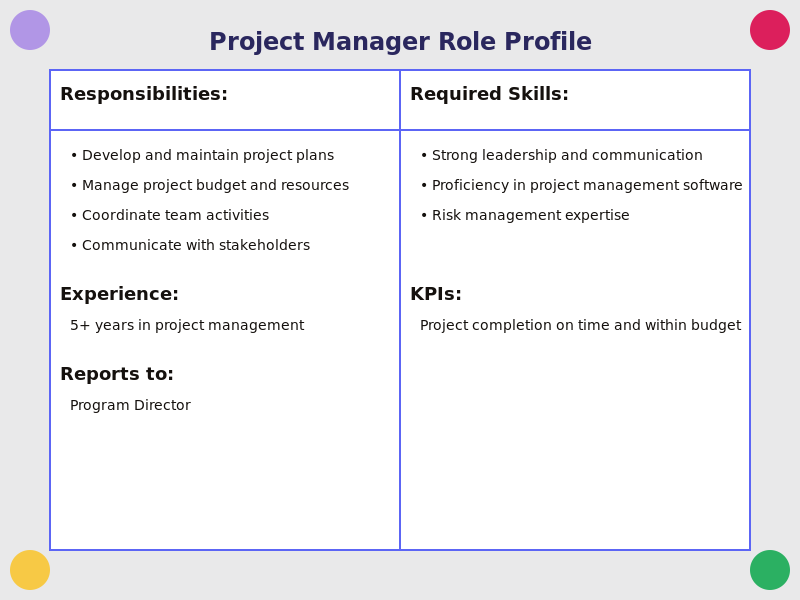
Pic. 1. Example role profile for a project manager.
Agile roles
In Agile methodologies like Scrum, roles are defined differently:
- Product Owner: Represents the stakeholders, defines product features, and prioritizes the product backlog.
- Scrum Master: Facilitates the Scrum process, removes obstacles, and ensures the team follows Agile principles.
- Development team: Self-organizing group responsible for delivering potentially shippable product increments each sprint.
These roles interact closely, with the Product Owner providing direction, the Scrum Master facilitating processes, and the Development team executing the work.
Using tools to define roles
Since articulating project management roles can be challenging, there are structured tools and methodologies available that can significantly streamline this process:
- RACI Matrix: Clarifies roles by designating who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each task.
- RASCI Matrix: An extension of RACI that adds ‘S’ for Support. This role helps complete the task but is not primarily responsible.
- PARIS Model: Stands for Participate, Approve, Responsible, Input, Sign-off. It’s similar to RACI but with more specific definitions.
- Linear Responsibility Chart (LRC): A matrix that shows the relationships between tasks and individuals, indicating levels of authority and responsibility.
- Stakeholder Analysis Matrix: While primarily used for stakeholder management, it can help define roles by mapping stakeholders’ interest and influence.
- Skills Matrix: A tool that maps team members’ skills against project requirements, helping to define roles based on competencies.
- Role-Skill Matrix: Similar to a Skills Matrix, but focuses on mapping specific roles to required skills.
- Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM): A more general term that includes RACI and similar models.
- ARCI Matrix: A variant of RACI where ‘R’ (Responsible) is replaced with ‘A’ for Accountable, and ‘A’ is replaced with ‘R’ for Responsible.
- DACI Framework: Stands for Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed. Used particularly in decision-making processes.
- RAPID Decision-Making Model: Developed by Bain & Company, it stands for Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, Decide.
- Role Activity Diagrams (RAD): A process modeling technique that focuses on roles, their activities, and interactions.
- Organizational Chart: While basic, it provides a visual representation of reporting relationships and hierarchical roles.
Each of these tools has its strengths and is suited to different types of projects or organizational structures. The choice of tool often depends on the specific needs of the project, the organization’s culture, and the complexity of the roles being defined.
Now, let’s explore the RACI Matrix in more detail to understand how it helps define roles and responsibilities.
The RACI Matrix
The RACI Matrix, also known as the Responsibility Assignment Matrix (RAM), is a powerful tool used in project management and organizational design to clarify roles and responsibilities. RACI is an acronym that stands for four key responsibility assignments:
- Responsible: Who does the work;
- Accountable: Who makes decisions and is answerable for the activity;
- Consulted: Who provides input;
- Informed: Who is kept up-to-date on progress.
To create a RACI matrix:
- Identify tasks or deliverables: List all tasks or deliverables down the left side of the matrix. Be as specific as possible to avoid ambiguity.
- Identify roles: List all relevant roles or job titles across the top of the matrix. These could include specific individuals or job functions.
- Assign RACI: For each task, assign one of the four RACI roles (R, A, C, or I) to each role or person.
- Validate: Review the matrix to ensure that:
- Every task has at least one ‘R’ and exactly one ‘A’.
- No task has too many ‘R’s or ‘C’s, which could lead to confusion.
- Resolve issues: Address any conflicts or gaps identified during validation.
- Communicate: Share the completed RACI matrix with all stakeholders and ensure everyone understands their roles.
Here’s a simple example of what a RACI matrix might look like:
| Task | Project Manager | Developer | Designer | Stakeholder |
| Requirements | A | C | C | R |
| Design | A | C | R | I |
| Development | A | R | C | I |
| Testing | A | R | C | C |
| Deployment | R | A | I | I |
👉What are the stages of a project team? Project teams typically progress through five distinct stages: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning, each requiring different approaches from various roles in project management. In the forming stage, team members are introduced and roles in project management are initially defined, while the storming stage involves addressing conflicts and clarifying responsibilities. The norming stage sees the team settling into their roles and establishing effective working relationships, followed by the performing stage where the team operates at peak efficiency with roles in project management fully realized. Finally, the adjourning stage occurs as the project concludes, involving task completion, documentation, and team dissolution, with project management roles focusing on knowledge transfer and closure activities.
Practical tips for team formation, task assignment, and role flexibility
Effective team management goes beyond simply defining roles and assigning tasks. It requires a nuanced approach that balances structure with flexibility, and clear communication with adaptability. Here are some practical tips to help you form a high-performing team, assign tasks effectively, and maintain the flexibility needed for project success:
- Collaborative role definition
Involve team members in the role definition process. This participatory approach increases buy-in and commitment to the project. It also leverages the diverse perspectives and experiences of your team members, potentially uncovering valuable insights that you might have missed.
Tip: Conduct a workshop where team members can contribute to defining roles and responsibilities. Use techniques like brainstorming or mind mapping to capture ideas.
- Clear and continuous communication
Clearly communicate roles and responsibilities to the entire team, not just to individual members. This transparency helps everyone understand how their work fits into the bigger picture and who to approach for specific needs or information.
Tip: Create a visual representation of roles and responsibilities, such as a team charter or a RACI matrix, and make it easily accessible to all team members.
- Regular role reviews
As the project progresses, regularly review and adjust roles. Projects are dynamic, and initial role definitions may need to evolve to meet changing project needs or to better align with team members’ emerging strengths.
Tip: Schedule periodic role review sessions, perhaps aligning them with major project milestones or phases.
- Open dialogue on workload and capacity
Encourage open communication about workload and capacity. Create an environment where team members feel comfortable discussing if they’re overloaded or if they have capacity to take on more work.
Tip: Implement a simple system for team members to indicate their current workload, such as a traffic light system (green for capacity, yellow for busy, red for overloaded).
- Support for new responsibilities
When team members take on new responsibilities, ensure they have the necessary training and support. This not only sets them up for success but also demonstrates your commitment to their professional growth.
Tip: Develop a mentoring system where more experienced team members can guide those taking on new roles.
- Embrace role flexibility
Be open to adjusting roles as the project evolves. Rigid adherence to initial role definitions can hinder project progress and team morale. Flexibility allows you to optimize your team’s performance as you learn more about the project and your team members’ capabilities.
Tip: During team meetings, regularly ask if the current role distribution is working well or if adjustments could improve efficiency.
- Encourage task-switching
Allow for task-switching to prevent burnout and promote skill development. This can keep team members engaged and help them develop a broader skill set, which can be valuable for future projects.
Tip: Implement a system of rotational assignments for certain tasks, ensuring knowledge transfer occurs during the rotation.
- Foster initiative
Encourage team members to take initiative beyond their defined roles when it’s beneficial to the project. This can lead to innovative solutions and a more engaged team.
Tip: Recognize and celebrate instances where team members have positively impacted the project by going beyond their defined roles.
- Balance structure and flexibility
While maintaining flexibility, ensure that there’s enough structure to keep the project on track. The key is to find the right balance for your specific project and team.
Tip: Use agile methodologies that inherently balance structure with flexibility, such as Scrum or Kanban.
- Continuous feedback
Implement a system for continuous feedback on role performance and team dynamics. This allows for real-time adjustments and improvements.
Tip: Use tools like 360-degree feedback or regular one-on-one check-ins to gather comprehensive insights on how roles are functioning within the team.
Remember, the goal is to create a framework that enhances productivity and creativity, not constrains it. Regularly revisit and refine your approach based on what works best for your unique team and project circumstances.
👉 Did you know that digital tools can significantly streamline the process of assigning and managing roles? The Virto Kanban Board App is an excellent example. This tool makes it easier to visualize task assignments, monitor task execution, adjust responsibilities, and facilitate collaboration among team members. By using such tools, project managers can ensure that roles and responsibilities are not just defined on paper, but actively managed throughout the project lifecycle.
How to Create and Manage a Project Team Effectively?
Assembling and managing an effective project team is both an art and a science. In this section, we’ll delve into the crucial aspects of creating and managing a high-performing project team that can navigate challenges and deliver outstanding results.
The project team formation process
A well-formed team can make the difference between a project that thrives and one that struggles. Let’s explore the process of forming a project team that’s tailored to your specific project objectives and requirements.
- Understanding project needs: Before you can begin assembling your team, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your project’s goals, scope, and requirements. This understanding will guide your team formation process.
- Analyze project objectives: Clearly define what the project aims to achieve. Are you developing a new product, implementing a system, or perhaps organizing an event?
- Identify required skills: Based on the project objectives, list out all the skills and expertise needed to complete the project successfully. This might include technical skills, soft skills, and domain-specific knowledge.
- Determine project complexity: Assess the complexity of your project. More complex projects may require a larger team with a wider range of specialized skills.
- Consider project timeline: Your project’s duration and deadlines will impact the number of team members you need and their required availability.
- Assembling the team: Once you have a clear picture of your project’s needs, you can start the team assembly process:
- Define roles: Based on the required skills and project complexity, define the specific roles you need to fill. Common roles might include project manager, technical lead, business analyst, and various specialists.
- Match skills to roles: Look for individuals whose skills and experience match the requirements of each role. Consider both hard skills (technical abilities) and soft skills (communication, leadership, problem-solving).
- Consider team dynamics: Beyond individual skills, think about how potential team members might work together. Aim for a mix of personalities and working styles that will complement each other.
- Assess availability: Ensure that the team members you’re considering have the necessary availability for the project’s duration.
- Review Past Performance: If possible, look at potential team members’ performance on previous projects. Past success can be a good indicator of future performance.
The importance of specialist selection
Selecting specialists with the necessary competencies is crucial for project success. Here’s why:
- Efficiency: Specialists can complete tasks in their area of expertise more quickly and with higher quality than generalists.
- Problem-solving: When challenges arise, specialists have the depth of knowledge to develop innovative solutions.
- Risk mitigation: Experienced specialists can foresee potential issues in their area of expertise and help the team avoid or prepare for them.
- Quality assurance: Specialists understand the standards and best practices in their field, ensuring high-quality outputs.
- Credibility: Having recognized experts on your team can boost the project’s credibility with stakeholders.
While specialists are crucial, it’s also important to ensure your team has some versatility:
- Cross-functional skills: Look for team members who, while specialists in one area, have working knowledge in related areas. This can improve team communication and flexibility.
- Learning potential: Choose team members who demonstrate the ability and willingness to learn new skills as the project evolves.
- Adaptability: In today’s fast-paced project environments, team members who can adapt to changing requirements are invaluable.
By carefully considering your project’s needs and thoughtfully selecting team members with the right mix of specialized skills and versatility, you set your project up for success from the very beginning.
Project team management strategies
Effective project team management involves a combination of clear communication, strategic planning, and the right tools. Let’s explore some key strategies and techniques for managing your project team effectively:
- Clearly assign roles: Ensure each team member understands their responsibilities. Use tools like RACI matrices to clarify who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed for each task.
- Constant communication and monitoring: Regularly check in with team members about task progress. Use daily stand-ups or weekly check-ins to keep everyone aligned.
- Apply Agile and Kanban methods: These methodologies promote flexibility and continuous improvement. Agile sprints and Kanban boards can help visualize workflow and identify bottlenecks.
- Monitor progress: Use project management tools to track progress against milestones. The Virto Gantt Chart App provides a visual tool for project planning and deadline management.
- Motivate the Team: Create a positive working atmosphere. Recognize achievements, provide growth opportunities, and foster a culture of mutual respect and support.
Team communication
Effective communication is the backbone of successful project management. Here are some strategies to enhance team communication:
- Choose the right channels: Use a mix of synchronous (real-time) and asynchronous communication tools. Video calls for complex discussions, chat for quick questions, and email for formal communications.
- Regular team meetings: Hold consistent team meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and upcoming tasks.
- Use collaboration tools: Platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack can centralize communications and file sharing.
- Encourage open dialogue: Create an environment where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas and concerns.
The Virto Calendar App for Microsoft Teams can be an excellent tool for scheduling tasks and meetings efficiently, ensuring everyone is on the same page regarding project timelines.
Conflict management
Conflicts are inevitable in team settings, but they can be managed effectively:
- Identify the source: Understand the root cause of the conflict. Is it due to miscommunication, differing priorities, or personal disagreements?
- Encourage direct communication: Facilitate a discussion between the involved parties to air out concerns.
- Focus on solutions: Guide the team towards finding a resolution that addresses the issue and moves the project forward.
- Mediate when necessary: As a project manager, be prepared to step in and mediate if conflicts escalate.
- Learn from conflicts: Use conflicts as opportunities to improve team processes and communication.
Team performance assessment
Regularly assessing team performance is crucial for continuous improvement:
- Set clear metrics: Establish KPIs that align with project goals.
- Regular reviews: Conduct individual and team performance reviews at set intervals.
- 360-degree feedback: Gather feedback from peers, subordinates, and superiors for a comprehensive view.
- Self-assessment: Encourage team members to reflect on their own performance.
- Continuous feedback: Provide real-time feedback rather than waiting for formal review periods.
👉 How to manage a project team? Managing a project team effectively requires a multifaceted approach that combines strategic planning, clear communication, and adaptable leadership. At its core, successful team management starts with clear role assignment and explicit communication of expectations to each team member. This foundation is reinforced by regular monitoring of task completion and overall progress, ensuring the project stays on track. Implementing project management methodologies like Agile or Kanban can provide structure and flexibility to your team’s workflow. Equally important is the maintenance of open and constant communication channels, fostering an environment where ideas and concerns can be freely shared. Proactive conflict resolution and the cultivation of a positive team atmosphere are crucial for maintaining team morale and productivity. Regular assessment of team performance, coupled with constructive feedback, helps in continuous improvement and personal growth of team members.
Effective planning and coordination
Proper planning and coordination ensure that all team members are aligned, resources are optimally utilized, and project goals are met within the specified timeframe and budget. In this section, we’ll examine the importance of proper task scheduling and progress tracking, and explore how modern tools can enhance these crucial processes.
The Importance of proper task scheduling
Task scheduling is more than just assigning due dates. It’s about creating a roadmap for your project that takes into account:
- Task dependencies: Understanding which tasks need to be completed before others can begin.
- Resource allocation: Ensuring that team members and other resources are available when needed.
- Realistic timelines: Setting deadlines that are challenging yet achievable.
- Buffer time: Allowing for unexpected delays or complications.
- Workload balancing: Preventing team members from being over or under-utilized.
Proper task scheduling helps prevent bottlenecks, reduces idle time, and keeps the project moving forward efficiently. It also provides clarity to team members about what they should be working on and when, reducing confusion and improving productivity.
Tools for tracking progress
Today, relying on manual methods to track progress is no longer efficient. Project management tools offer real-time visibility into project status, making it easier to:
- Monitor task completion: See at a glance which tasks are on track, behind schedule, or completed.
- Identify bottlenecks: Quickly spot where tasks are getting held up and address issues promptly.
- Manage resources: Ensure team members are efficiently utilized and not overloaded.
- Generate reports: Easily create status reports for stakeholders.
- Make data-driven decisions: Use actual progress data to make informed decisions about project direction.
Virto Calendar App: Enhancing Coordination
One tool that can significantly improve team coordination is the Virto Calendar App for Microsoft 365, SharePoint, and Microsoft Teams. This powerful application bridges the gap between task management and team communication, offering several key benefits:
- Centralized scheduling: All team meetings and deadlines can be viewed in one place, reducing scheduling conflicts and missed appointments.
- Task synchronization: Tasks from project management tools can be synced with the calendar, providing a clear visual of when deliverables are due.
- Team availability: Easily see when team members are available, making it simpler to schedule meetings or allocate tasks.
- Integration with Microsoft Teams: As it’s integrated with Teams, it fits seamlessly into your existing workflow, reducing the need to switch between multiple applications.
- Customizable views: Team members can customize their calendar views to focus on what’s most important to them, whether that’s their individual tasks, team meetings, or project milestones.
- Reminders and notifications: Automated reminders help ensure that team members don’t miss important deadlines or meetings.
- Shared calendars: Create shared calendars for different projects or teams, improving visibility across the organization.

Effective planning and coordination are vital for project success, and tools like the Virto Calendar App for Microsoft Teams can significantly improve these processes. By leveraging such tools alongside sound project management practices, teams can work more efficiently, reduce conflicts, and ultimately deliver projects more successfully.
PMO vs. Project Team: What’s the Difference?
In project management, two key entities often come into play: the Project Management Office (PMO) and the Project Team. While both are crucial for successful project execution, they serve different purposes and operate at different levels within an organization. Let’s explore these differences in detail.
Definition of PMO and its functions
A Project Management Office (PMO) is a department or group within an organization that centralizes and coordinates the management of projects across the entire organization. It serves as a strategic hub that standardizes project-related governance processes and facilitates the sharing of resources, methodologies, tools, and techniques across all projects.
Main functions of a PMO:
- Standardization: Developing and maintaining project management standards, methodologies, and best practices across the organization.
- Project portfolio management: Overseeing and prioritizing all projects within the organization to ensure alignment with strategic goals.
- Resource management: Optimizing the allocation of resources across various projects.
- Training and Development: Providing training and mentoring to project managers and team members to enhance project management skills.
- Performance monitoring: Tracking project and portfolio performance metrics to ensure projects are delivering value.
- Knowledge management: Capturing and sharing lessons learned from past projects to improve future performance.
- Tool selection and management: Selecting, implementing, and managing project management software and tools.
- Governance: Ensuring projects adhere to organizational policies, procedures, and compliance requirements.
- Stakeholder communication: Facilitating communication between project teams and high-level stakeholders.
What is the difference between a PMO and a project management team?
While a PMO and a project management team both play crucial roles in project success, they operate at different levels and have distinct responsibilities:
- Scope of responsibility:
- PMO: Oversees all projects within an organization, focusing on strategic alignment and overall project performance.
- Project Team: Concentrates on the successful execution of a specific project.
- Time horizon:
- PMO: Has a long-term, organization-wide perspective.
- Project Team: Focuses on the timeline of their specific project.
- Standardization vs. execution:
- PMO: Develops and enforces standards and methodologies.
- Project Team: Applies these standards in the execution of their project.
- Resource management:
- PMO: Manages resources across all projects, optimizing allocation.
- Project Team: Manages resources assigned to their specific project.
- Reporting:
- PMO: Reports on organization-wide project performance to senior management.
- Project Team: Reports on individual project progress to stakeholders and the PMO.
Support provided by PMO to project teams:
The PMO plays a crucial supporting role for project teams, acting as a centralized hub of expertise, resources, and standardization. This support is multifaceted and can significantly enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of project teams. Let’s delve deeper into the various ways a PMO supports project teams:
- Methodology and tools: Provides standardized project management methodologies and tools, which offers several benefits:
- Consistency: Ensures all projects across the organization follow similar processes, making it easier to compare and evaluate projects.
- Efficiency: Teams don’t have to reinvent the wheel for each project, saving time and effort.
- Quality: Standardized methodologies often incorporate best practices, leading to higher quality project management.
- Tool Selection: PMOs research, select, and implement project management software and tools that best fit the organization’s needs.
- Integration: Ensures that chosen tools integrate well with existing organizational systems.
- Training: Offers training and development opportunities to enhance project management skills:
- Skill assessment: Identifies skill gaps within project teams.
- Customized training: Develops training programs tailored to the organization’s specific needs and methodologies.
- Certification support: May provide support for team members pursuing professional certifications like PMP or PRINCE2.
- Continuous learning: Organizes workshops, seminars, and webinars to keep project teams updated on the latest trends and techniques.
- Onboarding: Helps new project team members get up to speed quickly with the organization’s project management practices.
- Mentoring: Provides guidance and mentoring to project managers:
- One-on-one support: Experienced PMO members can provide personalized guidance to project managers.
- Career development: Helps project managers plan and progress in their careers.
- Problem-solving: Assists project managers in tackling complex project challenges.
- Leadership development: Nurtures leadership skills in project managers.
- Knowledge transfer: Facilitates the transfer of tacit knowledge from experienced managers to newer ones.
- Resource allocation: Assists in securing and allocating resources for projects:
- Resource planning: Helps project teams forecast their resource needs.
- Optimization: Ensures efficient use of resources across all projects in the organization.
- Conflict resolution: Mediates when multiple projects compete for the same resources.
- Capacity planning: Provides insights into organizational capacity to take on new projects.
- Skill matching: Helps match available skills with project requirements.
- Conflict resolution: Helps resolve conflicts that escalate beyond the project team:
- Mediation: Acts as a neutral third party in conflicts between project teams or with stakeholders.
- Escalation path: Provides a clear escalation path for issues that can’t be resolved within the project team.
- Cross-functional conflicts: Helps resolve conflicts between projects or departments.
- Stakeholder management: Assists in managing conflicts with high-level stakeholders.
- Policy enforcement: Ensures that conflict resolution adheres to organizational policies and standards.
- Best practices: Shares best practices and lessons learned from other projects:
- Knowledge repository: Maintains a database of lessons learned and best practices from past projects.
- Cross-project learning: Facilitates the sharing of insights between different project teams.
- Continuous improvement: Uses lessons learned to continuously improve project management processes.
- Case studies: Develops case studies of successful (and unsuccessful) projects for learning purposes.
- Benchmarking: Provides benchmarks for project performance based on organizational history and industry standards.
| Characteristic | Project Management Office (PMO) | Project Team |
| Scope | Organization-wide | Specific project |
| Focus | Strategic oversight and standardization | Tactical execution and delivery |
| Time horizon | Long-term, ongoing | Project lifecycle |
| Responsibilities | – Develop and maintain standards- Portfolio management- Resource optimization- Performance monitoring across projects | – Plan and execute specific project- Manage project scope, timeline, and budge- Deliver project outcomes |
| Reporting | To senior management on overall project performance | To project stakeholders and PMO on specific project progress |
| Resource management | Across all projects in the organization | Within the specific project |
| Methodology | Develop and enforce standard methodologies | Apply methodologies to specific project |
| Knowledge management | Capture and share lessons across projects | Apply lessons learned and best practices |
| Stakeholder management | High-level stakeholders and cross-project communication | Project-specific stakeholders |
| Tools and technology | Select and manage organization-wide PM tools | Use tools provided/approved by PMO |
| Training and development | Provide training and mentoring for all PMs | Receive training and apply skills to project |
| Governance | Ensure adherence to organizational policies | Adhere to policies in project execution |
| Timeframe | Permanent organizational structure | Temporary, disbands after project completion |
Examples of Successful Project Teams and the Use of Tools
Effective team management when done right can lead to remarkable outcomes Let’s explore some real-world examples of companies and projects where successful distribution of roles and responsibilities, coupled with effective use of time and task management tools, resulted in timely completion and high-quality deliverables.
Examples of successful team management
Success stories serve as powerful learning tools and sources of inspiration. They demonstrate how effective team management, clear role distribution, and the strategic use of tools can lead to exceptional outcomes. In this section, we’ll explore real-world examples of projects where astute leadership, well-defined responsibilities, and cutting-edge management tools combined to achieve remarkable results.
NASA’s Mars Rover Missions
Project: Mars Exploration Rover missions (Spirit and Opportunity)
Success Factors:
- Specialized teams: NASA formed teams with specific expertise (propulsion, navigation, communication, etc.) with clear responsibilities.
- Rigorous planning and scheduling: Every aspect of the mission was meticulously planned and scheduled.
- Adaptive problem-solving: Teams were prepared to adjust plans quickly when faced with unexpected challenges.
Tool Usage: NASA employed sophisticated project management and simulation tools to plan and execute these complex missions.
Outcome: Both rovers far exceeded their planned 90-day missions, with Opportunity operating for over 14 years, providing invaluable data about Mars.
Airbus A350 XWB Development
Project: Development of the Airbus A350 XWB aircraft
Success Factors:
- Global collaboration: Teams from multiple countries worked together effectively.
- Clear communication channels: Despite geographical dispersion, clear communication protocols were established.
- Efficient resource allocation: Resources were allocated based on expertise and availability across different locations.
Tool Usage: Airbus used advanced PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) software to manage the complex supply chain and coordinate design efforts across global teams.
Outcome: The A350 XWB was delivered on schedule and has been a commercial success, competing effectively with its Boeing counterparts.
The Human Genome Project
Project: Mapping the human genome
Success Factors:
- International collaboration: Teams from multiple countries worked together towards a common goal.
- Clear milestones: The project was broken down into clear, achievable milestones.
- Open communication: Regular conferences and open data sharing accelerated progress.
Tool Usage: Specialized bioinformatics tools were developed and used to manage and analyze the vast amounts of genetic data.
Outcome: The project was completed two years ahead of schedule in 2003, revolutionizing genetics and medicine.
Why project management tools are important
In all these examples, the use of appropriate time and task management tools played a crucial role in project success. These tools provided:
- Visibility: Team members and stakeholders could easily see project progress and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Coordination: Complex projects with multiple teams were coordinated effectively, ensuring all parts came together seamlessly.
- Resource management: Tools helped in efficient allocation and reallocation of resources as project needs evolved.
- Communication: Many of these tools facilitated clear communication, crucial for projects with geographically dispersed teams.
- Accountability: Clear assignment of tasks and deadlines in these tools enhanced accountability among team members.
- Adaptability: Advanced tools allowed for quick adjustments to plans when faced with unexpected challenges or changes.
These successful projects demonstrate that when roles and responsibilities are clearly defined and supported by effective time and task management tools, teams can achieve remarkable results, often exceeding initial expectations.
How VirtoSoftware apps can help in team management
As you can see from the above examples, having the right tools can make all the difference. VirtoSoftware offers a suite of powerful applications designed to streamline project planning, task assignment, and monitoring. Let’s explore how these apps can revolutionize your team management process.
Virto Calendar App: Simplifying coordination
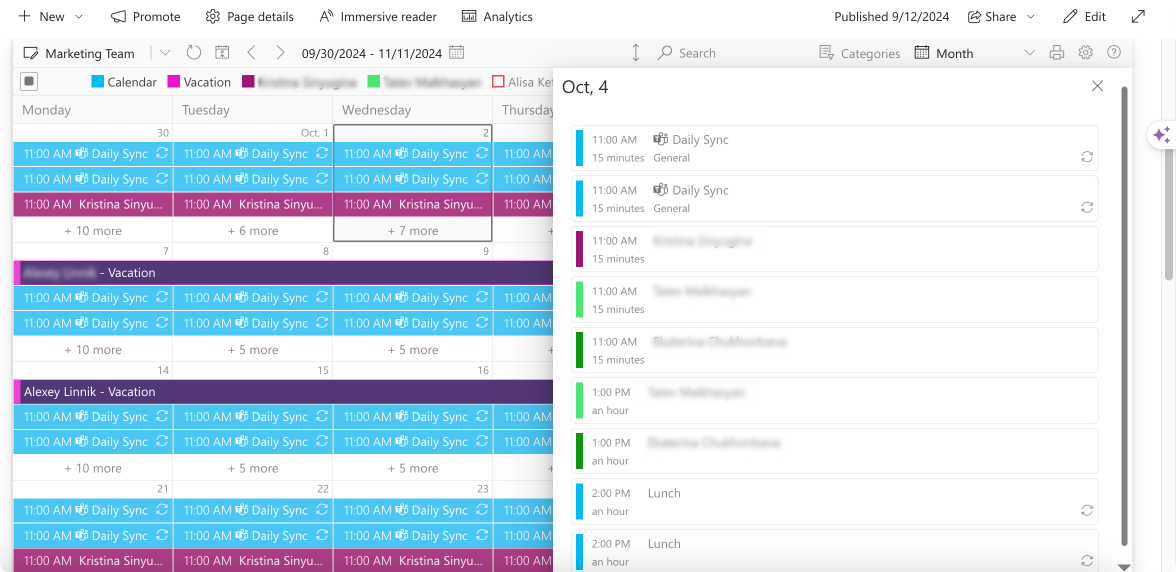
Pic. 2. Sample calendar overlay view for a month and a day in Virto Calendar.
The Virto Calendar App is a game-changer for project managers and team members alike. Here’s how it enhances team coordination:
- Centralized scheduling: All team meetings, important events, and task deadlines are visible in one place, reducing scheduling conflicts.
- Calendar overlay: Overlay Exchange Online calendars with other Microsoft 365 calendars in a single view, providing a comprehensive overview of all schedules.
- Multi-source event combination: Combine events from SharePoint lists, Outlook calendars, and meeting rooms for a complete scheduling picture.
- External calendar support: Add external calendars using an iCal link from Google or other popular calendar services, ensuring all relevant information is in one place.
- Integration with Microsoft Teams: Seamlessly works within your existing Microsoft Teams environment, improving adoption rates.
- Custom views: Team members can customize their calendar views to focus on what’s most important to them.
- Flexible timescales: Effortlessly switch between timescales to view events grouped by day, week, month, year, and tasks, adapting to different planning needs.
- Gantt view: Manage your project timeline with precision using the Gantt view. Visualize event durations in days or hours, create and delete events, and drag and drop to adjust scheduling—all within the calendar interface.
- Resource management: Easily see team member availability, making it simpler to schedule meetings or allocate tasks.
- Color-coding: Color-code events and their categories to establish a well-structured and clear SharePoint calendar overlay, improving visual organization.
- Mini calendar: Incorporate a mini calendar for a compact overview of all calendar events, perfect for quick reference.
By using the Virto Calendar App, project managers can ensure that everyone stays on top of deadlines and key events, significantly reducing miscommunication and missed deadlines.
Virto Kanban Board App: Visualizing workflow
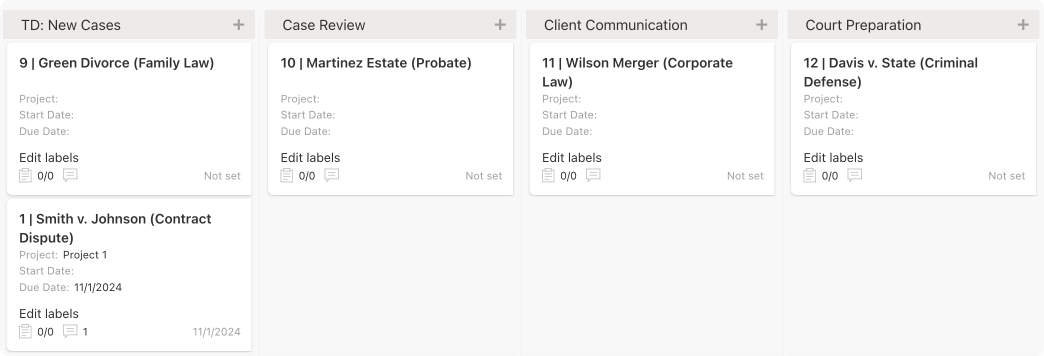
Pic. 3. Sample Kanban Board view.
The Virto Kanban Board App brings the power of visual task management to your team. Here’s how it can improve your project workflow:
- Real-time progress tracking: Team members can see the status of all tasks at a glance, improving transparency and accountability.
- Visual task management: The visual representation of tasks allows managers to quickly identify bottlenecks and blockers, reducing time spent on progress updates.
- Customizable workflows: Create columns that match your team’s unique process, from “To Do” to “In Progress” to “Done” and beyond.
- Task details: Each card can contain detailed information, attachments, and comments, keeping all relevant information in one place.
- Drag-and-drop Interface: Easily move tasks between stages, providing a visual representation of progress.
- WIP limits: Set work-in-progress limits to prevent bottlenecks and maintain a steady workflow.
- SharePoint integration: Display any SharePoint list as a Kanban board, dividing cards into columns and swimlanes based on their status.
- Visual task management: The visual representation of tasks allows managers to quickly identify bottlenecks and blockers, reducing time spent on progress updates.
- Flexible board creation: Three options for creating a new Kanban board, including from an existing SharePoint list, a quick board, and from a board template.
The Virto Kanban Board App helps teams visualize their work, identify bottlenecks, and ensure a smooth flow of tasks from start to finish.
Virto Gantt Chart App: Mastering project timelines
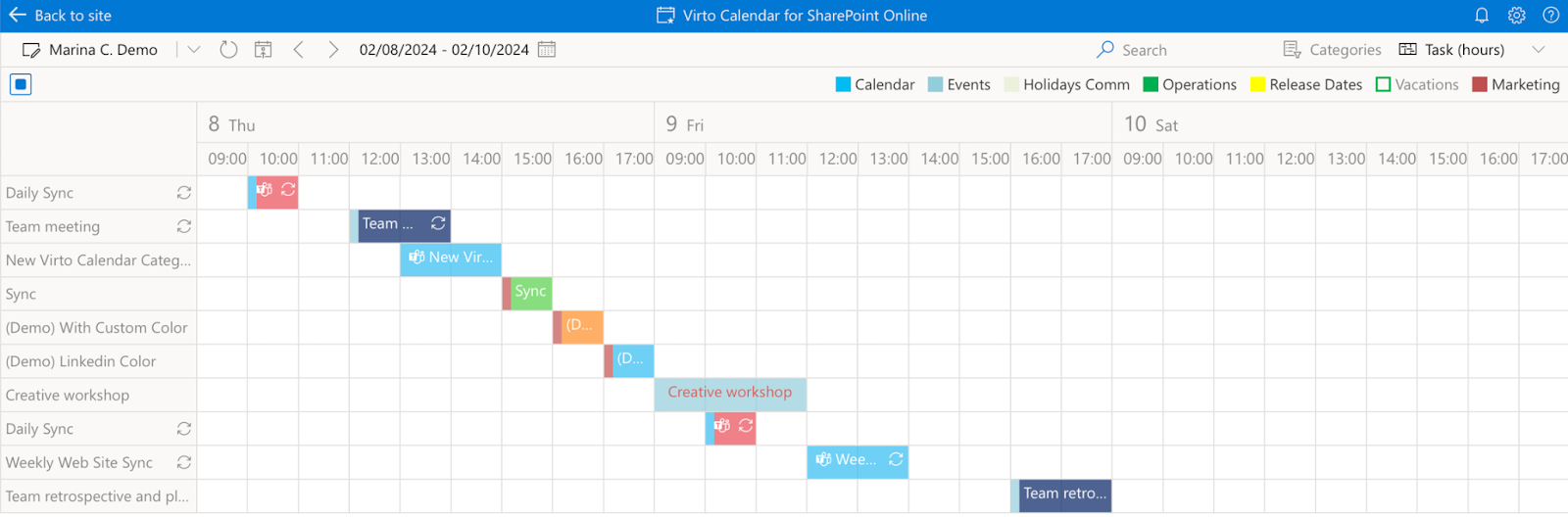
Pic. 4. Sample Gantt view in Virto Calendar.
The Virto Gantt Chart App is a powerful tool for planning and managing project timelines. Here’s a detailed look at its features:
- Visual timeline: See your entire project schedule at a glance, with tasks represented as bars on a timeline.
- Task dependencies: Easily set and visualize dependencies between tasks, ensuring proper sequencing of work.
- Critical path identification: Automatically highlights the critical path, helping you focus on tasks that directly impact the project completion date.
- Resource allocation: Assign resources to tasks and see their workload over time, helping prevent overallocation.
- Progress tracking: Update task completion percentages and see how they affect the overall project timeline.
- Milestones: Mark important project milestones for easy reference and tracking.
- Customizable views: Zoom in on specific time periods or zoom out for a bird’s-eye view of the entire project.
- Baseline comparison: Compare your current schedule against the original baseline to track deviations.
The Virto Gantt Chart App allows project managers to effectively plan and manage project deadlines, visualize task interdependencies, and keep the project on track.
Comparison with other popular tools
While tools like Microsoft Project and Trello are popular, VirtoSoftware apps offer unique benefits for the corporate environment:
- SharePoint integration: Unlike many third-party apps like Trello, VirtoSoftware apps integrate seamlessly with SharePoint, leveraging your existing infrastructure.
- Cost-effective: Compared to Microsoft Project, VirtoSoftware apps offer similar functionality at a more accessible price point.
- User-friendly interface: While powerful, these apps maintain an intuitive interface, reducing the learning curve compared to complex tools like Jira.
- Customization: VirtoSoftware apps offer more customization options compared to other apps, allowing them to fit your specific business processes.
- All-in-one solution: Unlike using separate tools for different functions, VirtoSoftware provides a cohesive suite of apps that work together seamlessly.
By leveraging these powerful tools from VirtoSoftware, teams can significantly improve their project planning, task assignment, and monitoring processes. Whether you’re managing a small team or coordinating large, complex projects, these apps provide the functionality and flexibility needed to drive success in today’s dynamic business environment.
Conclusion: Mastering Project Team Management
As we’ve explored throughout this article, the success of any project hinges on two critical factors: a well-defined team structure with clear roles, and the strategic use of tools for efficient task and time management. Let’s recap the key takeaways:
- A clearly defined project team structure is the foundation of effective project management. It ensures that every team member understands their responsibilities and how they contribute to the overall project goals.
- The right combination of tools can significantly enhance a team’s productivity, communication, and overall project outcomes. From visualizing workflows to managing complex timelines, modern project management tools are indispensable in today’s fast-paced business environment.
- Successful project management is not just about having a great plan—it’s about executing that plan efficiently. This is where the seamless integration of well-defined roles and powerful management tools becomes crucial.
- Solutions like the Virto Kanban Board, Virto Calendar App, and Virto Gantt Chart offer robust features tailored for the modern project management landscape. These tools can dramatically improve project coordination, resource allocation, and timeline management in your organization.
We encourage you to evaluate your current project management practices and consider how tools like those offered by VirtoSoftware could optimize your team’s performance. Remember, the goal is not just to complete projects, but to do so efficiently, on time, and with high-quality results. Why not schedule your demo today to see how VirtoSoftware can help make your projects a success?
For those looking to dive deeper into project team management, we recommend the following resources:





